For the effective operation of the site, you need not only to register a domain and rent hosting. Any web resource requires constant work, development, promotion in the network. And, of course, it needs to be protected from virus attacks.
What are viruses?
Viruses are malicious software that inject themselves into the underlying software code and make unauthorized changes to it. They can appear wherever there are programming languages—in operating systems, software, websites, and mobile apps.
Viruses can be both separate programs and sections of code that are embedded in ordinary files (for example, images).
The term is synonymous with malware, it stands for "malicious software". This is the name of any program capable of harming devices and network resources, working as a tool for fraudsters.
Viruses can steal information, damage files, destroy data, and disable computers. Due to the activity of malicious programs, the load on the server's capacity increases and its performance decreases.
Viruses got their names because their work resembles the life cycle of a real virus: they "reproduce" (but not all), cause damage to the environment in which they live, and then die.
The idea of a computer virus was voiced by John von Neumann in the 1950s, proposing the theory of self-replicating mechanisms.
The world's first computer viruses were written in the 1970s out of purely scientific interest, and the progenitors of virus programs were rather toys. But already in the 1980s, the Brain virus appeared, capable of harming computers (although it was designed as a protection against pirate copying). In the same decade, antivirus programs began to actively develop. The very term "computer virus" appeared in 1984 in the scientific work of Fred Cohen.
In the 2000s, there were many prank viruses that users sent to each other as pranks (innocent and not so).
Where do viruses come from and why are they used?
Viruses do not appear by themselves - they are written by programmers. The main goal is to make money. Hundreds of viruses appear in the world every day, collecting users' confidential data and forcing their devices to help attackers.
What are viruses used for:
DDos attacks on competitors' sites. Computers of many users are infected with the virus and they start sending requests to one site at the same time. Due to the colossal load, it cannot load normally or stops responding at all (usually this is called "the site has been put down").
Theft of personal data (account passwords, financial data, personal information). Viruses penetrate user accounts and their computers in search of logins, passwords, card numbers. With their help, attackers can see correspondence in mail and messengers or dig into files.
Remote control of the device. With the help of viruses, so-called zombie computers are created that perform certain actions. They can send spam, infect other computers, participate in virus attacks, and more. Moreover, the owners do not know at all that their device has joined the forces of evil.
Replacement of links, elements and entire pages on websites. For example, there is a link to download the program on the site. The virus replaces it with a link to malicious software that users download without noticing the deception.
Causing damage. A virus can delete or destroy code, destroying information.
This is far from the entire list of actions that viruses are capable of, but the main one. The authors of the virus can add any functionality to it — for example, scan user actions or secretly mine cryptocurrency on other people's computers or hosting servers.
Read also: Why Cloudflare is needed and how to connect a site to it
Types of viruses
There are many viruses and each one is unique. But still, they can be divided into categories based on typical characteristics:
Worms are independent malicious programs capable of actively multiplying and spreading themselves over the network. A classic scheme, when a worm breaks into a mailbox and sends itself to all contacts. Most often, the activity of worms consists in causing damage - corrupting files and slowing down the operation of devices.
Trojans cannot spread on their own, but they are dangerous because they disguise themselves as normal software or files. The user downloads a game, archive or program, but receives a "Trojan horse", after which the virus is named. A Trojan can be inactive for a long time, starting at a certain moment or at the command of the developer. It is used for various tasks — data damage, spamming, DDos attacks, disabling antivirus protection, identity theft, and much more.
Rootkits (maskers) are programs capable of hiding their actions or masking other pests (for example, Trojans). Rootkits have a very wide functionality — they can make changes to the system, block the operation of the antivirus, control bots, and more. It is one of the most dangerous viruses because it is difficult to detect and remove, especially if it has embedded itself at the kernel level.
Ransomware viruses block the operation of a computer or resource, demanding a ransom for regaining access. A separate type of ransomware is encryptors that encrypt all data, making it unusable. For ransom, they promise to decrypt everything back. But we do not recommend fulfilling the conditions - usually the attackers are not even going to return the files to a working state.
Adware embeds ads into browsers and applications. Advertising blocks can be displayed on a schedule, the browser periodically goes to the link to the advertising site.
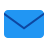
One of the famous viruses in Ukraine is Petya. In 2017, it caused mass infections of computers of Ukrainian companies, including banks, government organizations, and the energy sector (even the Chernobyl nuclear power plant was affected). Reports of infection were received from other countries of the world. The virus caused significant damage and turned out to be both a worm and an extortionist. The program encrypted the data, demanding a ransom in bitcoins. Upon careful examination, experts came to the conclusion that the pest was only disguised as an extortionist. There is a version that it was a targeted cyber attack on Ukraine with political motives, designed to harm important infrastructures.
