When we talk about fakes and disinformation, we first of all think about the information war that Russia launched against Ukraine against the background of a full-scale invasion. Indeed, this is the main source of false information, but we must not forget also about fraudsters, internal political quarrels and other factors that provoke the creation of fakes. Today we will talk about all disinformation in general, as well as about domains, because they can often be an indicator in recognizing fake sites.
How to check information for fakes?
You can catch a disinformation virus anywhere — on news sites, Telegram, Facebook, Viber, and any other media sources. Therefore, let's first talk about the basic rules of information hygiene, which are important in our time.
Check the original source
Each piece of information has a specific point of origin from where it was disseminated. If it concerns state affairs or military actions, these are most often comments by authorized persons or articles published on state websites.
If you see a news item that reads: "The Verkhovna Rada has approved a law according to which Ukrainians will pay for air," the first thing you should do is go to the official website of the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine . There is also the website of the office of the President of Ukraine , the Ministry of Social Policy , the Ministry of Defense , the website of the Armed Forces of Ukraine , the Ministry of Education , the Ministry of Health , and many other sites where you need to check information.
Another way to find the original source is to take a paragraph from the text and paste it into the search bar. You will see which sites published the news first. It often happens that a fake has been around for a dozen years, and people are still "going" for it.
Journalists and bloggers do not always spread fake news deliberately - sometimes they simply do not check the sensational news in order to publish it as soon as possible. Journalists often get into incidents, taking news from everywhere. For example, the humorous news site uareview.com has repeatedly provided our grief journalists with food for thought.
Check the image
It happens that a fake can be calculated by the image. To do this, you need to use Google image search. Load the image that illustrates the news into search and see which sources have used it before. If the news claims that this is a recent photo from the scene, and it has been published many times before... You get the idea.
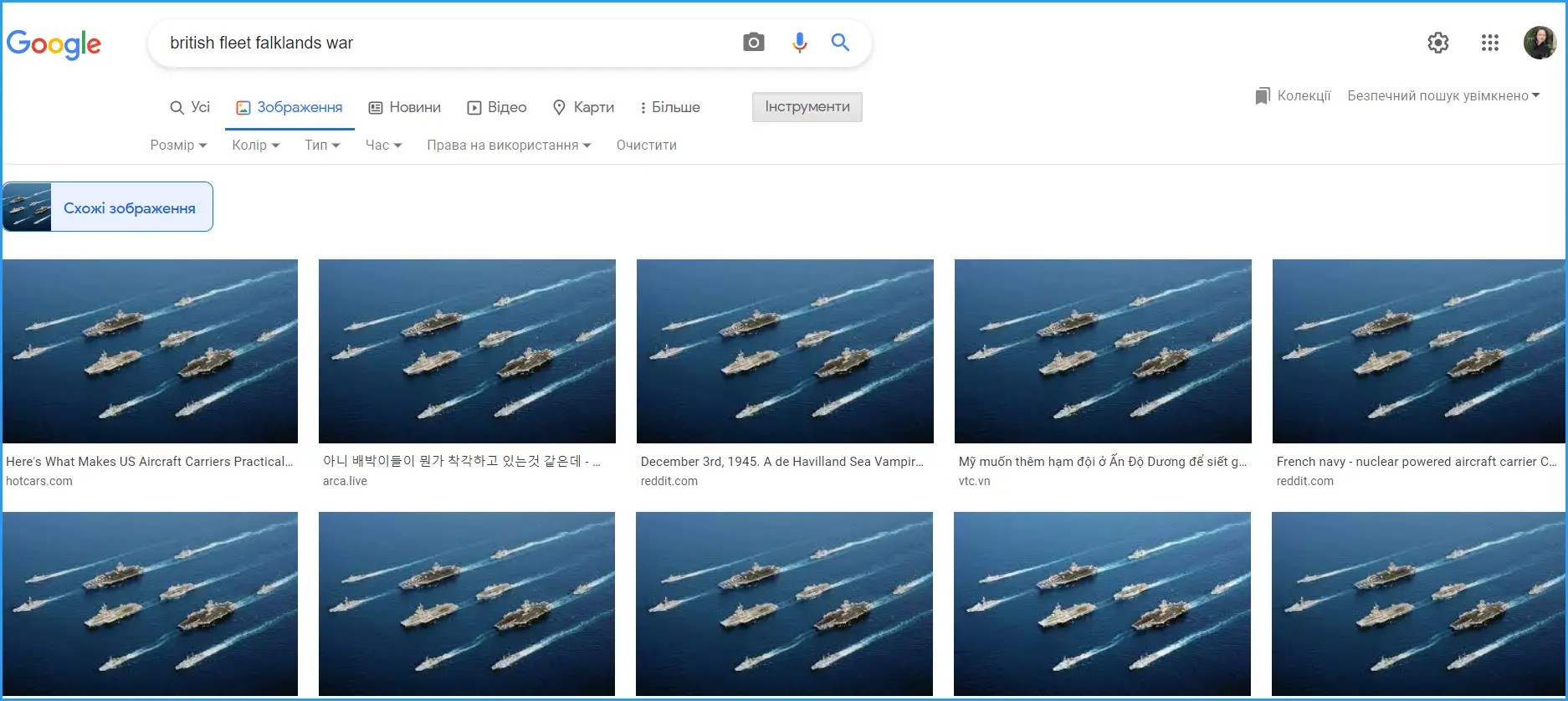 We took as an example a popular photo of American ships, which illustrates the news about the fleet around the world.
