Phishing is one of the most popular and widespread types of fraud on the Internet. Scammers create phishing sites to obtain users' personal information. They are most interested in bank card data.
Any sites that can be used to steal money from cards are faked — booking services, job search services, classifieds sites, online stores, sites of banks and credit organizations, and even government structures.
Inattentive or ill-informed visitors fall for their bait. Therefore, one of the main methods of combating phishing is to warn Internet users how not to become a victim of fraudsters.
Not only visitors suffer from phishing, but also the owners of the sites under which the forgery was made. This harms the company's reputation, besides, it is forced to solve the problem that the client had, sometimes even to compensate him for his losses.
Internet phishing has been around since the 1980s. And although it is as old as the world, there are always people who come across classic tricks.
How do phishing sites work?
A page identical to the site of a popular resource is created. They are exactly the same — fonts, arrangement of elements, colors. The design may be slightly different, but you need to carefully compare the two sites to notice this.
Even the domain names are similar - the difference can be only one letter. Many usually will not even pay attention to such a small thing. The site is uploaded to hosting and it begins to "catch fish".

But it's not enough to just send it to the Internet — you need to actively search for victims.
There are many such remedies, and some have been around for years, continuing to demonstrate their black effectiveness. These are usually spam messages in the mail and SMS or letters from hacked accounts of friends. They contain links to copy sites, where the user voluntarily enters logins and passwords, without suspecting a cover.
The lifetime of a phishing site is only a few days, but during this time the scammers manage to collect a significant harvest of personal data.
For example, in April 2021, a site designed in the style of "Actions" appeared on the network. Users were offered to check whether the payment of UAH 8,000, which was given to employees of enterprises affected by the lockdown, is available to them. For this, it was necessary to enter bank card data. Even if the visitor changed his decision at the last moment and did not press the "Send" button, the data entered in the fields was still read by a special scanner. The site existed for only 5 days, but this is quite enough to "earn" a round sum.
Please note that the phishing site had the address diia8000gov.me, while the real Diya is located on the state domain diia.gov.ua.
What are fraudsters hunting for?
They need everything that can be useful for illegal earnings:
- Card and account data, logins and passwords from bank accounts that allow you to transfer money to your account.
- Access to the contact database, which makes it possible to send "happiness letters" to friends and steal their data.
- Access to accounts of online stores, in which customers often log in through mail and social networks. And the card data is already saved there.
- Access to the user's personal information that can be used for blackmail.
Information is extorted from users with the help of cunning schemes aimed at making the victim lose their vigilance. We will talk about some of the most common schemes, knowledge of which will help you protect yourself from data theft.
Read also: Fakes and disinformation - we learn to recognize false data on the Internet
Safety sheets
Emails or SMS messages are created, the text is written in such a way as to frighten the reader as much as possible: "Your card is blocked and in two hours all funds will be canceled. Follow the link to restore access."
The email contains a link to a phishing site and offers to enter card data for recovery. Sometimes the links are hidden: the real address is written in the anchor, but the link leads to a fake site.
For example, we suggest you go to google.com . In fact, clicking on the link will take you to the main page of our site. Of course, it's not phishing - we just wanted to show how you can trick a visitor with a fake anchor.
There is a mobile type of such fraud, it is called vishing. The subscriber receives an SMS on his phone with a message that his card has been blocked and an offer to call or follow a phishing link. If you call the "manager", he will immediately start finding out your card number, expiration date and CVV. It even happens that fraudsters do not write which bank's card is blocked and try to find out this information in a conversation.
What shall I do? Check the address of the received link with the domain of the official site. It is located at the top, in the address bar.