This is what the computer screen looked like after rebooting.
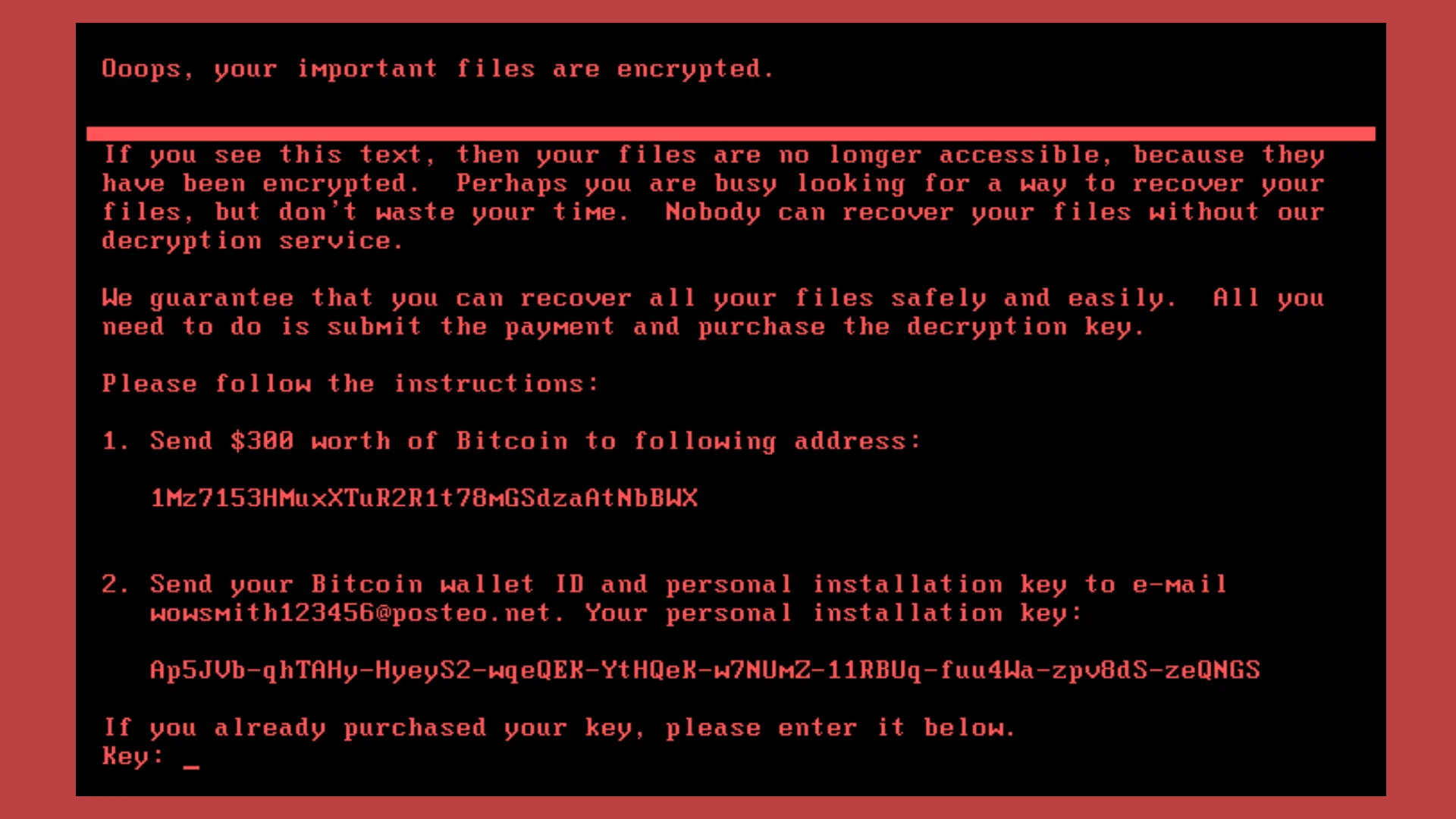
How do viruses appear on a website?
Viruses penetrate sites through vulnerabilities in software, utilities, and site code:
CMS and their plugins. Because many site engines are open source and many third-party add-ons are available, attackers can embed viruses into plugins and themes. After installing a harmless-looking plugin, the site becomes infected with a virus.
Interception of login and password from FTP. Having gained access to the FTP client, hackers can easily plant infected files on the site or rewrite the code.
Stealing access to the site's control panel. If it was possible to intercept the login and password from the panel, thieves can completely steal the site and post anything they want on it.
Vulnerabilities in the code. This refers to developer errors that make the site unreliable. Viruses leak through these errors.
How to understand that the site is infected?