We took as an example a popular photo of American ships, which illustrates the news about the fleet around the world.
Choose trustworthy sites
Look for Ukrainian and global news sites that have been around for a long time in their field and have a certain reputation. They employ qualified journalists who are also interested in their professional image. Therefore, it is best to get information from time-tested sources.
Disinformers also know about this, so hackers periodically break into official news sites and post fake materials on them. To prevent this from happening, administrators and owners of web resources make every effort to secure the site, in particular to protect their hosting account from hacking.
Telegram and Viber channels share information promptly and with a light, but you don't know who is sitting on the other side of the screen. Most of them are non-professional bloggers who care more about promoting their channel than giving people real data. Yes, official news comes out much later - precisely because time is spent on verification.
Even the channels of official persons or institutions can be duplicated with criminal intentions. You will hardly be able to find out where those duplicates came from, because in messengers there are options to hide the location, phone number and other privacy settings.
We are not advocating abandoning these sources of information—rather, we ask that they be treated with caution, as they are more difficult to verify.
By the way, there are special resources for checking fakes, such as StopFake . All the most resonant "throws" of disinformation can be found on them.
Watch the level of emotionality
If you were to create a top list of techniques used by disinformers, then the first place would be "Strike on emotions". Fake news is often designed to frighten, anger, create panic, and cause a sense of injustice. Professional journalists cover even disturbing and unpleasant events in a neutral tone — this is one of the rules of objectivity.
If you see a very emotional news, message, post (and especially with a lot of exclamation marks), there is a high probability that it is fake. Check it out, or if it doesn't apply to you, just ignore it.
These are the basic rules of hygiene that you may already know. Now we will tell you the professional subtleties of domain registration, thanks to which you can understand what kind of web resource is in front of you.
What the domain name of the site can tell
The site domain is a fixed value, it cannot be hidden or easily changed. By looking at the address, you can understand a lot about the site itself.
For example, the national domain .UA of the first level is allowed to be registered only if there is a corresponding trademark that is protected in Ukraine, and the TM name and the domain must match. For example, hromadske.ua is the site of "Hromadske televsionie", which is a public organization and has registered the relevant trademark domain.
At the same time, it is worth knowing that second-level domains, such as com.ua , net.ua , or city domains such as ternopil.ua, no longer undergo such serious checks, and any private person from any country can register them. Even the Russians, unfortunately, have ways of bypassing the blocking, although almost all Ukrainian registrars have banned them from accessing their sites and disconnected Russian clients from their services .
All state institutions are hosted on the closed domain GOV.UA (which means government). They can be registered only by public sector organizations — ministries, the Verkhovna Rada, the Cabinet of Ministers, regional and district administrations. Large state-owned Ukrainian companies, such as Ukrzaliznytsia (uz.gov.ua), can also have such a domain.
The Ministry of Defense of Ukraine has the domain mil.gov.ua, the Office of the President — president.gov.ua, Kyiv City State Administration — kyivcity.gov.ua, Mukachiv District State Administration — mukrayon.gov.ua, Chernihiv City Council — chernigiv-rada. gov.ua.
