- What Is an SEO Audit and Why Conduct One
- How to Collect Initial Data for a Website SEO Audit
- How to Conduct a Website SEO Audit Yourself: Step-by-Step Guide
- What to Do with the Data Obtained After an SEO Audit
Do you invest resources in creating content and building backlinks, but the traffic remains stagnant? After the latest algorithm update, have you noticed a significant drop in your website’s visibility in search engines? Or perhaps you haven’t worked on your online project for a long time but now want to update it properly to attract your target audience and create a source of income? Then it’s time to conduct an SEO audit of your website, which will help you identify key shortcomings and find opportunities for your project’s growth. While such a “diagnosis” can take anywhere from several hours to several days, skillful use of its results can finally get your website moving from a standstill and start attracting visitors — and therefore potential customers.
What Is an SEO Audit and Why Conduct One
An SEO audit of a website is a comprehensive check of a web resource for compliance with search engine requirements, aimed at identifying technical, content, and external issues that prevent it from ranking well in search results. During the process, you analyze both the entire online project (overall traffic, number of impressions and clicks, traffic sources, backlink profile) and each individual page (structure, quality and relevance of content, added value, meta tags). The process can take from 2–3 hours to 3–5 days if the web resource has a long history and tens of thousands of pages.
But why spend so much time on an SEO audit if you could invest it in creating new content? The thing is, there are what's known as ballast — pages without traffic that drag the whole project down. You can invest resources in new content, but it may not get indexed or may receive a low search ranking due to slow loading speed, inconvenient structure, or technical errors across the entire website.
Conducting a website SEO audit, on the other hand, opens access to important opportunities:
- Understanding whether the web resource is indexed. Sometimes during development, when switching to another template, or when changing robots.txt, a “noindex” tag is placed in the code, making any promotion efforts meaningless.
- Eliminating technical errors. The absence of an SSL certificate, duplicate content, 404 pages, incorrectly generated sitemap.xml, and low speed are just some of the problems that hinder website promotion.
- Getting traffic from old pages. You can find content that, after removing outdated information, adding target keywords, and updating meta tags, can bring even more traffic than a new page.
- Improving user experience. By increasing page loading speed, improving mobile responsiveness, eliminating issues, and adding extra value, you enhance user interaction, which increases the chances of gaining new customers.
- New sources of traffic. The more comfortable it is for a user to stay on a site page, the more likely they are to share it with others. Thus, diagnosing a web resource followed by improvements can increase not only search traffic but also bring in a target audience from social networks, forums, and niche platforms.
You already understand why diagnosing a web resource is important, but another question arises: when should you conduct an SEO audit? The optimal period is every 3–6 months. However, this is not a “hard rule”. Many webmasters register reliable hosting and a domain, install a CMS and template, add 20-30 pieces of content, and leave the project for 2–3 months. Once the web resource has started indexing, they move on to active content creation and promotion, but first conduct a comprehensive check to understand what got indexed, whether there is traffic, and for which queries.
An SEO audit should also be performed during a redesign or website migration. When the CMS, template, and/or structure are changed, diagnostics are critically important to ensure correct migration, preserve old traffic, and set up redirects. And don’t forget to check your online project after search engine updates, such as Google’s March 2024 update, especially in cases of a significant drop in traffic and visibility.
How to Collect Initial Data for a Website SEO Audit
The main goal of a website SEO audit is to find problems that drag the project down and pages with high potential. However, before running diagnostics and implementing changes, you should record the current state of the web resource.
The first free tool for this is Google Search Console. First, go to the Performance section and select data for the past 12 months. You can save them right away using the Export button or add them manually to your own table — the main thing is to record the current state in Google’s search engine.
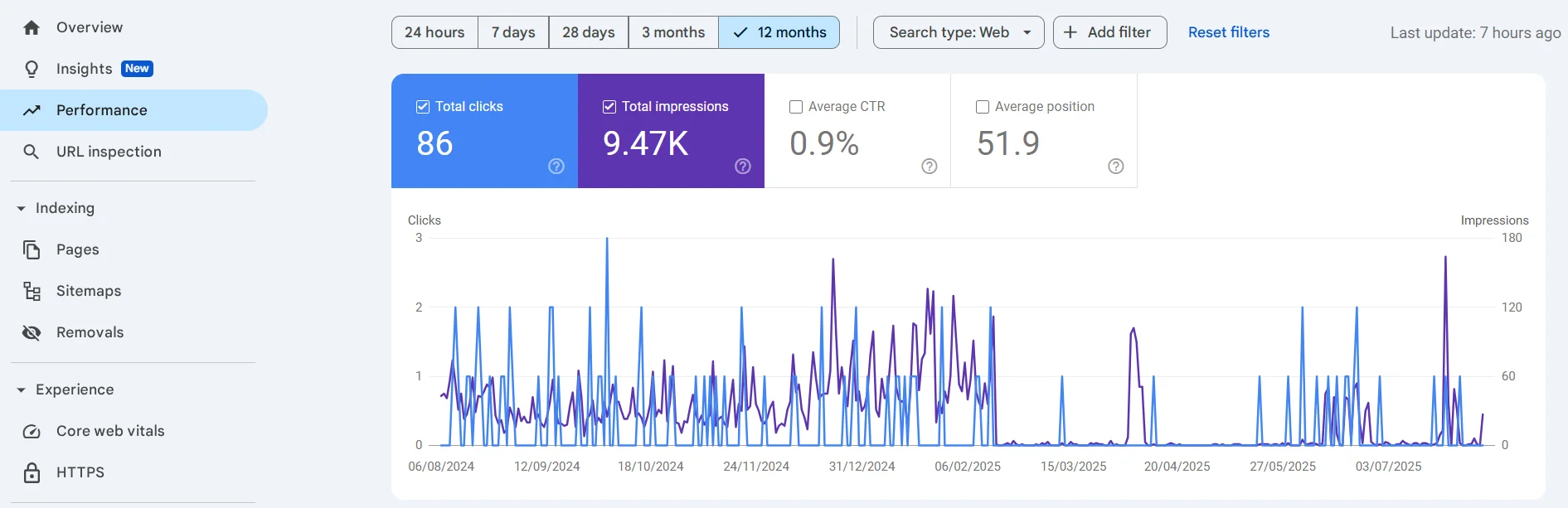
We are conducting an SEO audit of our English-language website. It has 4 blog articles and 32 online courses. Age — 2 years. A couple of months ago, only the template was changed and 1 article was published; no other work was carried out.
Now click on the date, select Compare and Compare last 6 months to previous period.
You will now see changes compared to the previous 6 months. In our case, all metrics have dropped, especially impressions and clicks.
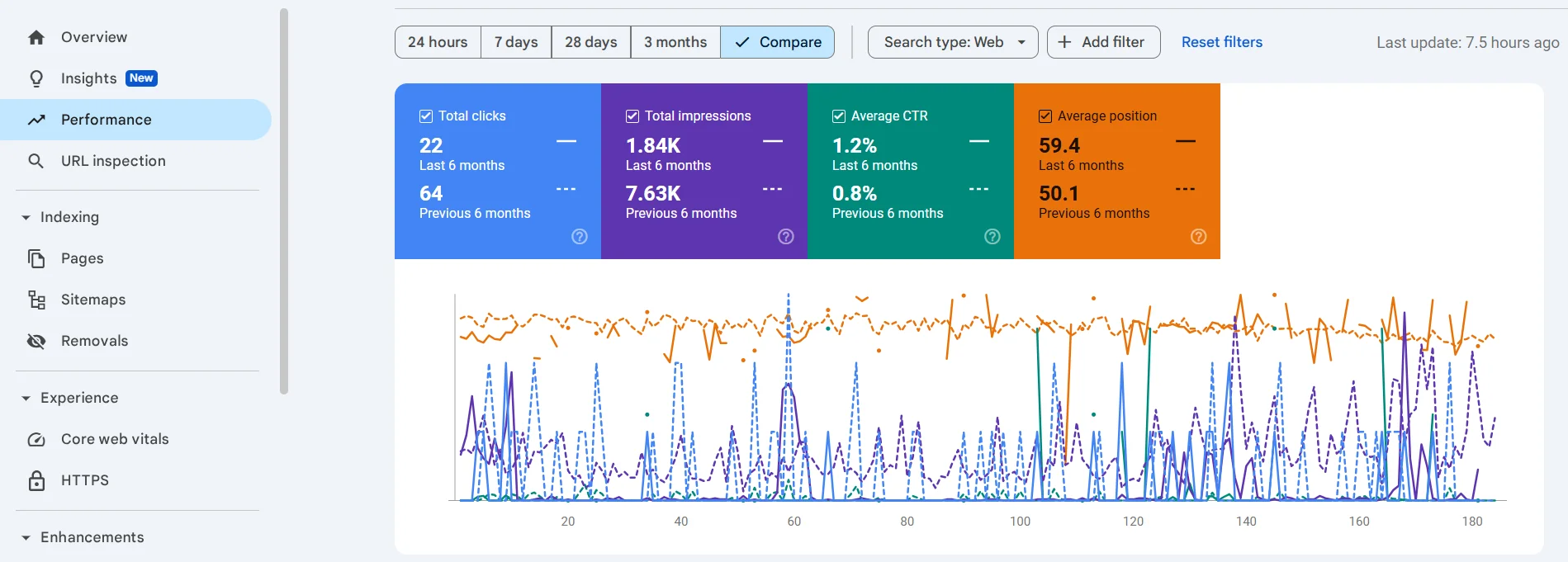
Below the graph, you can view changes by search queries, pages, countries, and other parameters.
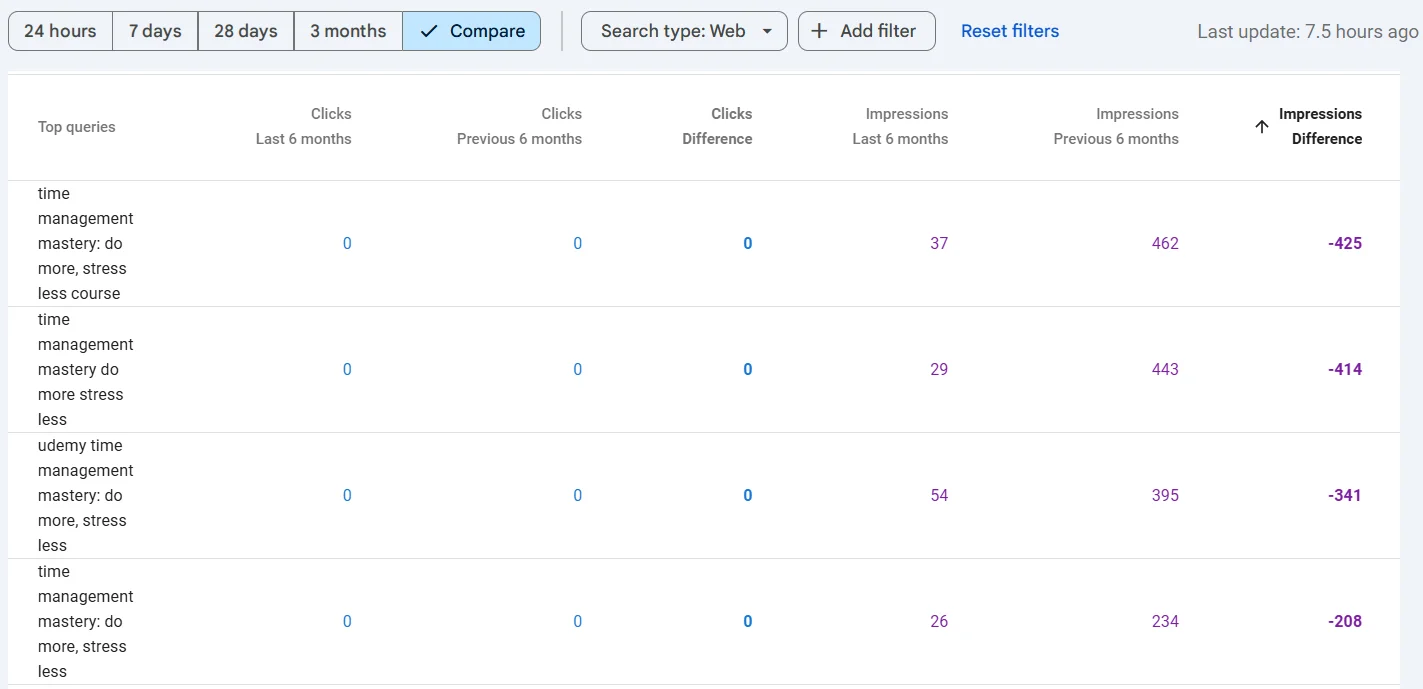
For example, one of our pages with an affiliate online course on time management has significantly dropped in impressions. As you can see, impressions for one query fell from 462 to 37, and there are dozens of such keywords.