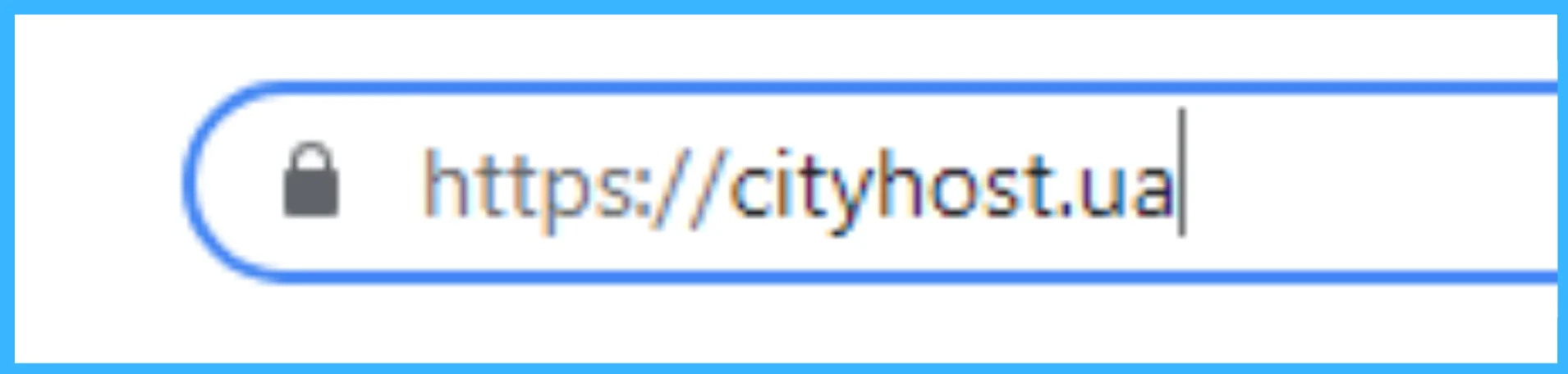
If you are worried that there really is a problem, call the official hotline or write to technical support by finding the real site yourself in the search engine. There you can submit the contacts of fraudsters and report their activity.
Promotions and bonuses from familiar stores
You find a letter in your mailbox from a well-known online store with an attractive offer: "You won 10,000 hryvnias! Take it!"
The store has a good reputation and does not arouse suspicion. You follow the link, getting to a copy of the site, where you are asked to enter the card number. Next, to receive a discount, you need to make a trial payment of a couple of hryvnias, enter the card's validity period and CVV.
They may also offer authorization via social media or mail if they are interested in your contact database and other personal information.
What shall I do? Official companies never hold promotions and discounts, for which you need to make a trial payment and leave your data. They usually offer to buy certain products at a reduced price or get a promotional code with a discount, but they do not give out large sums of money to their customers. If you are offered to carry out some trial financial transactions, this is already an alarm bell.
And let's repeat: check the address of the page you landed on with the domain of the real company.
Fraudsters on classifieds sites
They like to look for victims among the sellers and buyers of large private classifieds sites.
With the appearance of the "Secure payment" option, a new scheme appeared. The fraudster pretends to be an interested buyer and wants to transfer money through "Secure Payment". It sends a link to an allegedly already created purchase, where you need to enter the card data, its expiration date and CVV in the form.
If the victim has doubts, the scammer may even send a link to a technical support page with addresses and phone numbers. After calling the number, the seller will hear the assurance of the manager that everything is fine.
What shall I do? Fraudsters often lure the victim into messengers - Viber or Telegram. Allegedly, it is more convenient for them to communicate, or the program freezes. There is no need to leave the correspondence site - there the interlocutor cannot delete messages that could become evidence of his actions.