If you are offered to read the website of the Verkhovna Rada with some other domain, it is most likely a phishing page (a fraudulent copy of the website).
At the same time, small budget institutions, such as schools or libraries, no longer have such powers. Higher educational institutions can register in EDU.UA domains. Such an address can be obtained only on the basis of an official letter from the university, so the sites hosted on such a domain are 100% relevant in their name and content.
News sites hosted on free domains or domains from other countries should not be taken seriously. In many countries, national domain zones are open for free registration from anywhere on the planet, and they are used for completely extraneous purposes. The domains of a number of third world countries are not at all controlled by the local government, and they are actively bought by everyone. For example, Samoa's .ws domain is often used in Russia, and Tonga's .to domain is used by torrent trackers. As you understand, fraudsters are also very interested in such domains.
You can view the list of national domain zones and their registration conditions — you will learn a lot of unexpected and new things from it.
We would like to note that a free domain or an address from another country is not necessarily a sign of a "bad" site. You can safely use them for blogs, small business or portfolio. But if a web resource claims the role of a serious information source and has a similar address, you should think about it.
Cybersquatting as one of the tools of disinformation
You have to be careful when checking the domain. For example, you are used to reading news on the website "Ukrainian Pravda" with the address pravda.com.ua. If fraudsters register the domain ukr-pravda.com.ua, make a website exactly like this and start spreading disinformation, even attentive users may not notice it. Remember: even if the domain name differs by at least one letter, it is another domain that belongs to third parties and hosts a different site.
