- It Won’t Be Easy Anymore: From Simple to Complex SEO
- Why People Are Once Again Talking About the Death of SEO
- How to Adapt to Unpredictable and Complex SEO
- Flawless User Interaction Is the Key to Top Rankings
- Fighting the death of SEO with expertise
- Transitioning from Exclusively Google to a Comprehensive Traffic Acquisition Approach
- Optimizing for AI Search Results — Time to Join the Artificial Intelligence
- Personalization — Adapt to the Interests of Each Specific User
- Ukrainian Webmasters Are Not Facing the Death of SEO (for Now)
Impressive updates to search engine algorithms, the rapid development of artificial intelligence, changing user behavior, and the battle between large and small websites are leading to a new wave of talk about the death of SEO. Although this issue has been raised repeatedly over the past 10 years, it usually lost relevance after the search results stabilized. However, 2024 has truly made many consider switching to other sources of traffic, since after the March update, thousands of websites lost 90–100% of their traffic without any obvious reasons. And these changes are just the beginning on the path to... the death or inevitable transformation of SEO.
It Won’t Be Easy Anymore: From Simple to Complex SEO
Beginners in search engine optimization might think that SEO has always been this complicated and expensive, but things really were better in the past. In the early years of search engines like AltaVista, Yahoo!, and Google, algorithms relied heavily on keywords: a web page with basic formatting and lots of keywords would rank high in the results. There was almost no competition, and the informativeness and uniqueness of content played a minimal role. Even manipulative practices worked effectively back then — for example, keyword stuffing and mass linking from low-quality websites.
In 1998, the first blogging platform Open Diary was launched.
The easiest period for SEO was in the early 2000s. Although Google paid more attention to content quality than other search engines, keywords still played a huge role. The main ranking factor was the PageRank algorithm, which took into account incoming links — in other words, buying a large number of backlinks could significantly boost a site’s position. Everything worked in the simplest way: more keywords in the text, more backlinks (regardless of quality), and your site is in the TOP.
In 2003, the first changes arrived — namely, the Florida Update, which targeted manipulative practices such as keyword stuffing. The second major shock for webmasters was the 2011 Panda update: assessing page quality led to massive traffic loss on web resources with low-quality content. Then came Penguin in 2012, punishing websites for poor, purchased, or irrelevant backlinks.
This is approximately what blog posts looked like in 2007.
In 2015, after the release of the AI component RankBrain for processing unfamiliar queries, the importance of behavioral factors increased. Since 2018, Google has improved at indexing sites with mobile versions, so web resources with poor mobile adaptation began to lose positions. That same year, the Medic Update was released, introducing a focus on E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) — especially for YMYL niches (health, finance), meaning that texts by authoritative authors became more valued.
After 2018, many more updates were released, but they all pursued a common goal: to turn Google from a “website directory” into a responsible platform. And it was partially successful: SEO began to require more effort, time, and money, owners of Internet projects began to choose reliable hosting with improved performance, improve user experience, pay attention to creating truly useful content, and work on comprehensive brand development.
Read also: What is a Search Engine Robot and How to Manage It
Why People Are Once Again Talking About the Death of SEO
After every update, webmasters would recover, adapt their web resources to the changes, and restore or even improve their rankings. So why talk about the death of SEO again, when it would be more reasonable to analyze the latest changes and focus on improving the website?
The reason lies in the largest algorithmic update in Google’s history, which lasted over a month (from March 5 to April 19, 2024). The main goal of the March 2024 Core Update was to clean the index of “junk” content — that is, to reduce the amount of unhelpful content in search results by 40%. After the update, 80–100% of traffic was lost by new or lesser-known websites without E-E-A-T, web resources with fully AI-generated material, and internet projects with non-unique or overly spammed content.