Don't use links sent by the client. Do all operations only in your account.
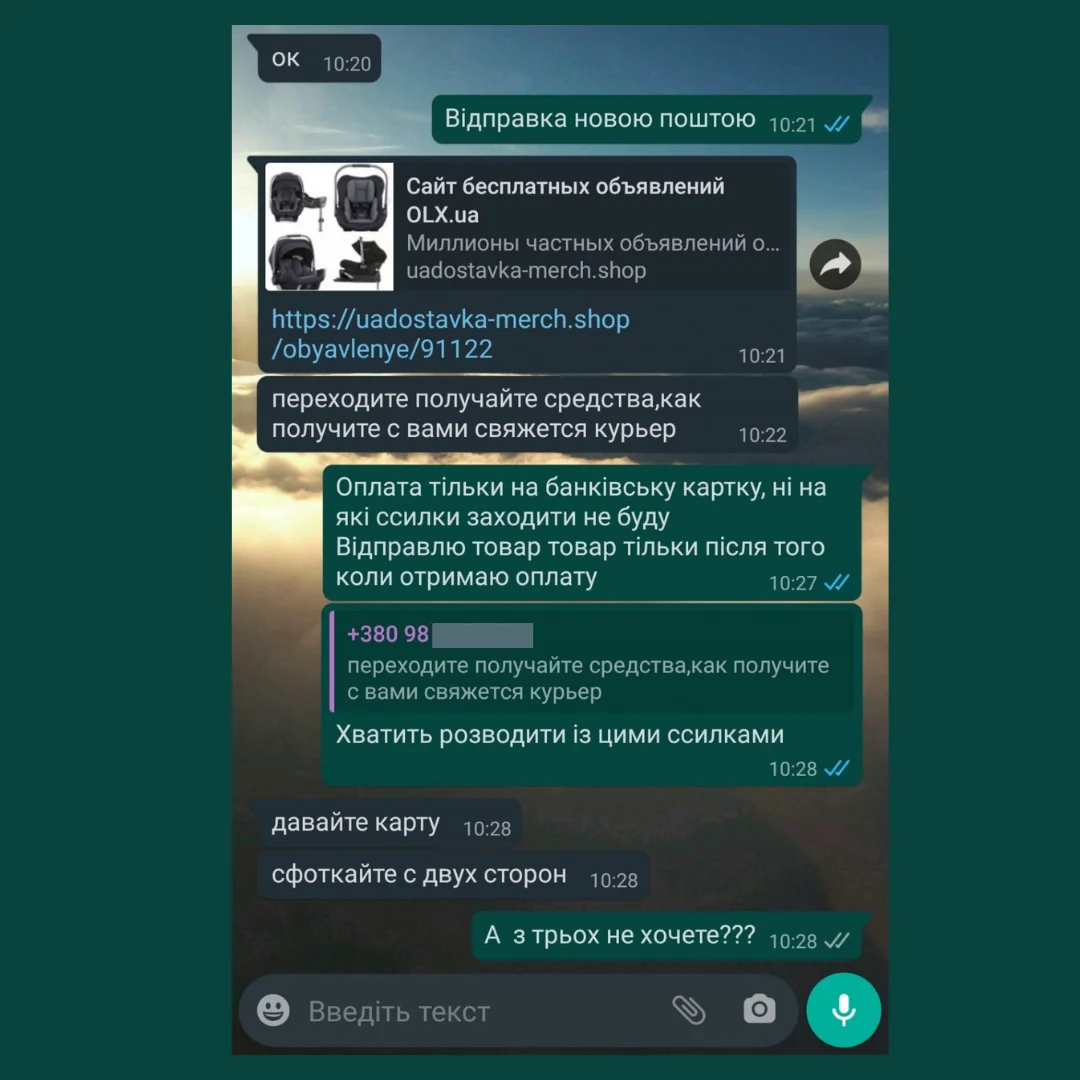
Under no circumstances should sellers enter the expiration date of the card and the three-digit code on the reverse anywhere - only its number is enough for payment.
A lot of scammers use OLX. To help its customers, the company has created a special instruction on phishing in OLX delivery .
Letter from "friend"
A friend sends a message asking you to vote for him in a contest, sign a petition, share a link to a cool promotion. Having hacked the account, the scammer had the opportunity to read the correspondence and communicates in the style of a friend, so the message is not suspicious.
Then everything will follow the well-known scenario - the message contains a phishing link and is waiting for you to peck at the bait.
What shall I do? Call a friend, find out if he sent such a message. If not, then it has been hacked.
Pay attention if there is a difference in behavior, habits or communication. For example, you know that a person is completely indifferent to sales - and suddenly he sends a link with an appeal to save up for a promotion. This is also an opportunity to call.
Your business project
Fraudsters can even create a unique "online store" or other resource on which they will conduct raffles and sell goods. Of course, their customers will not see any gifts or purchases.
In this case, the link to the payment system will be phishing. Those who want to receive a reward or make a purchase enter the card data in the fields of the fake page - the job is done.
What shall I do? Cooperate only with verified stores. Before you start buying on a new site, look for reviews on the Internet. Do not trust personal data to unfamiliar resources.
Basic safety precautions that must be followed at all times
-
We've said it before, but we'll say it again - always check the address of the received link with the address of the real site. But in general, it is better not to open links in suspicious emails at all - they may contain viruses.