Now click Export → Download Excel. You can store the data in one general table or create a separate page in Notion.
How to Conduct a Website SEO Audit Yourself: Step-by-Step Guide
We already have the initial data, so now we move on to step-by-step diagnostics. For the website SEO audit, we will use partially or completely free tools whose functionality is sufficient to obtain the necessary data for further improving the web resource. The key services include Google Search Console, PageSpeed Insights, Screaming Frog SEO Spider, Ahrefs, and Semrush.
Indexing Check — Make Sure Your Website Is in Search
We have confirmed that the web resource has impressions and even some traffic from Google’s search engine. Now it’s time to analyze whether all the content we need is in the search results, and conversely, whether there are any unnecessary pages there. To do this, go to Google Search Console → Indexing → Pages.
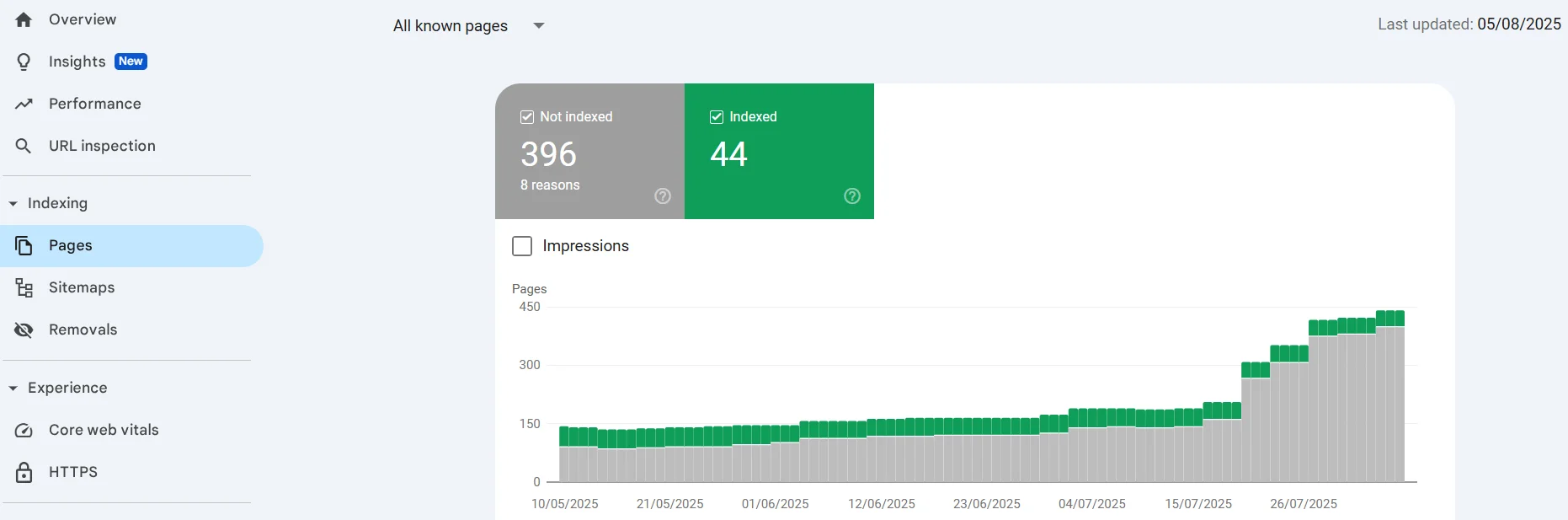
Here, we are interested in the overall indexing trend of the site. On the graph, we see a gradual increase in the number of pages in the index, without sharp spikes or drops — this is good. But 44 pages are indexed, while 396 remain unindexed. For better analysis, go to the table below the graph.
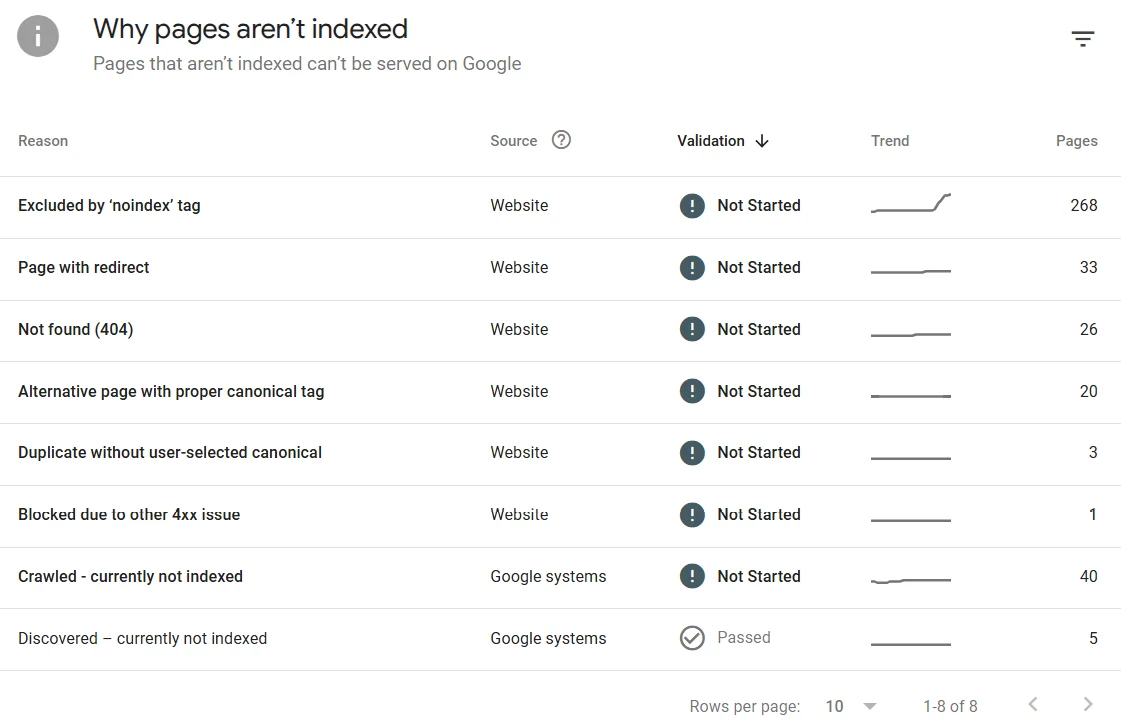
Let’s look at common reasons why a page may not be indexed:
- Excluded by noindex tag — indexing is blocked. In our case, all unnecessary pages are there, such as online-courses/?terms[0]=66&category[0]=66&course_category=content-marketing. If your important content is blocked, simply remove the noindex tag.
- Page with redirect — there is a 301 or 302 redirect to another address. Review the pages and check whether the redirect is needed. If not — remove it; if yes — do nothing, as Google does not index redirect pages, and that’s normal.
- Not found (404) — the search bot tries to check the page, but it does not exist. If the page should exist — change the URL or restore the content; if not — it’s better to set a redirect to another relevant page.
- Alternative page with proper canonical tag — a canonical link to another page is set. If the canonical is correct — do nothing; if you need this specific content indexed — remove the rel="canonical" tag.
- Duplicate without user-selected canonical — Google considers the page a duplicate, but it has no canonical link. First, determine which content is primary, then add a rel="canonical" tag from duplicates to the main one. It’s also possible the content is identical to that on another page, in which case it makes sense to rewrite the material.
- Blocked due to another 4xx issue — the search bot gets another 4xx code, such as 403 (forbidden). Check why the server is returning the 4xx code. If it’s an error — change the server configuration or allow access.
- Crawled – currently not indexed — the page has been crawled but, for now, is not being added to the index. Check the content quality: it may be weak or duplicated. Try adding internal links to it.
After the comprehensive website SEO audit, you will need to work with the collected data, so we recommend saving it right away. To do this, click on each reason and then on Export.
How to Supplement a Website Page Indexing SEO Audit
Additional useful data can be obtained with Screaming Frog SEO Spider — software that has a functional free version. You simply download the software from the official website, install it, paste the link to your web resource, and click Start.
Once the software finishes the website SEO audit, go to the Response Codes tab. Here you’ll find a list of pages with all server response codes that affect indexing. We recommend immediately sorting the data by the Indexability Status parameter so that pages with issues appear first.
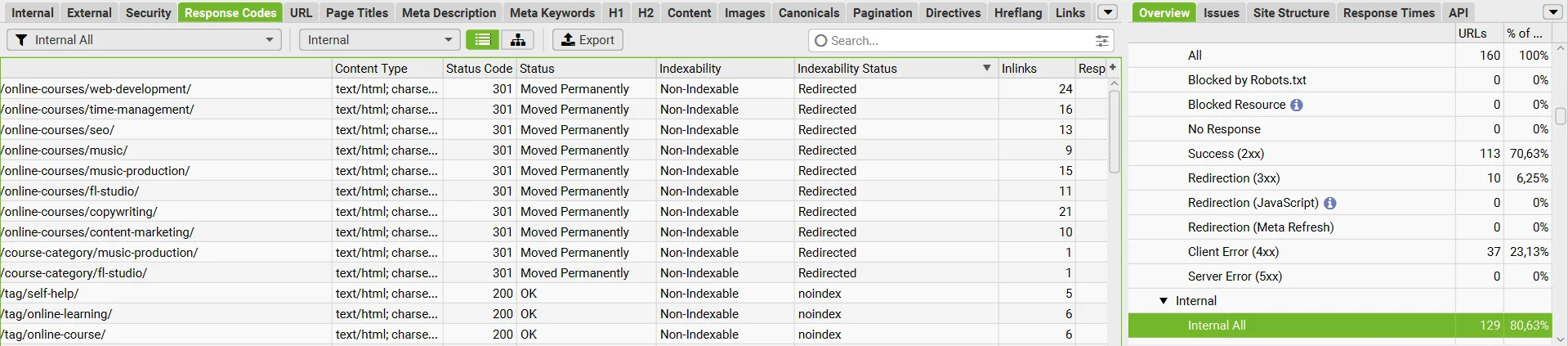
You will now see all the website’s pages that have a redirect, a noindex tag, a canonical tag, or that return a 404 error. To save the data, click Export, choose the format, and select the download location.