You can read more about this phenomenon in our article: " What is domaining and cybersquatting ".
Checking the country of origin of the site by domain and hosting
Most of the sites from Ukraine or Russia are easy to identify by domains - we often have the .ua extension, Russians - .ru.
But there are also international domains, by which you will not be able to guess in which country the web resource is located - .com, .biz, .info, .org, etc. To check the domain name registrar, you can use the free Whois service . You need to enter a domain name without http and start the verification. We chose one Ukrainian and one Russian news site for our experiments. Of course, you can understand their concept just by opening the main page. But we are interested in the information that can be gleaned from the technical characteristics, because you can write anything on the site, but the domain will always tell the truth.
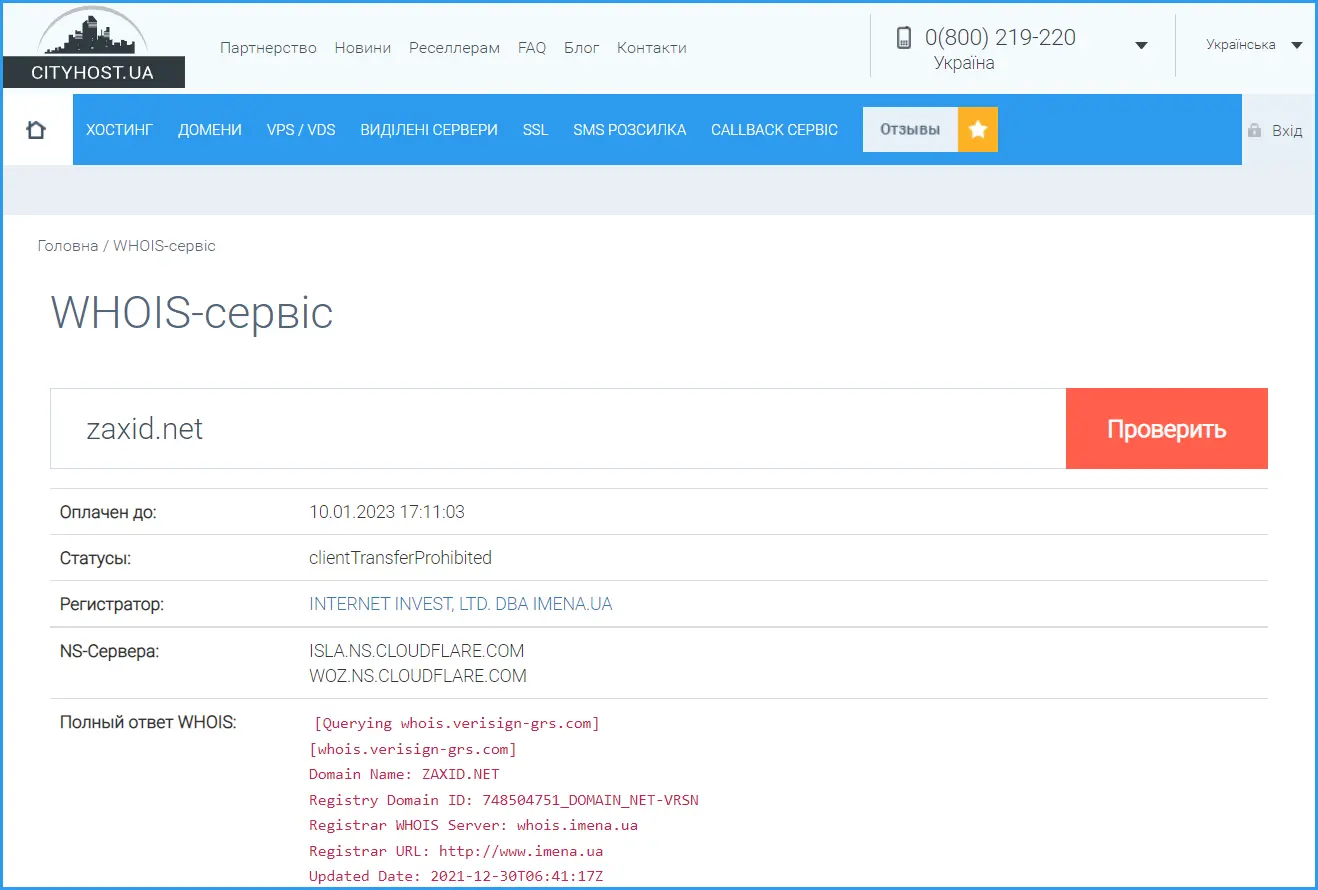 As you can see, the zaxid.net site is registered in Ukraine, the domain was issued by the Ukrainian registrar imena.ua.
As you can see, the zaxid.net site is registered in Ukraine, the domain was issued by the Ukrainian registrar imena.ua.
Cloudflare.com is often listed under NS servers. This is an American company that has organized a network of servers around the world and created a service thanks to which users can increase the speed of their sites and protect themselves from DDoS attacks. The platform simply directs the website user to the server closest to him, on which the static elements of the pages are cached.