First of all, the antivirus will notify you. In addition, the site has characteristic symptoms:
Work slows down, freezes or completely fails.
Traffic growth despite the fact that the number of visitors and transactions performed remained unchanged.
Appearance of new folders and files in the file system on the hosting .
The appearance of new sections, pop-up windows, elements on the site, redirection to other sites.
Consequences of site infection
In addition to the fact that the site will have to be restored (it is good if there is a fresh backup), there are more global losses for a resource that has come under a virus attack:
A decrease in visits, because the user who saw the warning of the browser antivirus or caught a pest on the site will be afraid to visit it for a long time.
Reputational losses for the company that owns the site.
A drop in performance, as search engines strongly discount sites with viruses and may even block them.
How to cure a site
There are two ways to check for viruses on the site:
View all site files on your own. It is not easy, because you need to know all the manifestations of viruses and recognize malicious code.
Scan with antivirus software: online services or built-in tools on hosting.
The antivirus on the hosting compares the site's code with the signatures of already known pests. For this purpose, there are special repositories (virus databases) that contain the characteristics of virus families.
Cityhost provides customers with the opportunity to check the site with the help of an antivirus created on the basis of AiBolit.
To start the scan, you need to go to the Hosting tab and click on "Manage". You will be taken to a section where you will need to click on another "Management" tab, after which a menu of additional settings will appear. Select the AiBolit scanner and run the scan.
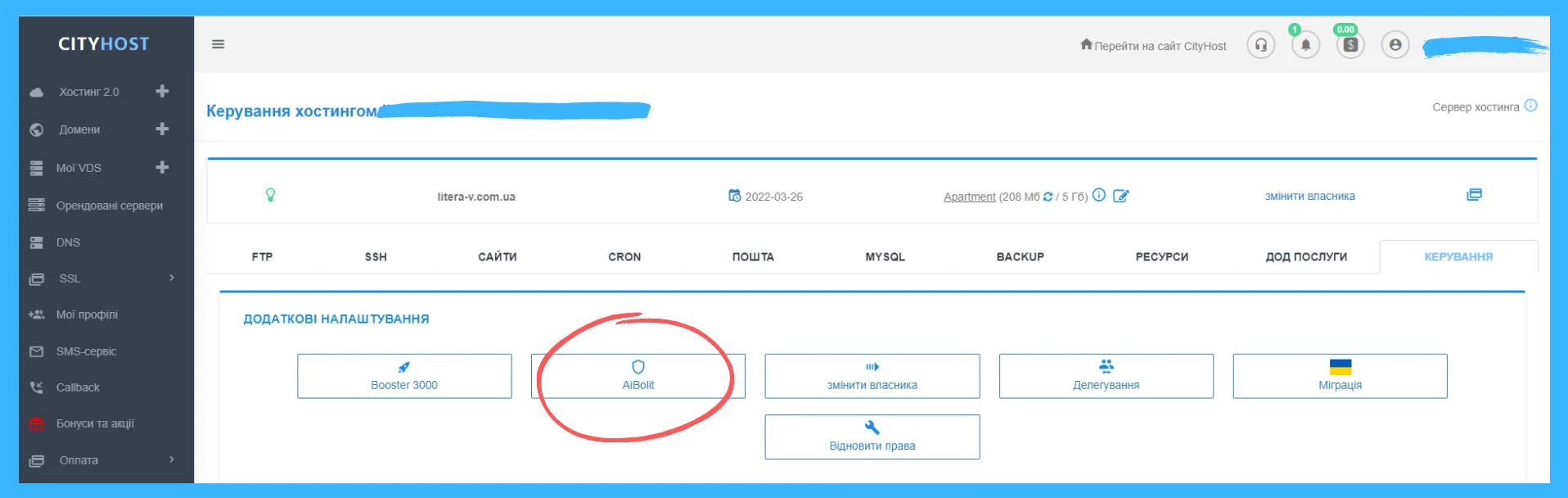
After the scan is completed, a report on the presence/absence of viruses will be sent to the registration mail. If there are viruses, the site will receive restrictions on the transmission of outgoing traffic to avoid infecting other resources.
You can clean the site code from the virus only manually by yourself or with the help of a specialist. The virus is able to replace useful sections of the code, and simple deletion of infected files can bring the site to a non-working state.
After removing the virus code, you will need to return to the additional services section and click the "I have cleaned" button. It runs the scan again, and if the site is already safe, the restriction will be removed.
After cleaning, you should track the possible ways of the appearance of the virus. See when changes were made to the infected files and check through the logs how the attackers made the changes. Update all passwords, check scripts for vulnerabilities and fix them, update CMS.
Normal cleaning without further use of protection measures is ineffective, because after some time the site can be infected again in the same way.