-
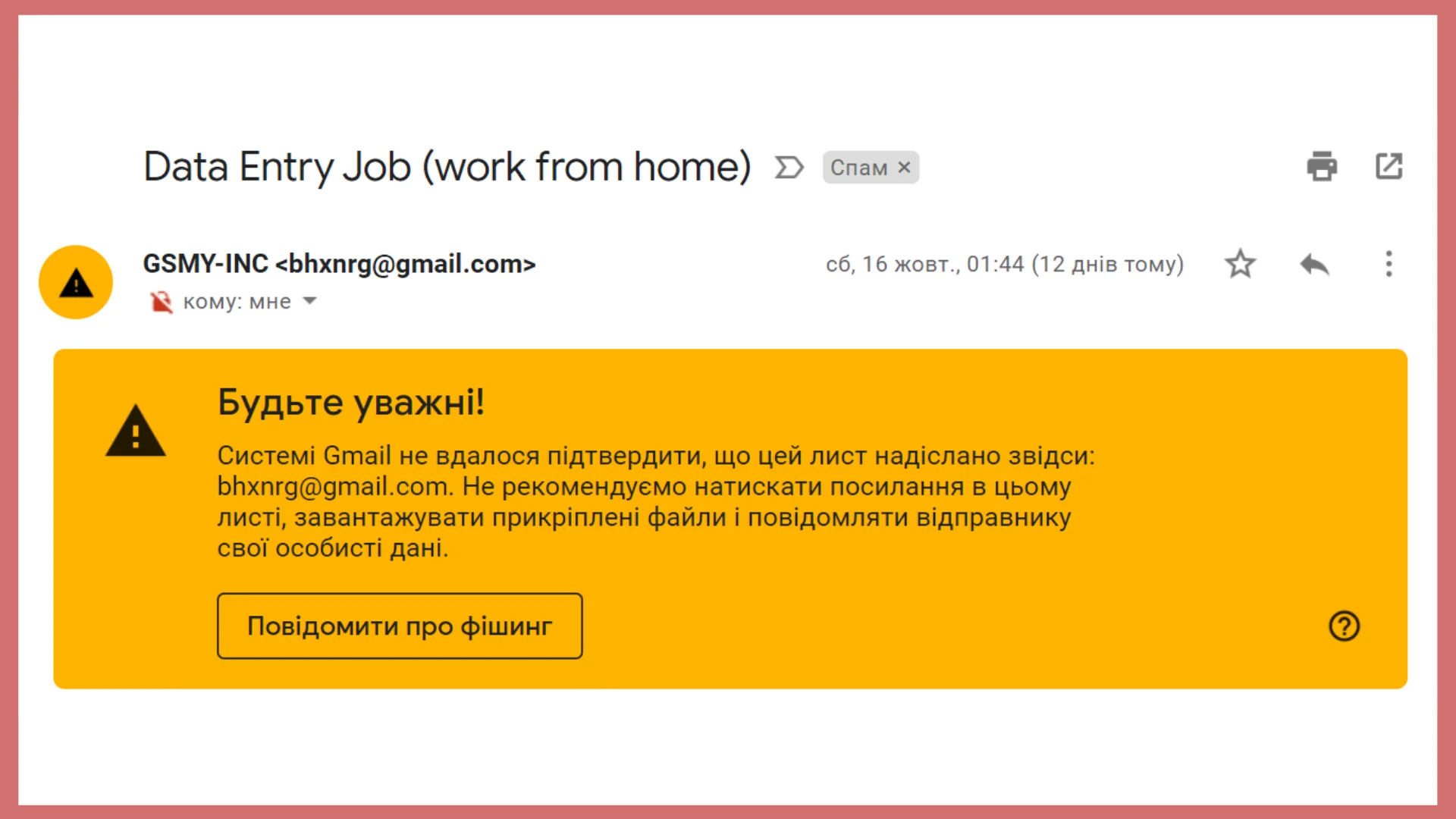
All browsers have protection against phishing attacks. If the site is not reliable, the browser will report: "Warning! Dangerous software!" or "Potential phishing threat". When such a message is displayed, it is better not to go there. Mail has its own filters. If the postman qualifies the letter as dangerous, you need to obey him.
-
Install a good antivirus. In addition to protecting against phishing attacks, it has many useful features for saving personal data — it prevents fraudsters from intercepting messages with codes, closes access to programs that steal data from online banks, etc.
-
Set up two-factor authentication on all important resources — banking applications, mail, and social networks. This way, fraudsters will not be able to log into the account, even with a login and password, because the system sends a notification to the owner's mobile phone when a login attempt is made from a different IP address. Only after entering the code from a verified device will it be possible to enter the account.
-
Pay attention to the presence of an SSL certificate on the site. Fraudsters do not create a site for a long time and may not care too much about having a certificate. In this case, in the address bar next to the domain name, you will see the inscription "Not protected!", crossed out red letters https, an exclamation mark in a triangle, or a crossed out lock. However, a phishing site may have a security certificate because it is easy to obtain one for free. But if you see a warning in the address bar, be careful.
-
Many people use the same password for all accounts. Having hacked a social network, it will be easy for fraudsters to log into all other accounts. Try using different passwords.
-
Report detected phishing sites to the company whose web resource was copied or to the cyber police . The sooner the phishing site is closed, the fewer people will fall for the fraud.