Most domain addresses on the Internet are paid. They have different prices: some are quite cheap, up to 100 hryvnias per year of use, and some are more expensive. An average domain can be bought for 300-500 hryvnias, which is what site owners usually do.
There are also premium domains , which cost many times more and are determined by the owners of the domain zone. Such an address can be worth several thousand dollars due to its brevity and cuteness. It is easy for users to remember it, and it is convenient for marketers to promote the site using a beautiful name.
Sometimes on the Internet you can read that a premium domain is any expensive domain. But this category includes only those that have been assigned a value by the owner of the domain zone. This is the purchase of an address on the primary market, from the registrar.
When an already registered domain is resold to another owner, it is a secondary market. It is full of many different mechanisms of domain price gouging, and not all of them are legal.
After entering some attractive addresses in the search engine, sometimes you can find not a site, but an advertisement for sale. Someone trades addresses of well-known brands bought in other zones (in the hope that the company itself will buy it), while others simply reserve business-friendly words such as sale, market, clothes, shop, product, and so on.
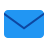
For example, not all Wikipedia addresses belong to the resource itself — someone sells one of the domains for $800. By the way, wikipedia.tech is already sold for $4,399.
Prices for domains are set "manually". In this case, the cost is determined not by the registrar, but by resellers, who often take these addresses at the usual price.
How much can a domain be resold for?
Companies are ready to pay insane amounts of money for beautiful domains, and sometimes these sums cause genuine surprise.
How many? Note for yourself: the voice.com domain cost the owners $30 million, sex.com bought Payboy for $14.5 million, and internet.com cost $18 million.
The most expensive domain registered on the network is lasvegas.com, which was sold for $90 million.
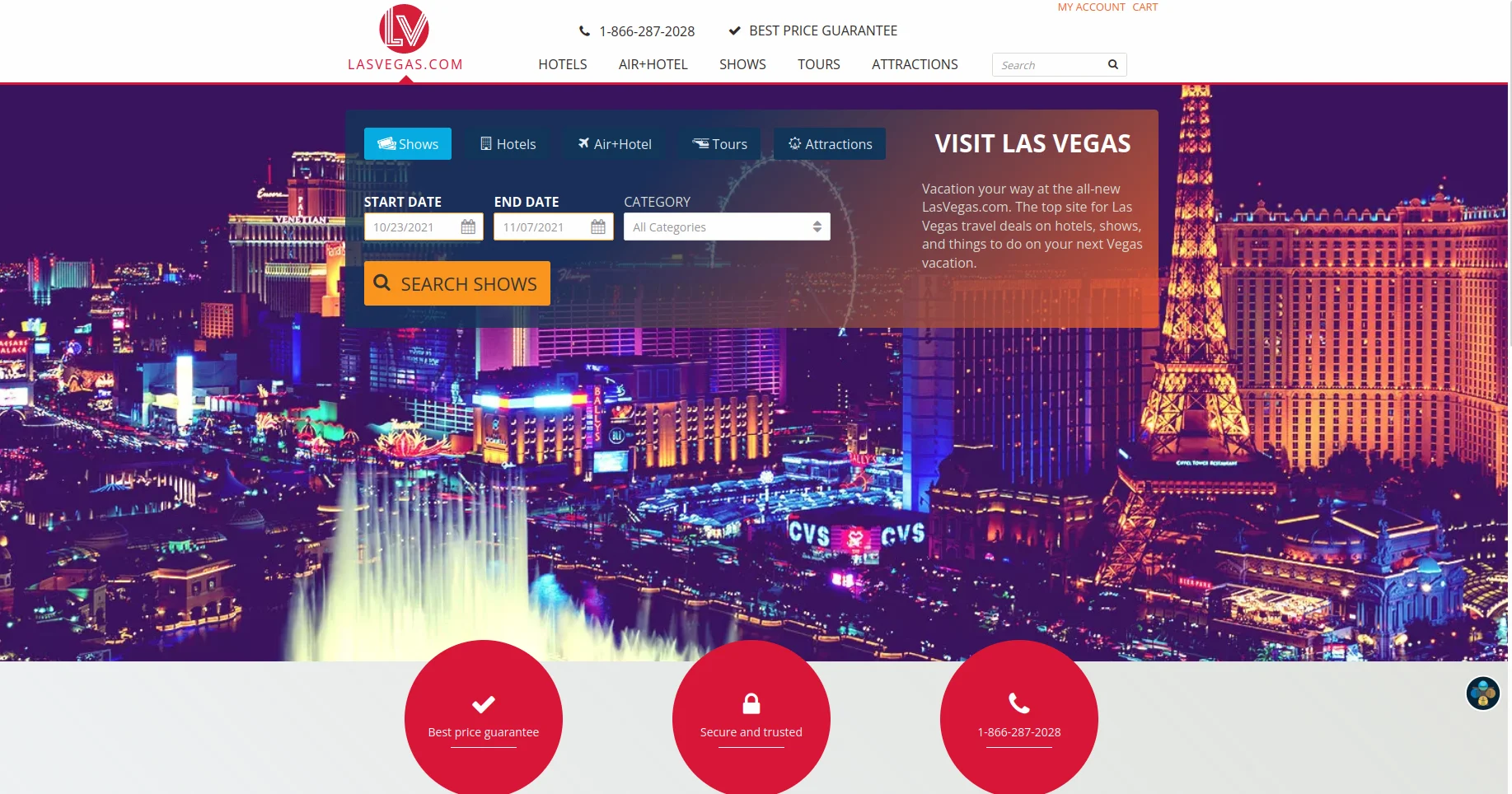
This is what an "average" site looks like, which sits on a "golden" domain - you will never guess how much it cost the owners of the address.