Important! Screaming Frog SEO Spider does not replace Google Search Console, but it can give you a more detailed technical snapshot in just a couple of clicks. While GSC shows actual Google data with a longer historical range (up to 16 months), Screaming Frog shows the state of the web resource right now — at the moment of scanning.
Another useful service for a website SEO audit is Semrush. For working with your own project, the free plan is sufficient. After registering and connecting your web resource, go to On Page & Tech SEO → Site Audit → Crawled Pages.
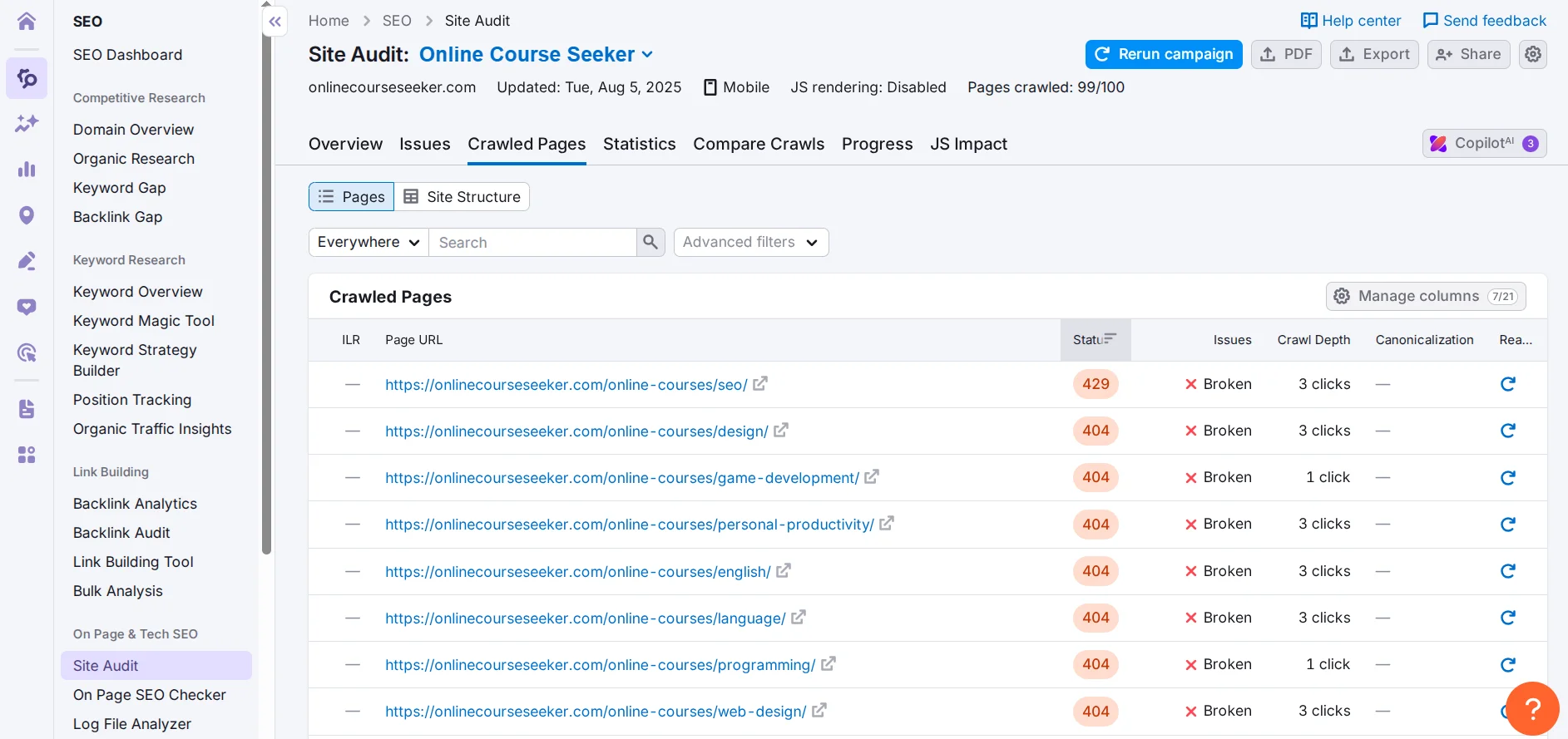
The table contains a list of URLs, status, issues, depth, and presence/absence of a canonical address. We also save this data by clicking Export. Although it doesn’t differ critically from Screaming Frog SEO Spider, it can be useful when creating your website audit report.
Technical Audit — Finding Common Errors
A technical SEO audit is needed to determine whether search engine bots can properly crawl and index the web resource, and whether it is convenient for visitors to use it. The main task during this process is to assess the foundation — that is, security, speed, adaptation for different devices, and other similar aspects.
Let’s look in more detail at specific points to check during a website technical audit:
- Robots.txt file. It should be available at site.com/robots.txt and contain a link to the sitemap. Always check the correct use of Disallow, meaning there should be no accidental blocking of important pages.
- XML sitemap. It should be created and accessible at site.com/sitemap.xml, update automatically after changes to the site, and contain only the necessary pages. On our test WordPress site, we use the Rank Math SEO plugin to manage the sitemap — it automatically updates it, allows you to configure separate sitemap.xml files for posts, pages, and special materials (in our case, online courses). You can check the sitemap via Google Search Console → Indexing → Sitemaps.
- Mobile responsiveness. The online project should be adapted for different devices, including tablets and smartphones.
- Loading speed. The optimal page loading speed is up to 2 seconds. To check, use Google’s official tool — PageSpeed Insights: simply paste the link to the web resource and click Analyze.
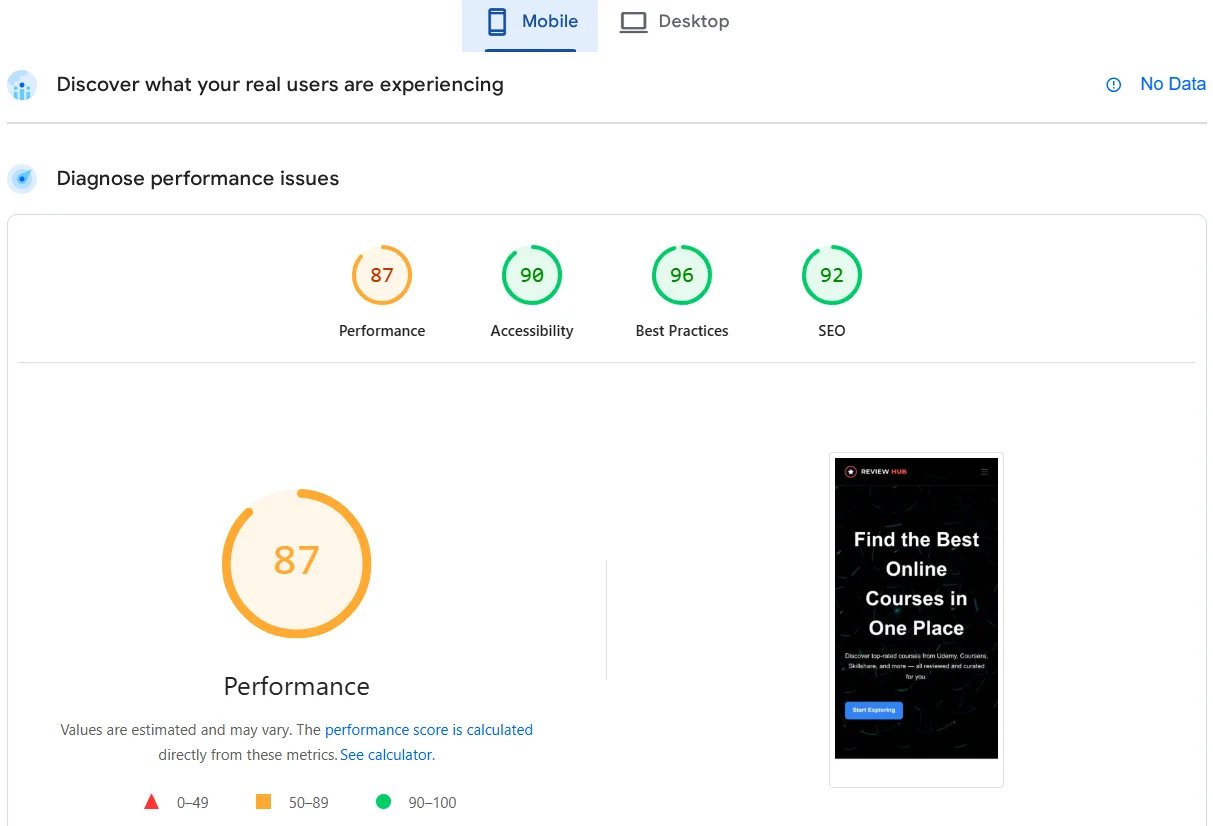
To work effectively with the collected data later, we recommend reading our article on the main website loading speed metrics.
- Security. First, make sure the online project opens via HTTPS, not HTTP. Check for the absence of mixed content so that HTTPS pages do not contain images, scripts, or other resources over HTTP. Analyze the project for broken pages, redirects to third-party platforms, and suspicious scripts.
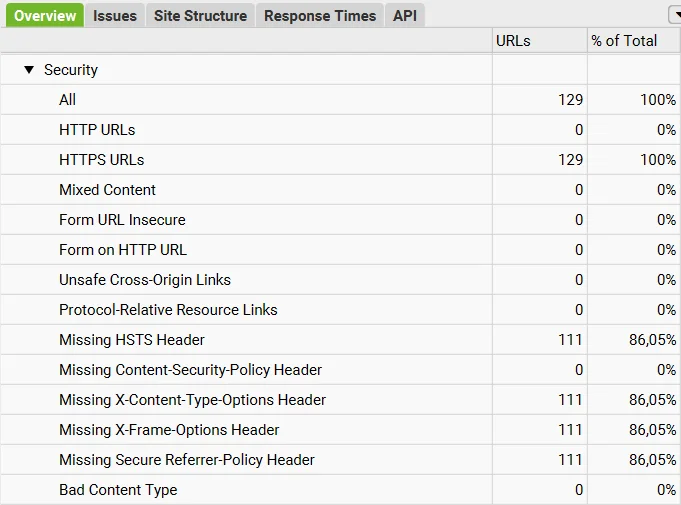
Website security check via Screaming Frog SEO Spider. This appears immediately after a full scan, to the right of the main data.