Despite the massive changes, talk of SEO’s death is clearly exaggerated. According to Exploding Topics, Google processes 16.4 billion search queries daily (6.3 million per minute), and the average user performs 4.2 queries. In comparison, the most well-known AI chatbot, ChatGPT, received about 37.5 million search queries per day — only 0.25% of the market share. Of course, artificial intelligence is still in its early stages, and this share will only grow in the future, but traditional search is clearly in much higher demand than AI.
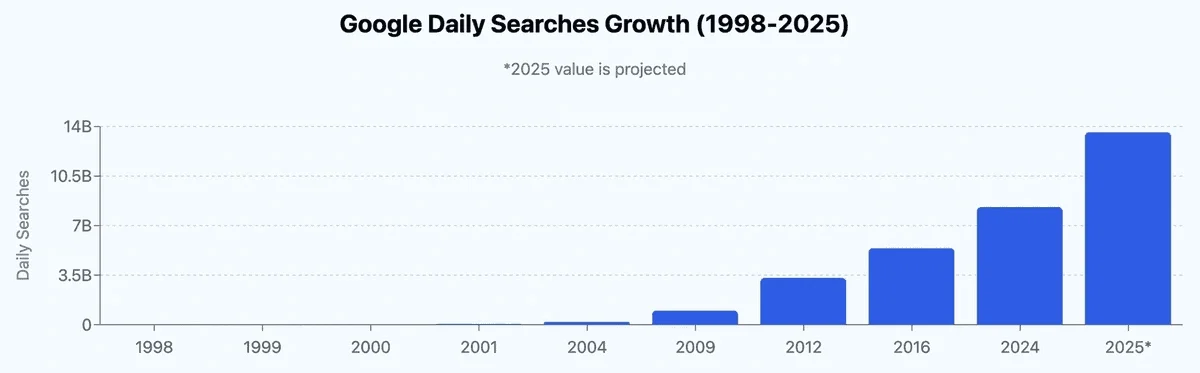
Chart of daily search query growth on Google
The question of SEO’s death could be closed if not for another sad statistic. According to SparkToro, 58.5% of search queries in the U.S. and 59.7% in the EU do not result in a website visit. That’s why, to better understand the relevance of search engine optimization, it’s worth highlighting several major threats to SEO.
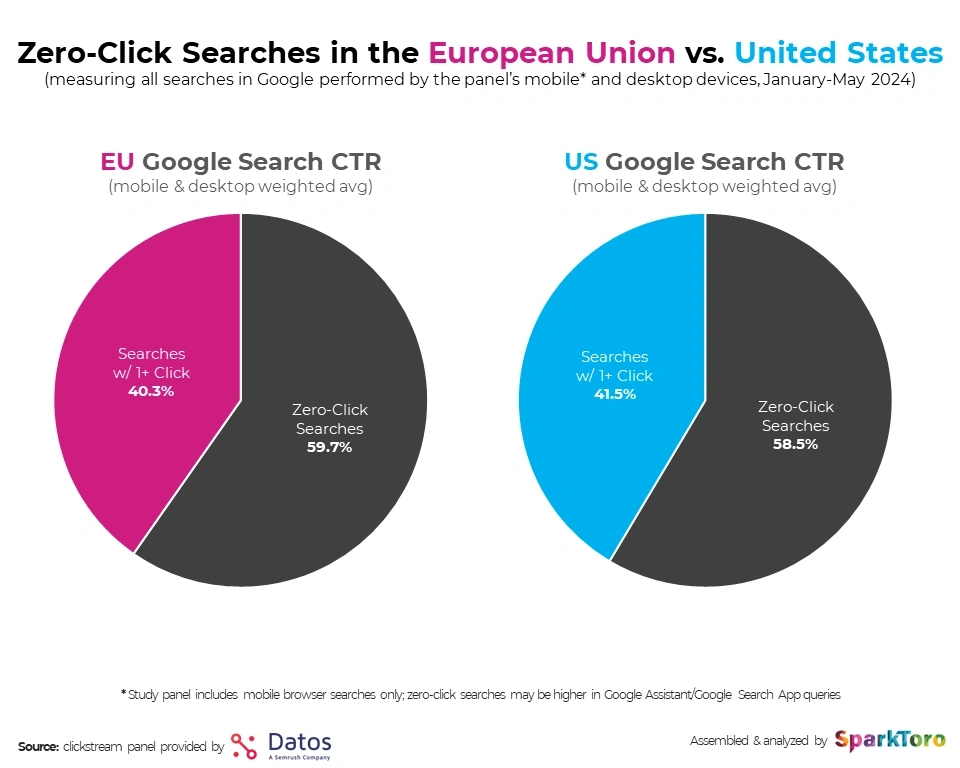
Percentage of Zero-Click in Total Search Queries
Artificial Intelligence Is Taking Over Search Results
Modern webmasters have to compete for placement in search results not only with contextual ads but also with AI-generated responses. In May 2024, Google made the Search Generative Experience (SGE) available to all users — a block that appears above the classic search results and immediately provides an AI-generated answer to the user's query. It is currently available in 120 countries (not in Ukraine), but the list is constantly expanding.