Now let's talk about how the secondary market for selling addresses works. There are two main types of earning on domains in the network: cybersquatting and domaining.
Domaining
Domaining (or domain investing) is buying sweet-sounding domain names and reselling them to interested companies. These can be industry names or phrases that can be used in business (nails.best, town.info). It happens that at the time of purchase they are already not cheap, so the investor risks money, trying to predict how to sell the domain more expensively and what will be popular in the market.
Domainers buy many different addresses, and for resale they create sites with showcases, order advertising, promote their products. Domains are auctioned and can bring a very good profit.
You can never guess how much you can earn from a domain. It's like trading in art objects - to sell a product more expensively, you need to be able to properly generate interest in it.
Of course, such activity does not bring much joy to buyers - they could have registered the same domain much cheaper if it had not been intercepted by domainers. But this method is considered legal because it does not violate any laws.
One of the important differences from cybersquatting is that domainers buy addresses that do not contain the names of already registered trademarks. And the second difference is the methods used by cybersquatters to sell domains. We will talk about them below.
Cybersquatting
Cybersquatting is the registration of domain names that contain the names of existing companies or sound similar to them.
What do cybersquatters do?
- They buy domain names with the names of trademarks in other domain zones. If the site has the address daewoo.com, then daewoo.biz or an address with any other extension after the dot is purchased.
- They choose a site and buy a domain with a similar combination of letters - for example, the original site bag.com, and beg.com is bought.
- They find new companies in the trademark register and buy addresses that match their names, until the owners had time to register them. The company is usually forced to buy back addresses for a higher price.
- They buy domains that the owners could not or forgot to renew. Such vicissitudes may be associated with financial difficulties, legal proceedings and other problems. When the company gets back on track and tries to rebuild its site, the domain may already be bought by cybersquatters.
What then happens to these addresses? There are a number of techniques that cybersquatters use to make money.
- A direct offer to TM owners to buy the address.
- Blackmail of company management with the aim of selling addresses at a higher price, threats of placing negativity on domains with the TM name in order to undermine the image.
- Selling counterfeit goods from a clone site hosted on the domain or committing fraudulent transactions.
Most cybersquatting methods harm TM owners and buyers, so you need to know how to protect yourself from the actions of fraudsters.
Cybersquatting: how to fight
Cybersquatting can be combated not only by detecting domain theft, but also by preventive methods. What to do to preserve the reputation of your business and prevent domain name misappropriation?
Sue and file complaints
First of all, you need to know that according to the law, a trademark takes precedence over a domain name. The owner of the TM has rights to the address, so he can condemn it to a cybersquatter.
Most of such disputes are resolved in court in favor of the TM owner, you can also contact the Antimonopoly Committee.
But there are certain difficulties that prevent justice. For example, cybersquatters often provide fictitious personal data during registration. Since you can only sue a real person, this becomes a problem.
There is another way to defend your rights — the UA-DRP procedure. This is an out-of-court practice of resolving domain disputes, which is carried out at the WIPO Arbitration and Mediation Center (nofollow). This practice applies to general international domain zones, and in Ukraine it applies to the following zones:
- u.a
- com.ua
- kyiv.ua
- kiev.ua
- ivano-frankivsk.ua
- if.ua
- poltava.ua
- pl.ua
- uzhgorod.ua
- uz.ua
Not so long ago, Ukraine was not included in the list of countries that can file complaints under the UDRP procedure, but since 2019, this opportunity is available to us as well.
A special procedure has been developed for the .ua domain zone, according to which domain registration in this zone is available only to owners of the trademark of the same name. When submitting an application for ua domain registration, you must provide the TM number and specify the details of its owner. Thanks to this, domains with the .ua extension are protected from cybersquatters.
Buy all possible domains yourself (defensive cybersquatting)
This is often done by large Internet resources.
If you check the domains with the name of the social network Facebook in the address, you will see that they are purchased in almost all major domain zones. Some of them redirect users to the main facebook.com address, the other part does not contain any content.
All adjacent addresses are purchased by the companies themselves so that fraudsters cannot create copies of the site and so that when the user enters a name with an error, he gets to the main site, and not to a fake page.
Let's take a look at the well-known YouTube.com. All addresses are also purchased, but try to visit: youtube.site, youtube.club, youtube.tech, youtube.space, youtube.review and others. It's empty there. How it actually happened can only be found out on YouTube, but it is likely that the video host bought these domains to avoid creating duplicates of the resource.
This method of protection is not cheap, but the businessman knows exactly who owns all these domains and is calm about their inviolability.
The day after purchasing a domain from Cityhost.ua , the client receives a letter with an offer to register domains in other, free zones.
An outsider cannot simply find out who registered the address. Each domain contains data about the owner, but in most cases this information is hidden. The registrar is obliged to protect the client's personal data, therefore, even if there are documents on TM, the registrar will not provide information about the person who bought the domain. Data can be obtained, for example, through the court or the police in case of criminal proceedings.
Domaining and cybersquatting differ in methods. Cybersquatting is a direct violation of the law, and domaining refers more to investment methods. But still, the best way for site owners is to look for addresses on the primary market, which will be much cheaper.
We recommend that you always take domains only from accredited registrars, and if your rights are violated, do not hesitate to go to court or arbitration.