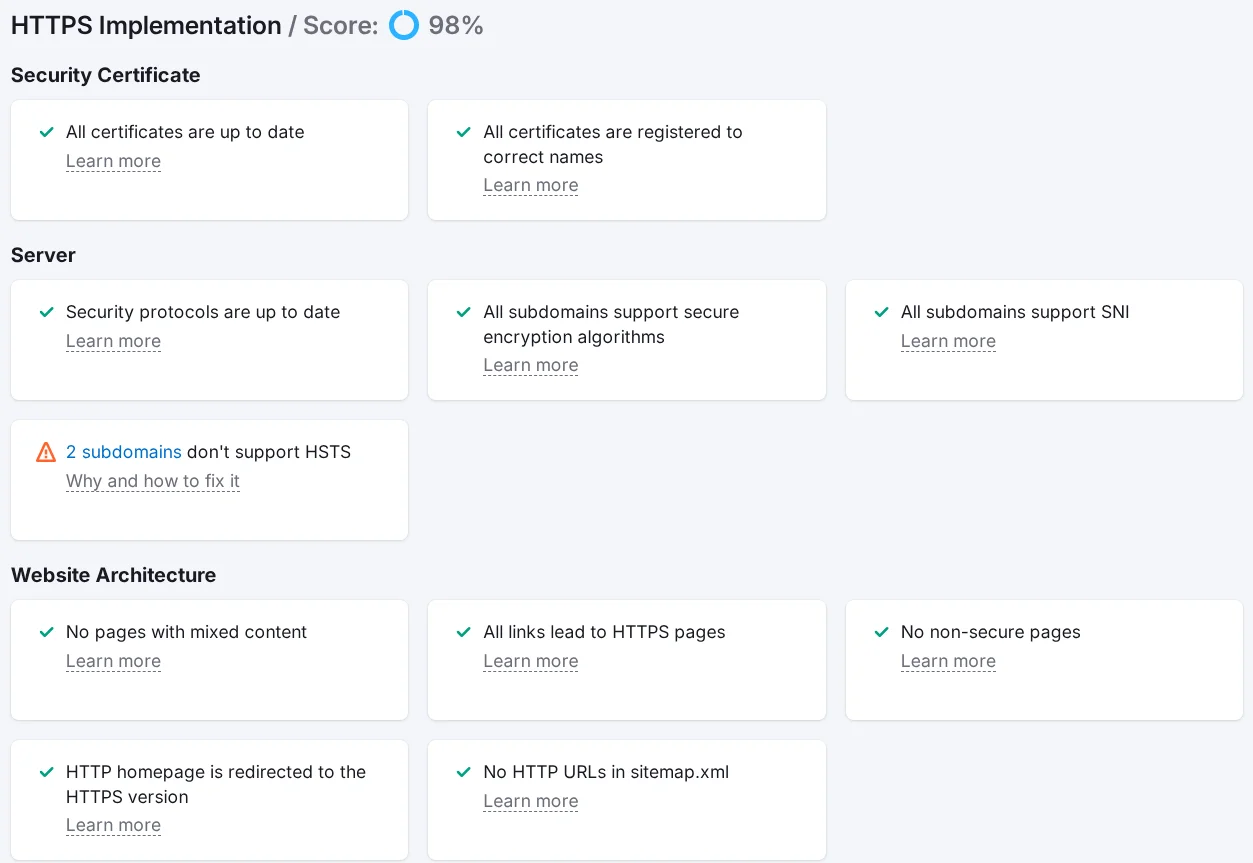
HTTPS check via Semrush. The data is located in On Page & Tech SEO → Site Audit. Here you can see whether all certificates are updated, registered with the correct names, whether HTTP is redirected to the HTTPS version, and so on.
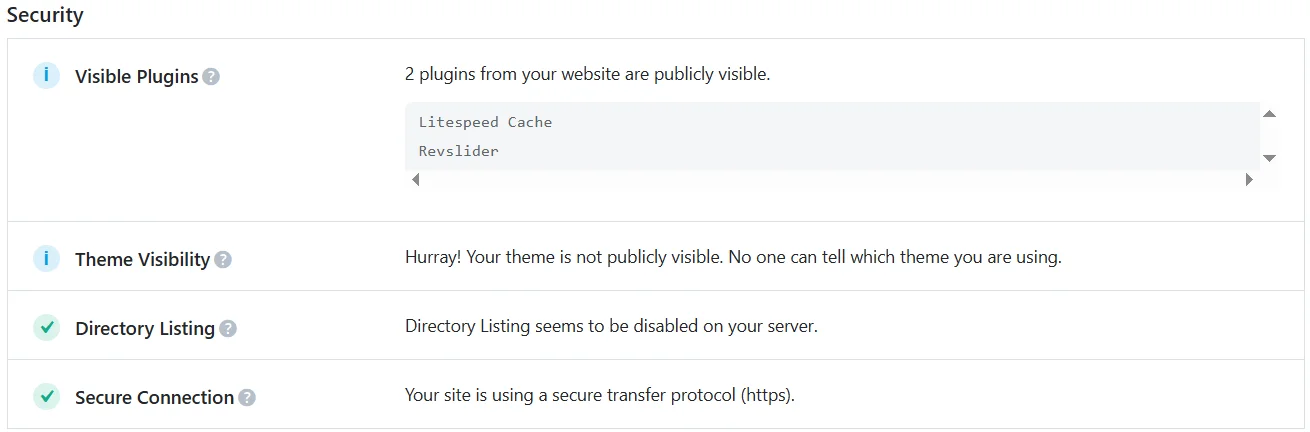
Rank Math SEO plugin allows for a comprehensive site analysis, including security. Simply go to the SEO Analyzer section and scroll to the very bottom of the page. Here you will see publicly visible plugins and themes, the presence/absence of a directory listing on the server, and the secure data transfer protocol status.
Content Analysis — Taking Pages to the Next Level
In our article about pages without traffic, we already mentioned that sometimes simply updating the content, optimizing images, and/or refreshing meta tags is enough for a page to reach the top of search results, start getting impressions and clicks. This is especially true for evergreen content, which has every chance of attracting a target audience for years, but as a result of poor optimization becomes ballast, dragging the entire online project down.
When conducting a website SEO audit, pay special attention to the following points:
- Relevance. Make sure the texts contain only up-to-date information. In our case, most courses were published in 2023–2024, so the curriculum, prices, ratings, and so on should be updated.
- Uniqueness. The text posted on a web resource can be partially or fully copied and published on another project, so we recommend checking uniqueness periodically. For materials in English, you can use DupliChecker.com.
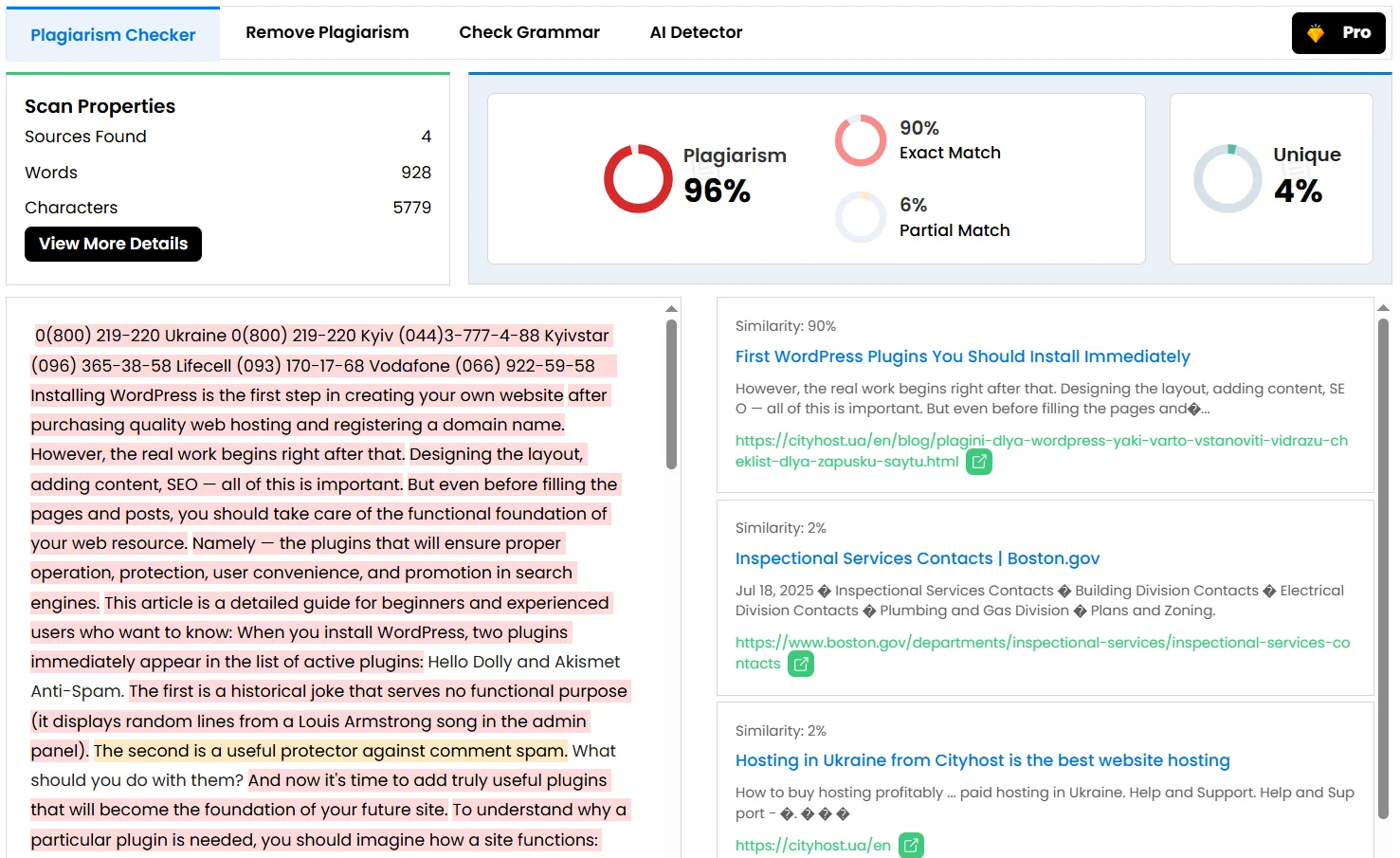
Example of analyzing our already published article “Plugins for WordPress You Should Install Right Away — A Checklist for Launching Your Website” through DupliChecker. Here you can directly paste the page link, and the system will automatically transfer its text into the check form.
- Image optimization. Make sure there are only media files on the pages. Check the image size and, if necessary, reduce it using Online Image Compressor, TinyPNG, iLoveIMG, or similar tools. Analyze whether all images have an alt attribute, its length, and whether it contains a keyword. You can learn more about image optimization in our blog.
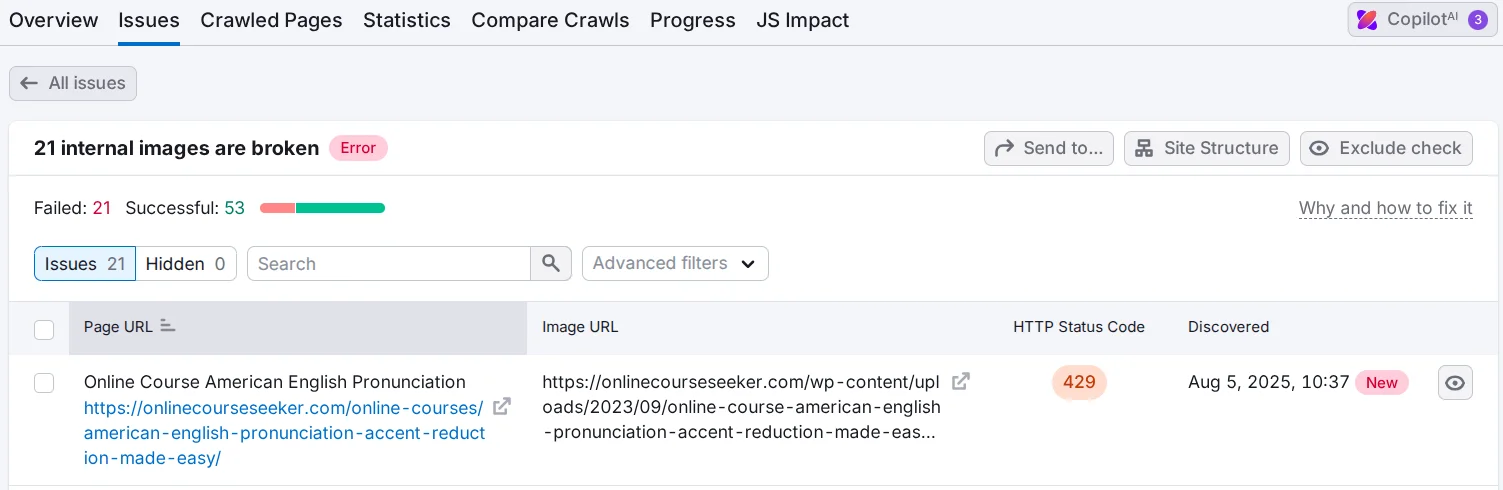
In Semrush, the Site Audit section shows all non-working images.