The user enters a query, and Google displays a generated answer in the form of a paragraph/list with brief instructions or advice, and below or to the side — links to sources. Along with the answers, the user also receives related questions and logical follow-up queries. Given these capabilities, this innovative feature could eventually fully replace traditional results for many informational queries. And webmasters will have to compete not for a spot in the top 10 results, but for a place among the top 3 sources.
Search Engine Optimization Is Becoming Extremely Unpredictable
SEO is no longer a precise calculation and increasingly resembles a game with an invisible opponent who changes the rules daily without any warning. That same March 2024 update caused many websites to lose 70–90% of their traffic, even those that created useful content following all the rules. At the same time, sites with worse usability and low-quality content remained at the top of the search results.
Let’s recall the first part of our article about the early development of search engine optimization. Back then, there were proven strategies: add keywords to the text and meta tags, buy a few backlinks, and your site would already be ranking high in Google results. Of course, algorithms changed, but typically there were 2–3 major updates per year that could be tracked, studied, and adapted to.
Now Google releases updates almost monthly, and either says nothing about the changes or provides vague explanations. Proven strategies no longer exist: you can follow all the advice, do everything “right”, and still lose rankings without explanation. Even drawing clear conclusions during experiments is difficult: one site consisting solely of AI informational articles may consistently grow, while another — with expert content and significant backlink mass — may lose positions.
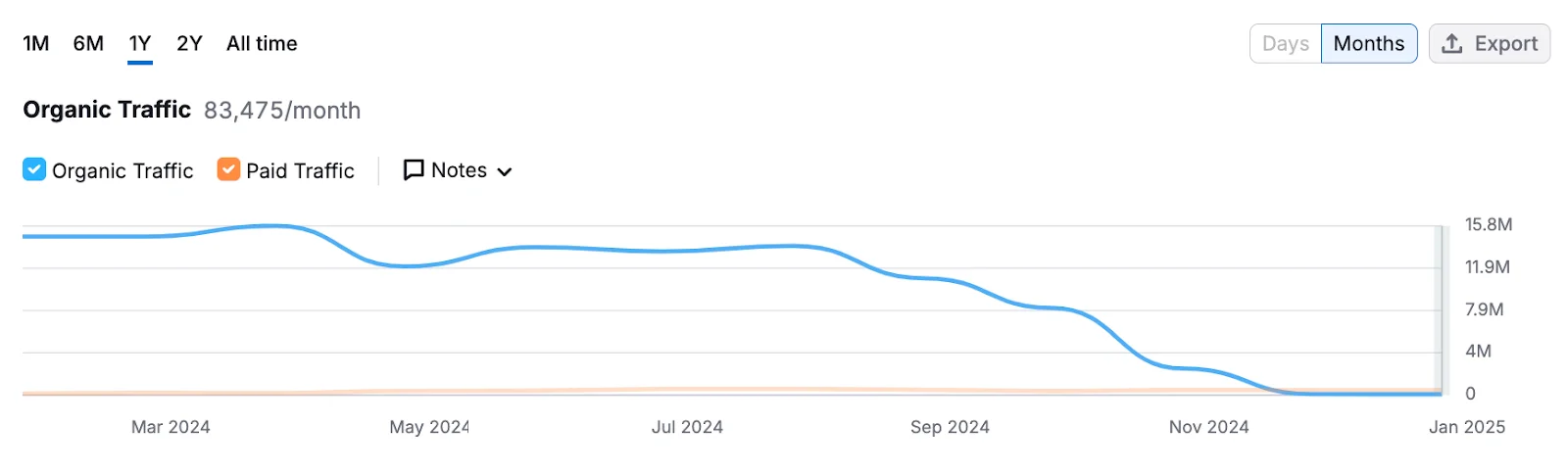
Even a global financial platform like Forbes Advisor lost a huge amount of traffic by the end of 2024.