If you see such a server name, it only means that the site owner uses this service. By the way, after the start of the war, Cloudflare refused to disconnect Russian clients, citing the fact that "Russians need more Internet, not less." Therefore, we will not be able to calculate the origin of the site according to this criterion. But you will still see the name of the registrar that issued the site domain.
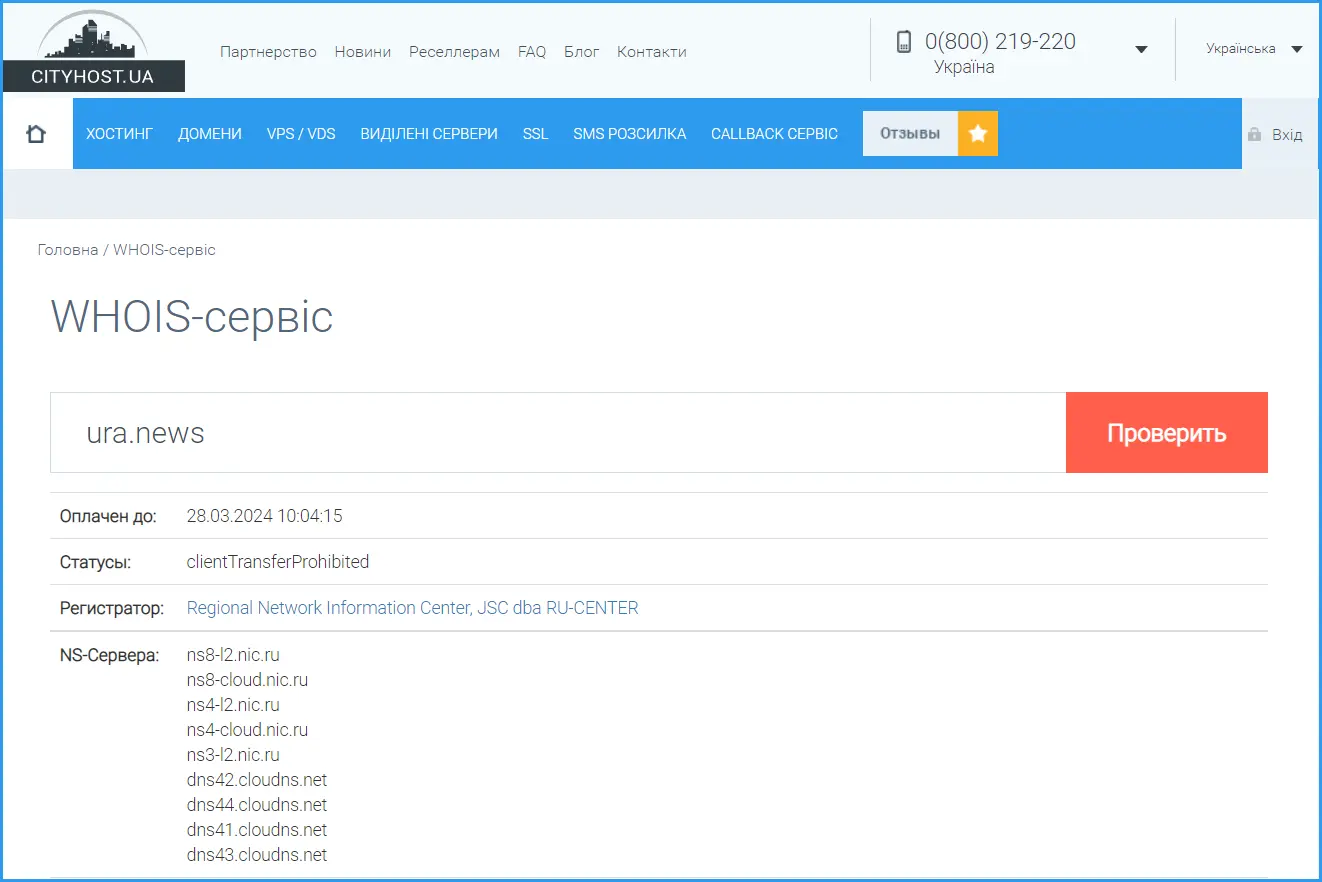 Now let's look at ura.news - it is definitely a Russian site, the domain for which was issued by the registrar RU-CENTER, also a hosting provider. And in the NS-servers section, we see the nic.ru extension — this is the domain of the provider's website.
Now let's look at ura.news - it is definitely a Russian site, the domain for which was issued by the registrar RU-CENTER, also a hosting provider. And in the NS-servers section, we see the nic.ru extension — this is the domain of the provider's website.
Issuance is different for each domain, but it is at least always possible to understand who issued the domain and find the country where the registrar is located. If you scroll down, you will find a lot more interesting things - up to the city where the registrar is located, telephone numbers and addresses for feedback.
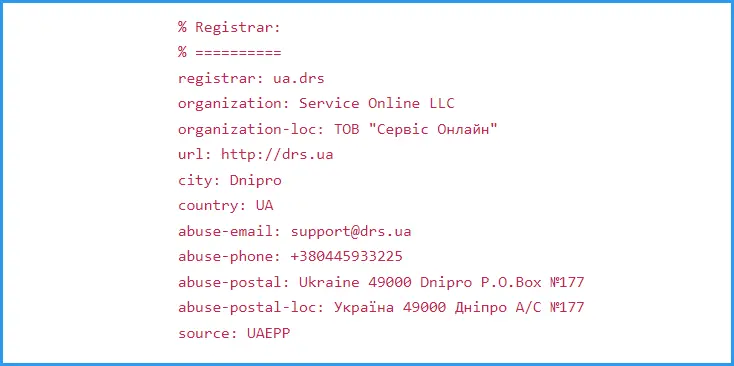
For example, this is what the information about the focus.ua domain registrar, which is called ua.drs, looks like. All contacts with the abuse prefix are intended for complaints that users can send if they believe that the site is engaged in illegal activities - for example, spreading misinformation.
There is also an opportunity to send complaints to Cityhost - we accept them through all available channels, in particular through technical support. If you see that a site that spreads fakes is hosted on our hosting or domain, write to us. After a thorough review, we manually block sites that engage in fraudulent activity, disinformation, or support Russian aggression in Ukraine.