Checking image optimization on a site via Screaming Frog SEO Spider.
- Internal linking. Check for broken internal links on a page and the presence of the nofollow tag in links — they should actually help distribute link equity evenly across the online project.
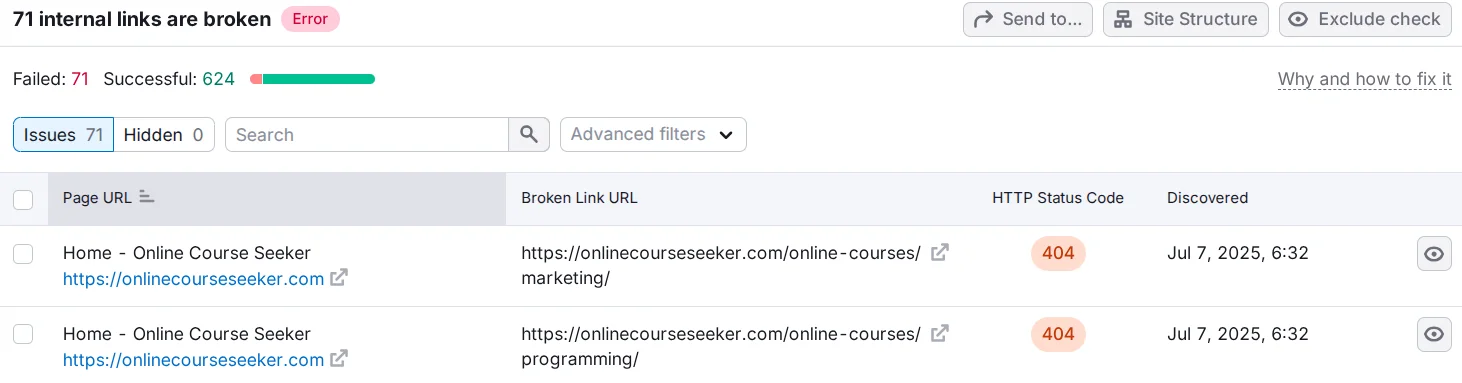
You can check non-working internal links in Semrush in the Site Audit section.
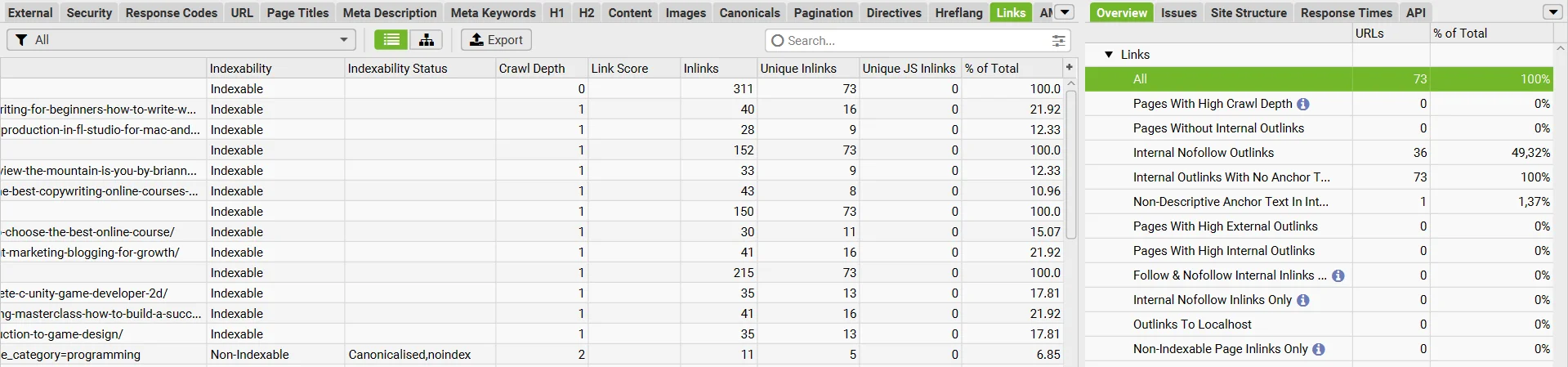
Screaming Frog software helps get a comprehensive report on internal links.
- Links to other web resources. Make sure all external links open in a new tab and contain rel="nofollow" — here, it is necessary. Check for broken links. Avoid recommending unsafe online projects, linking only to authoritative sources.
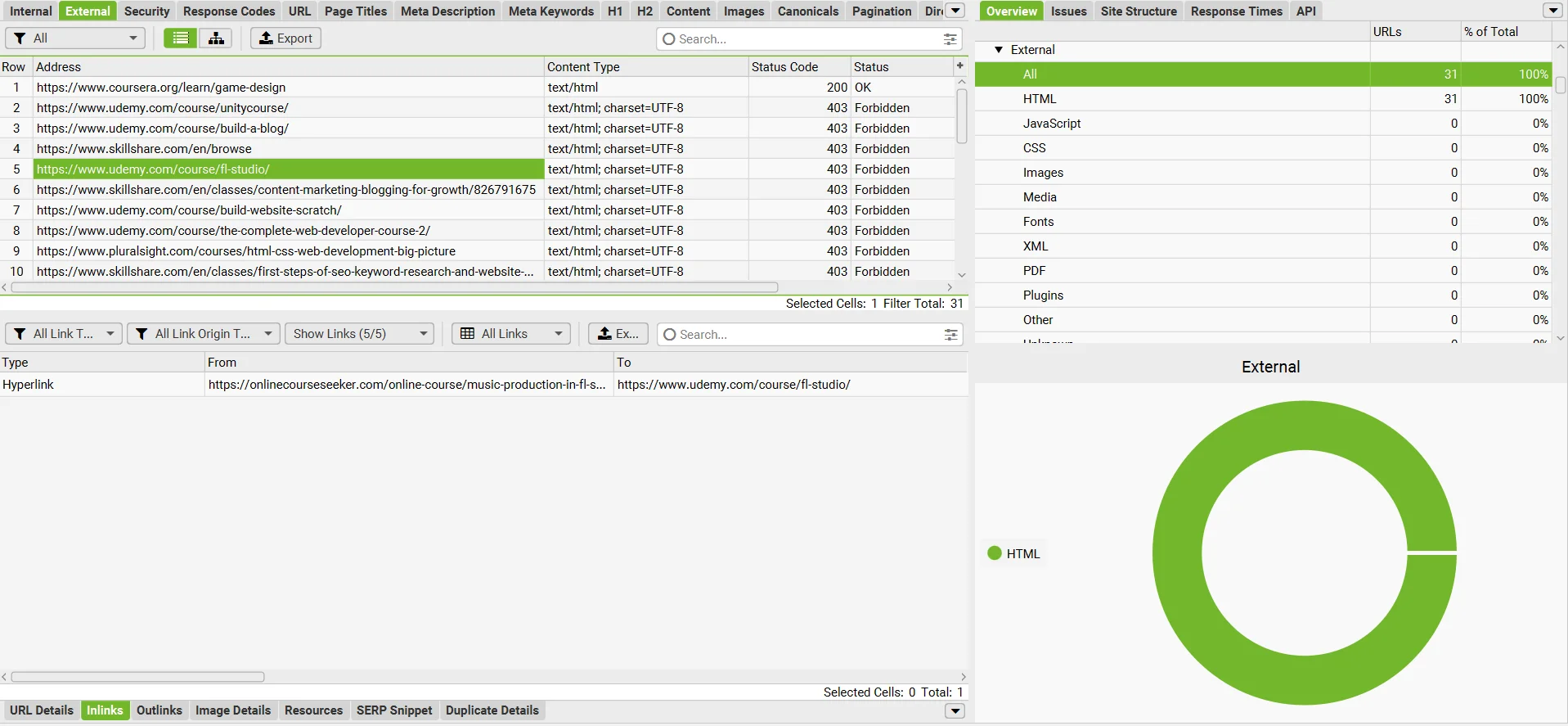
Screaming Frog SEO Spider allows you to see all the links leading from your site to other web resources and their status. By clicking on a link, you can find out on which page it is located.
- Markup. Analyze whether structured data is created and configured for articles and special pages (products, online courses, movies, and similar). If your site runs on a content management system, you can work with it using the Rank Math, Yoast SEO, or All-in-One plugins.
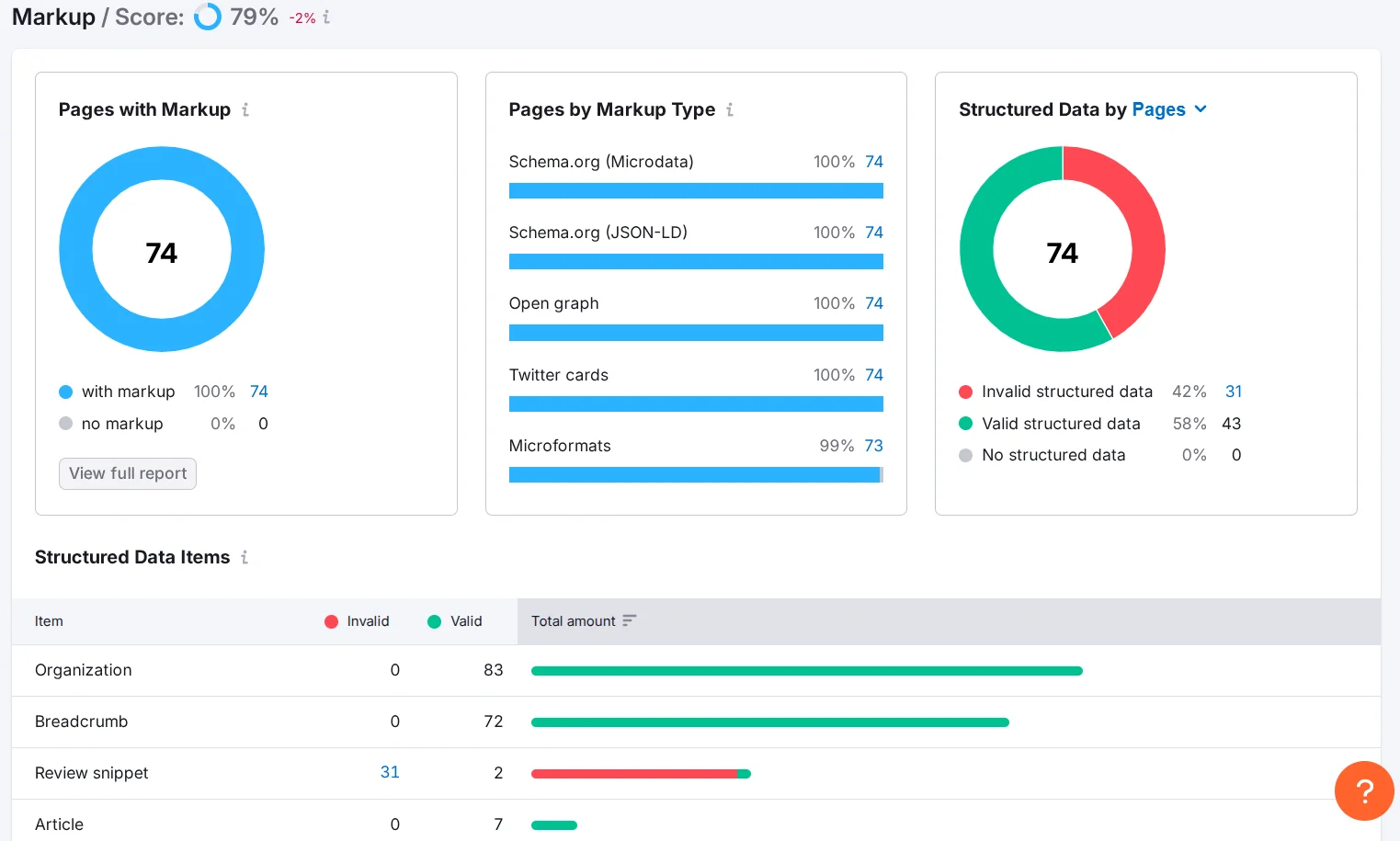
You can check site markup in Semrush in the Site Audit section.