Parasite SEO and Content Monopoly Are Changing the Search Landscape
Search engine algorithms increasingly favor large, authoritative internet projects that are continuously filled with content and have a substantial backlink profile. These include major media holdings (Future PLC, Dotdash Meredith, Hearst), authoritative English-language resources (Forbes, CNET, Healthline, WebMD), giant websites and forums (Reddit, Quora, LinkedIn, Pinterest). As a result, it’s nearly impossible for small web resources to reach the TOP, even with quality content.
The strengthening of this monopoly also raises the issue of parasite SEO — when a person or company doesn’t promote their own website directly, but publishes content on an already authoritative platform to rank in Google. This method is used to generate income through affiliate programs (e.g., a page titled “Best VPNs in 2025” on Medium with referral links), collect leads (an article like “Top courses for learning Python” linking to a paid course), or drive traffic to their own site by posting articles with links on high-authority platforms.
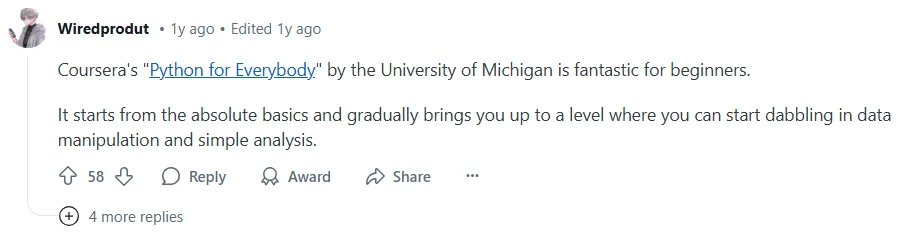
A forum post on Reddit in the thread “Best online course to actually learn to use Python” looks like a regular recommendation with a handy link for analyzing the course. However, the link includes `utm_source=impact` (Impact is a popular affiliate network) and other clear signs of affiliate marketing.
With the rise of artificial intelligence, the problem of parasite SEO has become even more relevant, as people are massively publishing AI-generated content, usually of poor quality and lacking new information. Although this practice was targeted in the March 2024 Core Update, where Google attempted to identify parasite pages on authoritative domains, the overall situation has not fundamentally changed.
How to Adapt to Unpredictable and Complex SEO
The growing influence of artificial intelligence, the strengthening of monopolies and parasite SEO, and the unpredictability of algorithms do not indicate the death of SEO, but rather its significant transformation. To successfully promote an online project, it’s finally time to abandon outdated traffic acquisition methods, like mindless backlink purchasing, make smart use of AI, and apply a comprehensive strategy to find your target audience.
Flawless User Interaction Is the Key to Top Rankings
In 2025, user experience is not just a “bonus” but a necessity for attracting and retaining a target audience. That’s why you should regularly audit your site using Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, or Ahrefs — removing 404 errors, duplicate content, incorrect canonical URLs, and pages without HTTPS. Always maintain a clear hierarchy (home → categories → subcategories → articles/products), include breadcrumbs, and have a sitemap for both crawlers and users.