- Title. Each page must have a unique Title of 50-60 characters. Also, avoid duplicates with the H1 title. To prevent common mistakes, we recommend reading our article on how to correctly write a page Title.
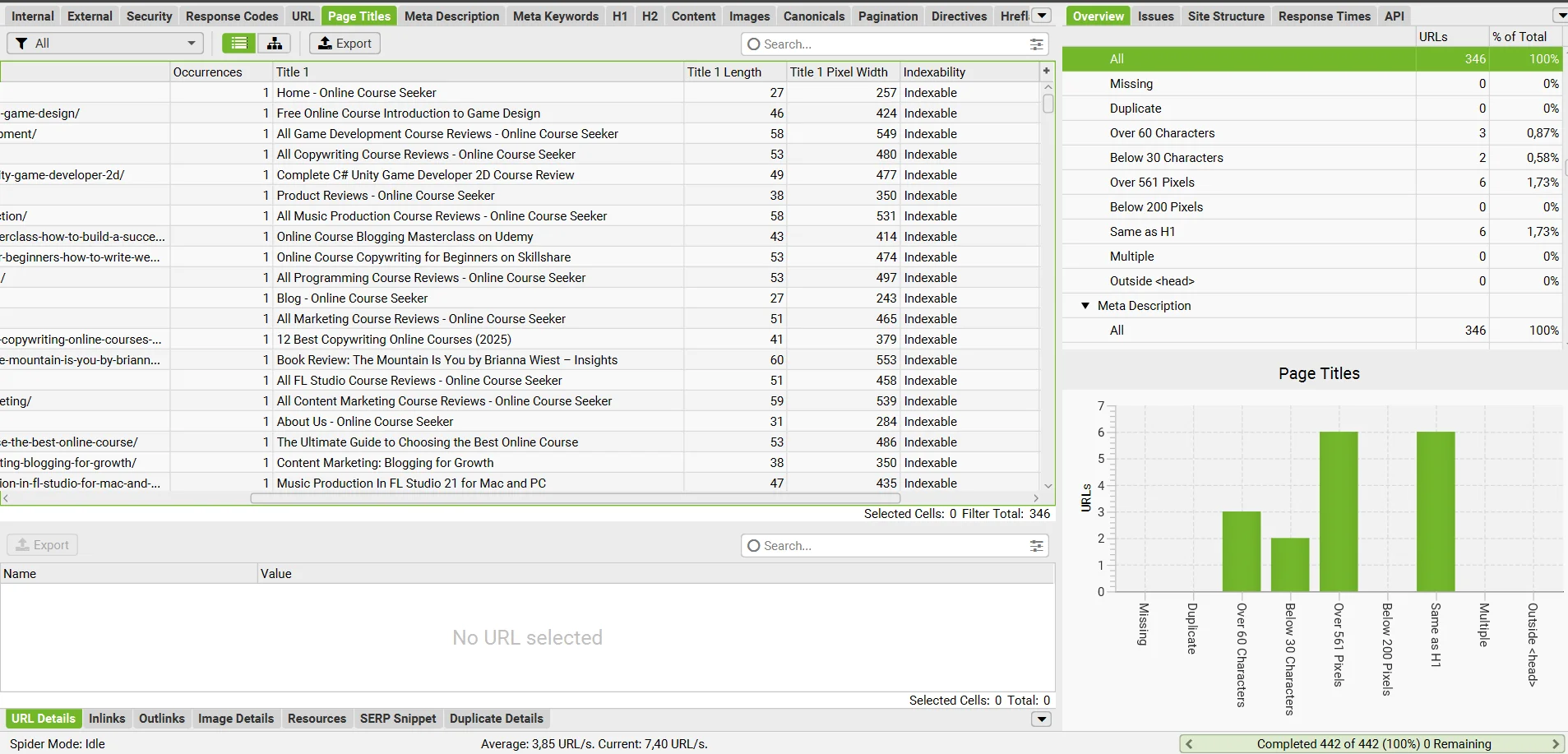
You can check the Title length with Screaming Frog SEO Spider.
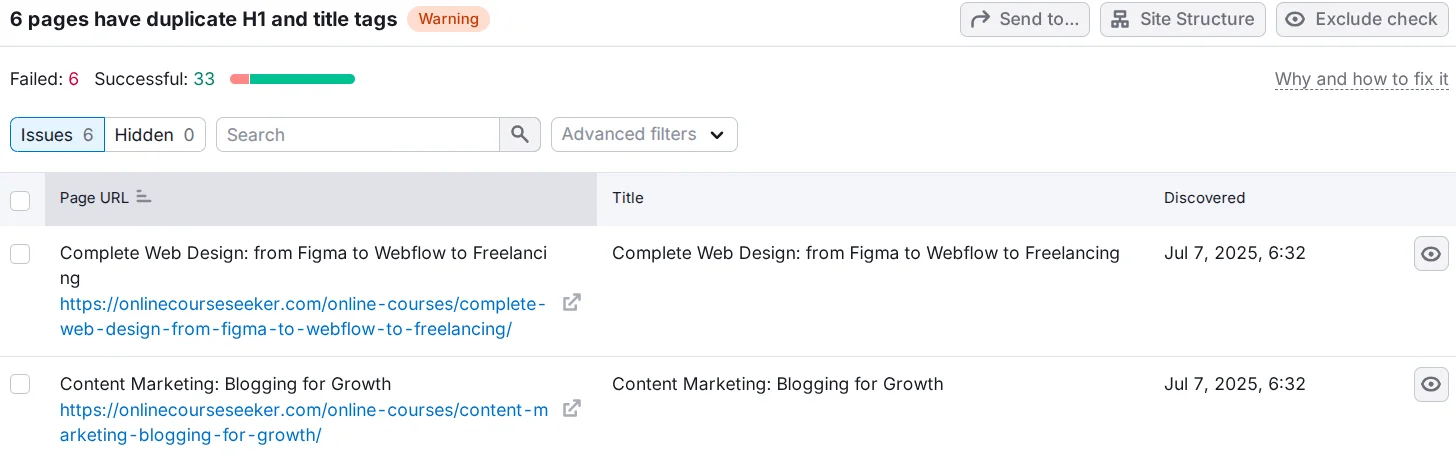
You can find H1 and Title duplicates in Semrush via Site Audit → Issues.
- Description. Each page should have a unique, content-relevant Description of up to 155-160 characters. More tips can be found in our article on how to write a Description.
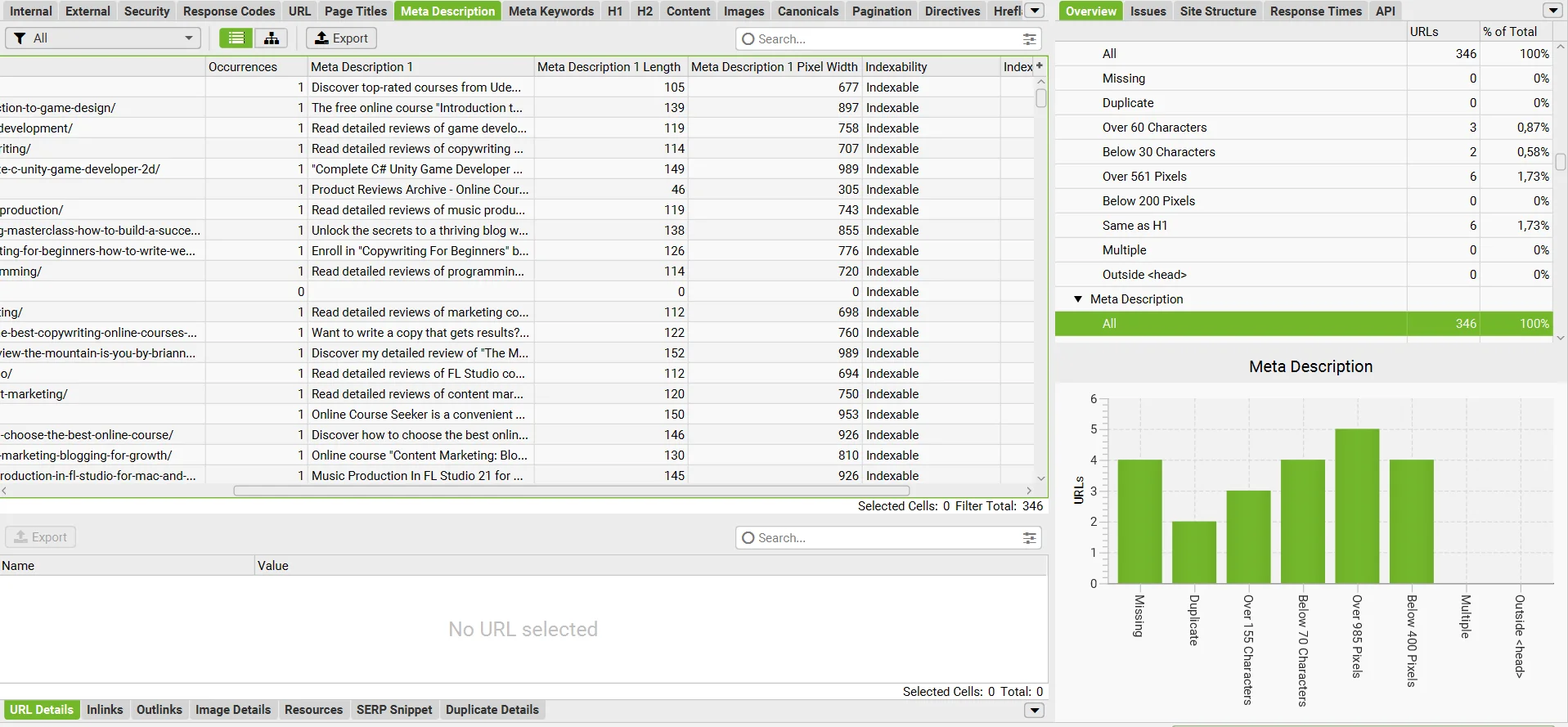
You can view the Description and its length with Screaming Frog.