As before, internal linking plays an important role in SEO. However, don’t add links just because a keyword or phrase is mentioned in the text. Each link should lead to a relevant article that complements the existing content and helps the user get a more comprehensive answer.
Continuously analyze Core Web Vitals — a set of site speed metrics, among which the most important are:
- LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) — loading time of the largest element, such as an image, should be under 2.5 seconds;
- INP (Interaction to Next Paint) — try to reduce the delay between user click and site response to 200 ms or less;
- CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift) — unexpected shifts in page layout during loading should be minimized to 0.1.
The best free tool for evaluating site speed is PageSpeed Insights. Go to the main page, paste the link to your web resource, and click Analyze.
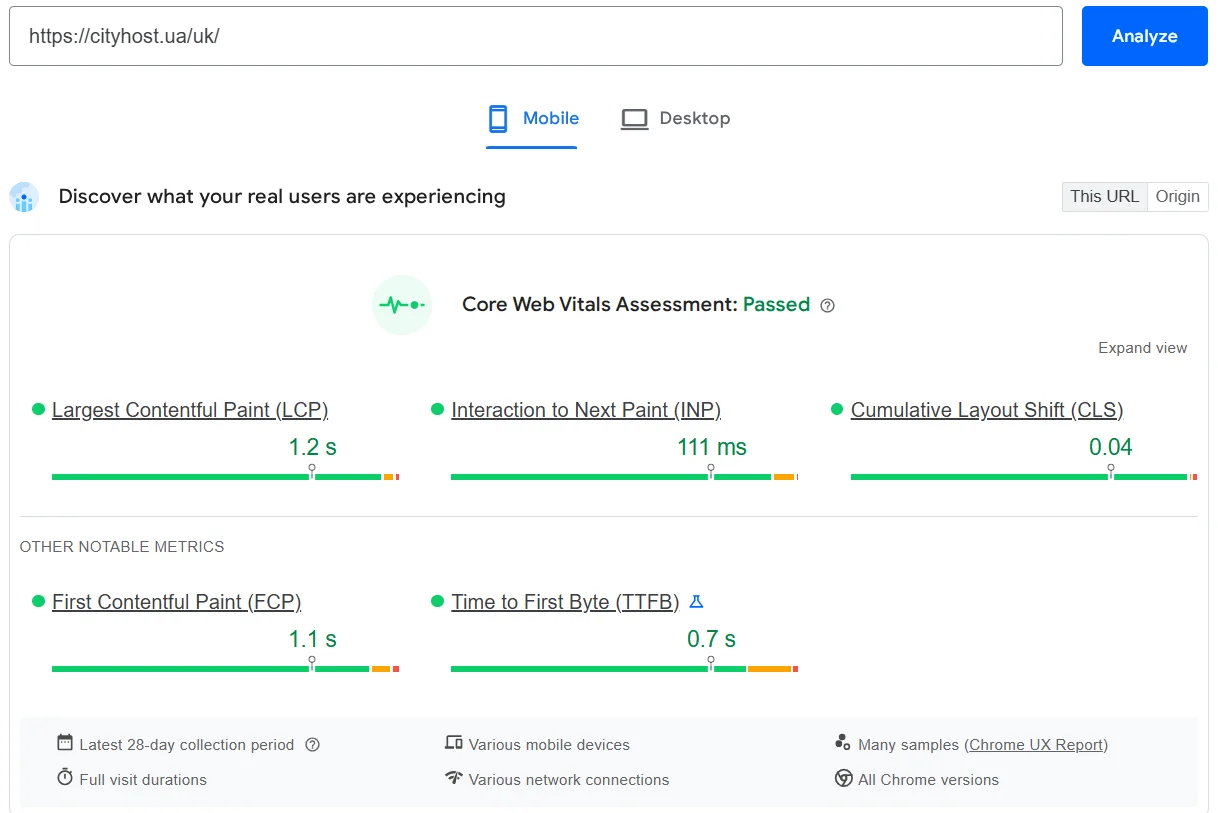
Speed analysis of the Cityhost mobile site version for Core Web Vitals compliance
Fighting the death of SEO with expertise
Artificial intelligence has changed the content market, but not only in a positive way. Indeed, now it’s possible to quickly write an informative, well-formatted, and optimized text in just a few minutes — it's enough to create a clear prompt for the AI. However, the problem is that AI services don’t provide anything new, but merely rewrite texts from pages that are already in the search results. And now the search engine is overwhelmed with low-quality AI content.
To ensure that your website pages don’t get lost in the spam, the content must provide value that artificial intelligence cannot reproduce. You can use AI to find basic data and create a draft, but the final version of the text must contain original information, real experience, and expert analysis.
In the era of AI, the following types of content perform well:
- experiments — “We compared 5 VPN services — the results were surprising”, “I spent $500 on Google AdWords ads — here’s what happened”;
- reviews — “Google Analytics 4 for beginners: what is GA4 and how to use it”, “Review of the Weblium platform after 2 months of use: pros, cons, failures”;
- expert analysis — “Which businesses will suffer from AI first: a digital specialist’s opinion”, “Green communication with performers — how not to become a customer that everyone hates”;
- stories from practice — “Punishment for Cybersquatting — Cityhost Participated in the Resolution of a Domain Dispute Under UA-DRP”, “How Oleksandr created a family digital team that develops a forum, websites, and YouTube channels”.
Not only content matters, but also who wrote it. The E-E-A-T concept comes to the forefront: authors with experience in the topic (Experience), actual experts (Expertise), brand (Authoritativeness), and trust (Trustworthiness). Therefore, every page must include an author block (name and surname, photo, biography), and the person must have real experience in the subject and preferably publications on other authoritative platforms.
Transitioning from Exclusively Google to a Comprehensive Traffic Acquisition Approach
The practice of focusing solely on simple pages with optimized texts no longer works, unless your online project is part of the "elite list". Now, it’s necessary to focus on the comprehensive development of the website, increasing the brand’s presence on the internet.
To increase your brand’s visibility, you should use various popular platforms:
- Social media. Publish short dynamic videos with popular hashtags on TikTok and long informative videos on YouTube. For example, we manage to attract a new audience through the Cityhost TikTok channel.
- Forums. On Reddit and Quora, you can participate in discussions, answer questions, give advice, thus drawing attention to your brand. You can leave a link in the posts, but it should be done as naturally as possible to avoid looking like spam. Also, it’s a good idea to add a brief biography and a few links to your profile.

Example of a user profile on Quora with links to personal web resources
- Content platforms. Publish expert articles on Medium, LinkedIn Articles, Differ.blog, HubPages, and other similar platforms, showing your expertise and building trust in your brand. You can add links to your website in the articles, but it should be done in a way that makes people want to click on the link and get more information on the topic.

An article on Medium with a link to the author's website. The material includes links to other pages on the author's web resource.
Your task is to create conditions where users encounter your brand in various places, not just on Google. Later, brand queries, strong reputation, and mentions on the aforementioned platforms will enhance the site’s authority, thus improving page rankings in search results. Additionally, this will reduce dependence on a single traffic source, which is especially beneficial in the context of Google’s high algorithmic instability.
Optimizing for AI Search Results — Time to Join the Artificial Intelligence
Answer snippets (Featured Snippets) and AI Overviews (Search Generative Experience) are leading to a significant drop in traffic from search results. For example, when a user enters the query "What is SEO", instead of going to various web pages, they see an answer generated by GPT-like models from Google. Or, when they search for "weather Kyiv", they immediately see the forecast, and the site gets no clicks.