When conducting an SEO audit, we recommend recording data in a table with a mandatory “classification” column. Here, mark which page needs updating (content is interesting but some information is outdated) and which needs to be completely rewritten (full review and editing of the material). There may be cases where the content overlaps significantly with similar pages, in which case it makes sense to merge them into one.
Backlink Audit — Removing Unnecessary Links and Getting New Backlinks
Although search engine algorithms are constantly changing, backlinks remain one of the key ranking factors. For example, the Backlinko team analyzed 11.8 million pages from Google’s search results. One of the main factors for reaching the TOP was the overall link authority: the more quality backlinks a page had, the higher it ranked compared to competitors who did not have as many backlinks.
That’s why during a website SEO audit it’s important to conduct a comprehensive backlink profile check:
- Overall status. Check the current DR — the domain’s authority score, calculated based on the quantity and quality of unique domains linking to your website. Also check the total number of backlinks and referring domains, and review overall backlink trends over time: whether there is growth or decline, and if there were sharp spikes or drops.
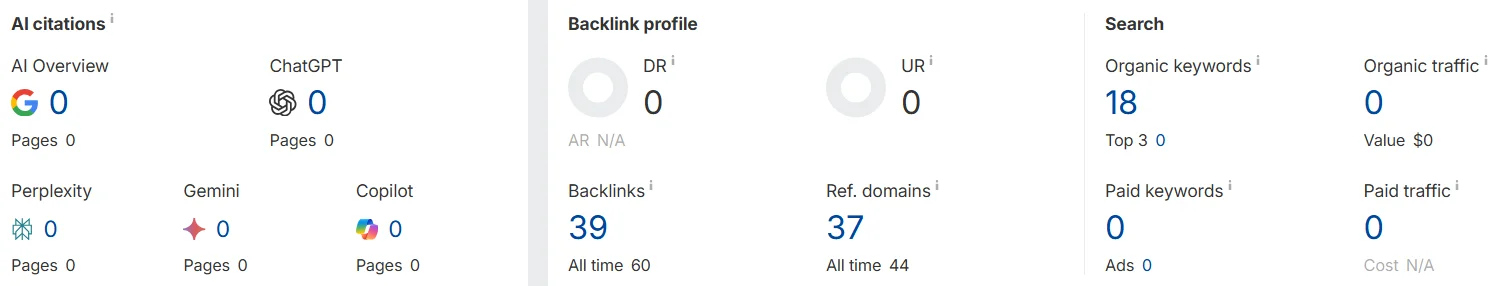
You can check the overall backlink profile status in Ahrefs → Overview even with a free account.
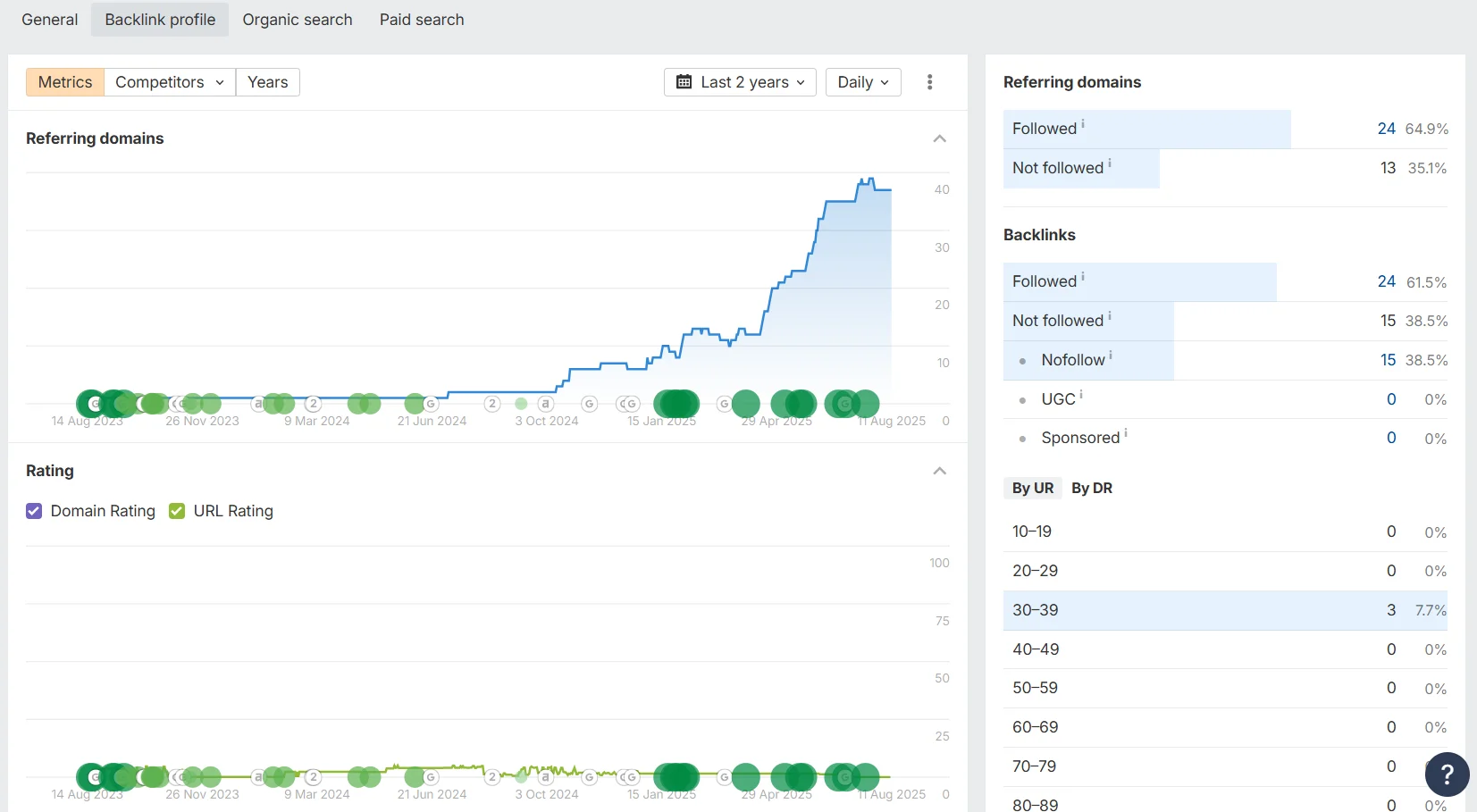
A bit lower, in the Backlink profile tab, you’ll see a general graph of changes in the number of referring domains, domain ratings, and their type (followed, not followed).
- Backlink quality. Review all backlinks: DR and UR (another authority metric, but for the specific page), type (follow, nofollow), the donor’s traffic, and anchor text. Check for toxic links, i.e., links from adult sites, gambling platforms, or broken resources.
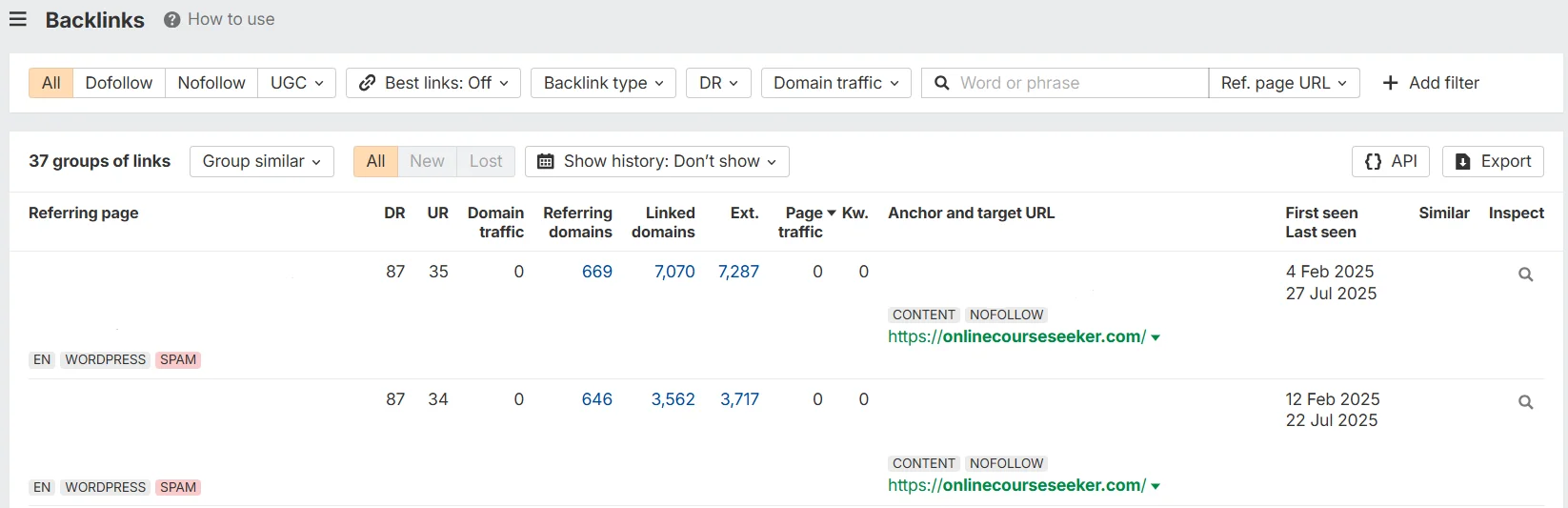
In Ahrefs, you can check not only the main parameters of the donor page for free, but also find spammy links.
- Donor quality. Analyze the domain’s authority, traffic, country, and topical relevance to your website.
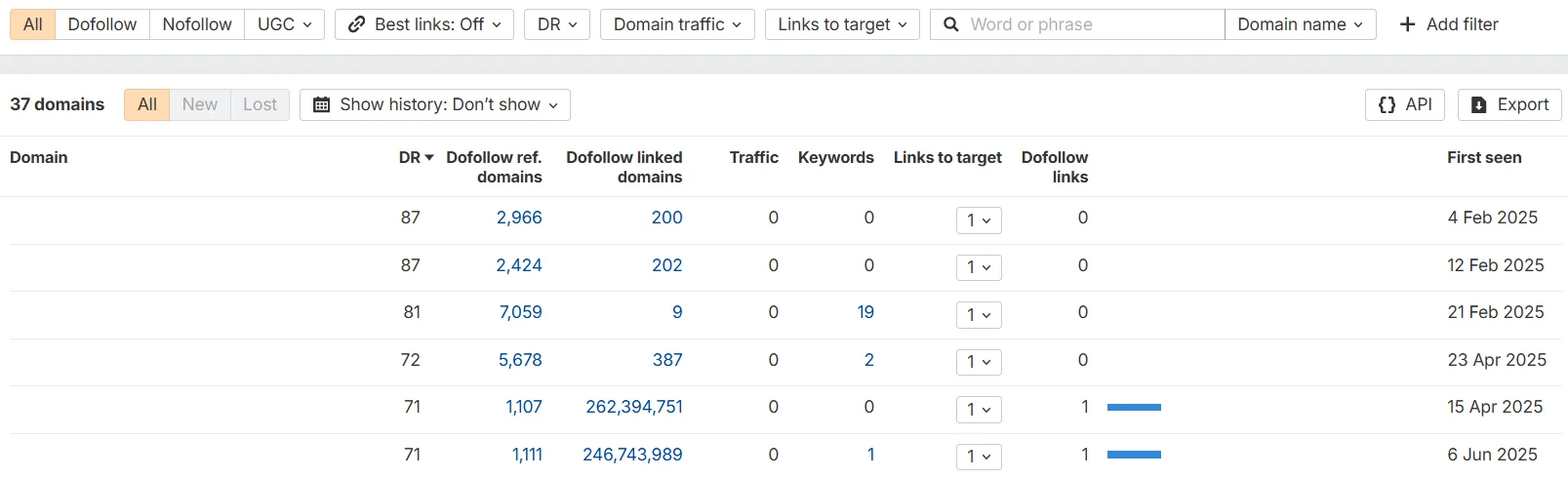
The free version of Ahrefs lets you find all donors and check their authority, traffic, links, etc.