Of course, one can continue to boycott artificial intelligence and the development of search engines altogether, but this will not stop the decline in SEO traffic. The best solution to this problem is adaptation to the new realities, specifically getting into AI-generated results. For this, you need content with a logical structure, clear definitions, specific data, dates, prices, examples, as well as lists and/or tables. In other words, instead of large articles filled with excessive information, it's better to create concise texts that immediately help the user and provide clear answers to their questions.
Personalization — Adapt to the Interests of Each Specific User
Classic SEO was "the same for everyone" for a long time, but it's time to adapt to the interests of each specific user. Companies are already collecting an incredible amount of data about each individual and using it to create personalized search results. For example, Google considers search history, location, language, and the user's device. As a result, each person gets the result they are truly interested in.
Search results are already personalized, so the question arises: how can your website personalize the experience:
- Online stores can use dynamic recommendations ("You previously viewed", "Frequently bought together"), recently viewed products, personalized email or push notifications, and interest-based promo blocks.

Example of personalization in the online store Amazon.
- Online services should integrate feature suggestions or prompts based on previous activity, unique onboarding instructions based on role and skills, and a personalized dashboard with statistics.
An example of personalization on the music listening platform Spotify.
- Informational websites should use "Read more" sections, subscriber segmentation, and regular recommendations through other channels (email, social media) based on reader behavior.

An example of the simplest personalization is the "Also read" section. Of course, it's not fully personalized, but people who read an article about designing a homepage are most likely to be interested in adapting a website for mobile devices.
Artificial intelligence also helps personalize content on the website. For instance, Algolia Recommend can create models ("Frequently bought together", "Product trends", etc.) from your index and user events based on managed machine learning algorithms. The Mutiny service can modify content in real time for any visitor. Klaviyo is suitable for creating personalized email, SMS, and mobile push message campaigns. Doofinder AI displays personalized search results based on each user's behavior and preferences. And of course, countless AI chatbots (Tidio+Lyro AI, LivePerson, Intercom+Fin AI) are capable of having conversations based on the site visitor's history and interests.
Ukrainian Webmasters Are Not Facing the Death of SEO (for Now)
The talk about the death of SEO repeats every year, but in reality, it is changing, and everyone has two options: either ignore the changes and lose traffic, or adapt to the new reality. Modern search engine optimization is no longer about purchasing links from low-quality platforms, running through directories, or text blocks stuffed with keywords. SEO is no longer a set of manipulative techniques; it is becoming part of a comprehensive brand-building strategy. Now, those who can win are the ones who know how to:
- create high-quality expert content;
- improve user experience;
- adapt to artificial intelligence and AI search results;
- provide personalized content for each user;
- attract a targeted audience from various sources.
The Ukrainian market actually has a unique advantage — key algorithms and AI integrations are still running in a simplified mode. Usually, most Ukrainian webmasters are disappointed that they get access to major updates and best services nearly last. However, in this case, such delays work in their favor, giving them the chance to act in advance.
In Ukraine, AI-generated search results have not yet been launched: SEO works as it did before, and the first page of the search results is not taken over by AI-generated answers, and zero-click results are not observed on the same scale as in the U.S. The Ukrainian language is supported by many AI models, but ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and other chatbots work with it worse than with English. This means that it is much easier for us to stand out with real, interesting, expert content. At the same time, we have time to strengthen our position in the niche before new algorithms arrive, analyze how changes have affected the English-speaking market, and adapt content and strategies to meet the new requirements before AI Overviews are launched in Ukraine.
And don’t forget about the “youth” of the Ukrainian market. In many industries, there is little high-quality SEO content in Ukrainian, which provides an opportunity to establish a foothold right now and create a content advantage that will be difficult to catch up with. Moreover, the comprehensive development of one’s brand (not just search engine rankings, but also social media, email newsletters, forums) will help retain the target audience if search traffic decreases.
So, SEO is not dead — it’s evolving. And Ukrainians have a unique opportunity to act in advance by developing their brand, collecting traffic from various sources, and creating high-quality content with unique information. The key is not to miss this opportunity!