- Anchor list. Review anchor text distribution: branded, containing keywords, and generic ones such as “here”, “click here”. The main goal is to ensure that the anchor list looks like the result of genuine content distribution. Check how often and on which websites the anchor is used.
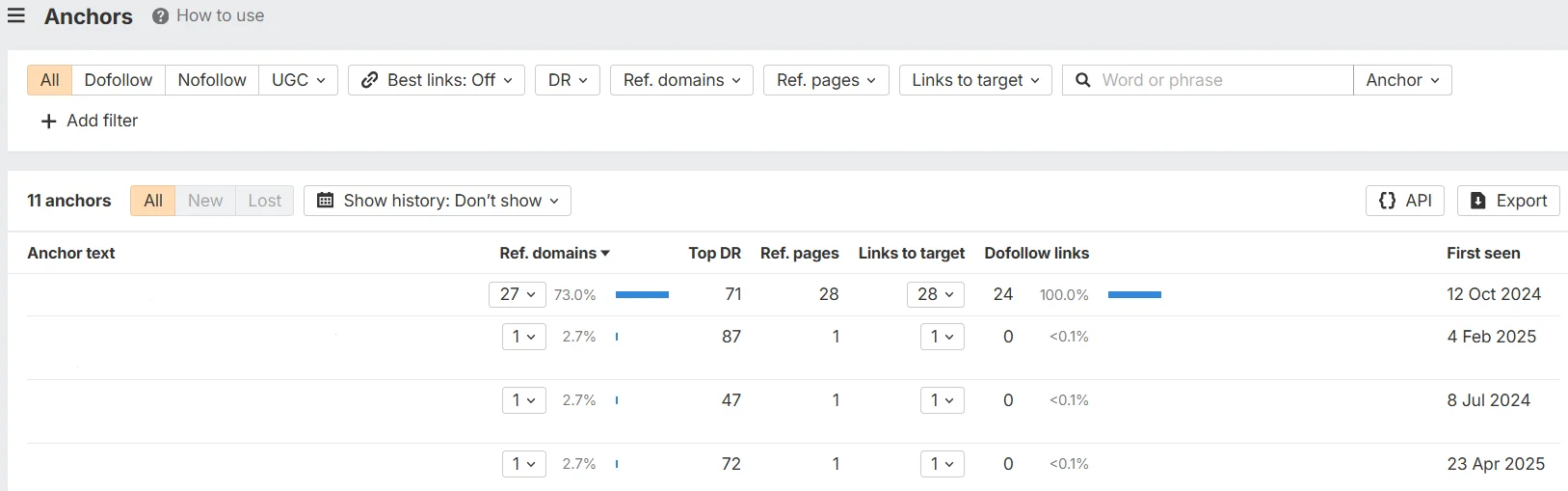
Example of anchor list analysis in Ahrefs.
You may have noticed that for backlink profile analysis we switched from Semrush to Ahrefs. The reason is that the free version of Semrush allows only 10 queries per day even for a verified project. If you’re not in a rush, it’s generally better to use both platforms, gradually saving the data from each.
As an alternative, we recommend Open Link Profiler. You need to register, confirm your email, insert your website link, and click Get Backlinks. The service instantly shows the total number of backlinks and broken links, the domain rating, backlink types, and platforms. At the bottom, you can view details for each donor: backlink type and rating, as well as page and domain evaluation.
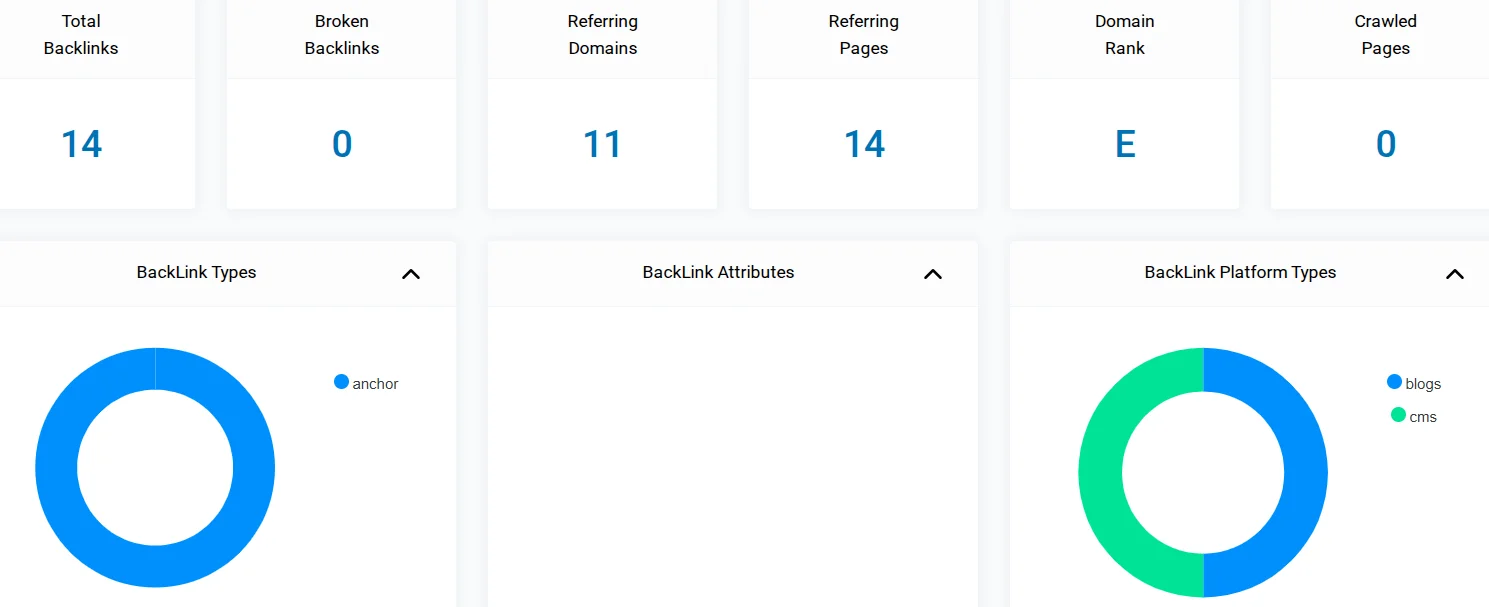
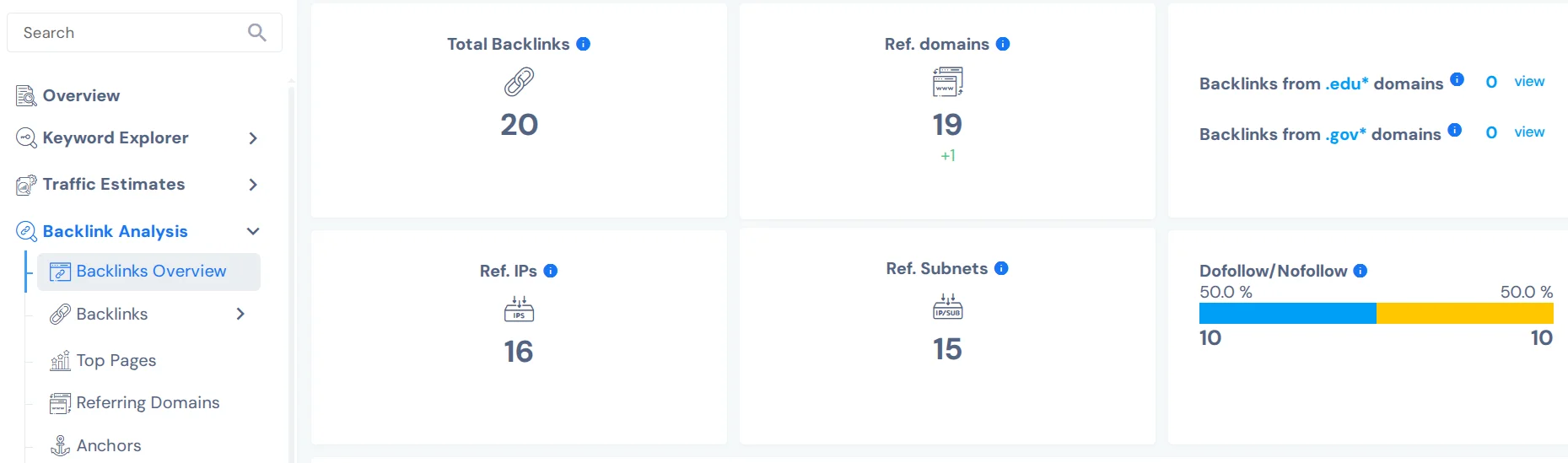
Another useful tool is SEO Insider. To access backlink analysis, you also need to register and confirm your email, then insert your site link to get analytics. It displays the total number of backlinks and referring domains, the dofollow/nofollow distribution, and below — a report for each link, including spam rating. However, with a free account you only get up to 10 reports per day.
Considering the limitations of these tools (usually 10 checks per day), save the obtained data right after analysis. When you refresh pages or explore individual metrics (total number of backlinks, donors, anchors), the available number of checks decreases. It’s better to save the information first and then analyze it in your preferred format in a ready-made table or PDF file.
What to Do with the Data Obtained After an SEO Audit
During the SEO audit, we collected data in separate tables from different services. Now we can create one large table with a list of URLs and corresponding parameters, taking into account the date of creation and last update, indexing status, presence in sitemap.xml, content relevance, internal and external links, and so on. You can add a comment directly in the table to each parameter explaining exactly what needs to be fixed.
Now let’s look at the main actions you can take after a website SEO audit to improve its visibility in search engines and increase traffic:
- Eliminating critical technical errors. Instead of broken links (404 error), set up redirects. Fix indexing issues, for example, remove noindex where it is not needed, or add valuable pages to the index. If necessary, update and optimize sitemap.xml and robots.txt.
- Increasing loading speed. Configure caching, remove unnecessary scripts, compress images.
- Improving content. Expand “thin content” — articles with too few characters. Rewrite outdated and/or non-unique information with new keywords. Optimize H1-H6 headings, Title and Description meta tags. Add internal links for better interlinking and to avoid “orphan pages”.
- Implementing structured data. Add rich snippets to articles, products, services, and other similar pages to stand out among competitors in search results.
- Building link mass. First, remove or disavow toxic backlinks via the Disavow Tool (Google Search Console). Then start building link mass: it is not necessary to immediately buy expensive backlinks from top platforms, as you can start with social networks, forums, and content platforms like Medium.
An SEO audit is not a one-time action. Search engine algorithms change, as do the needs of the target audience, and competition is constantly growing. If you do not check the website every 3-6 months, you may face worsening indexing of new pages and removal from the index of existing ones, loss of visitors due to slow loading of the online project, outdated and uninteresting content, and a drop in rankings due to spammy backlinks.
Regular SEO audits with mandatory changes, on the other hand, will help improve rankings in search results, increase traffic, and achieve higher competitiveness. And all the time and effort you spend on analyzing and improving the website will return in the form of a satisfied target audience, and consequently, new customers and increased income!