What is site traffic?
The phrase "site traffic" is used in two meanings:
User-generated technical load on hosting;
Attracting visitors from various channels (Google, social networks, email newsletters ) in order to increase attendance.
Although these concepts are denoted by the same word combination, in fact they are two completely different phenomena. The first is technical indicators, the second refers to the promotion of the resource among users. Therefore, in order not to get confused, let's immediately agree that today we will talk only about the technical traffic of the site on hosting and will not touch on the topic of promotion.
And then the definition of the term will be as follows:
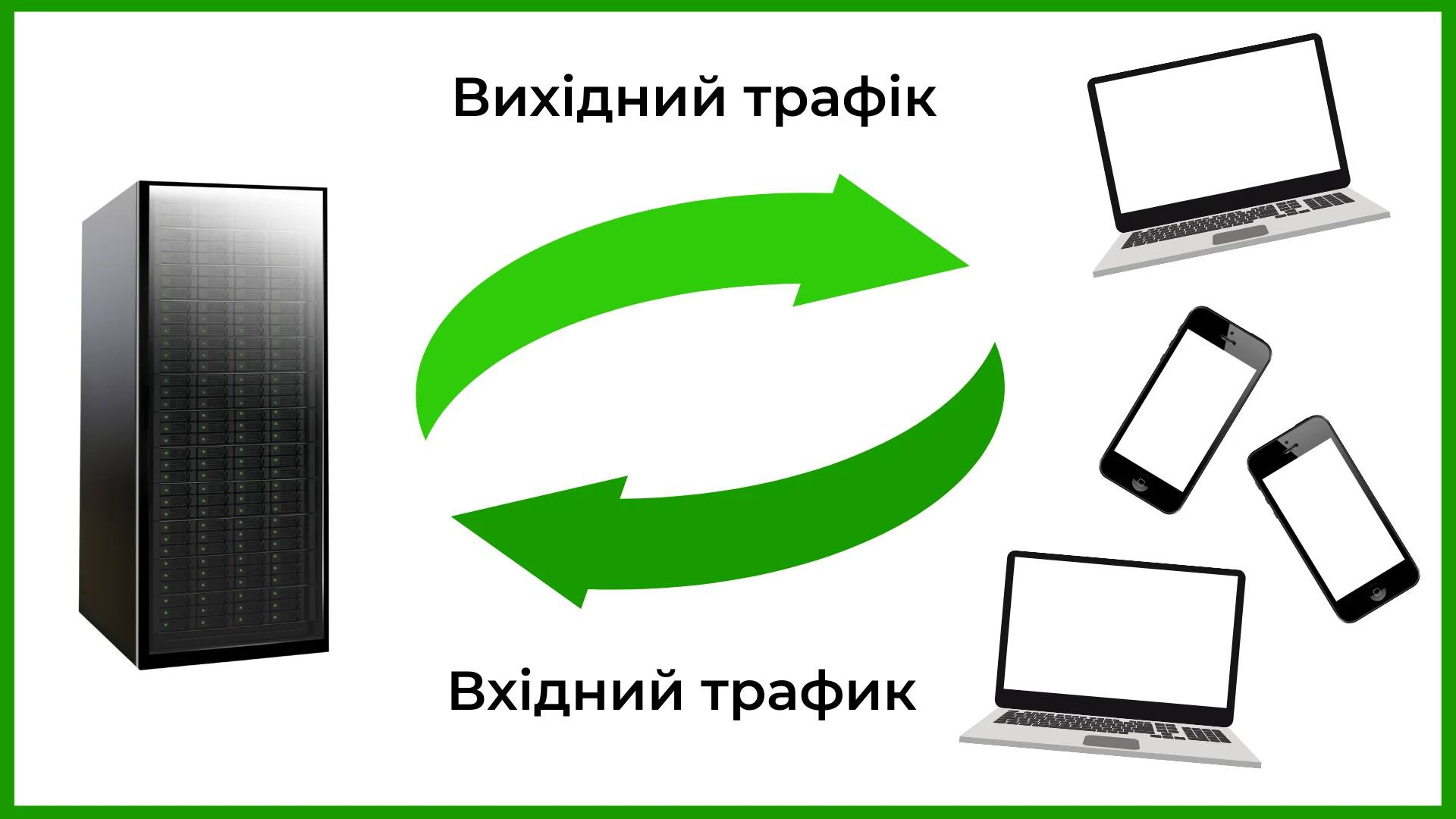
Site traffic is the flow of incoming and outgoing data processed by the server.
So there is inbound and outbound traffic. Inbound is the arrival of data to the server, for example when new content is added to it, a user sends a request or uploads their media files. Output is data that is sent to the outside: for example, when a user receives a compiled site page. Together, they form a load on server capacity.
The more visitors come to the site and perform some actions on it, the more server power the site consumes.
What happens to the site if the traffic exceeds the permissible threshold
Many providers write in their tariffs that the amount of traffic is unlimited. This is only partly true. Indeed, for most of the sites hosted on the hosting, the capacity allocated on the server is more than enough. Providers place exactly as many clients on one hosting as the machine can efficiently serve.
But in fact, the resources of each account are fixed and far from unlimited. They are calculated in the amount of memory on the hard disk, RAM, load on the processor.
If the web resource begins to develop and the number of visitors increases tenfold, the site stops "getting into" its tariff. It starts to hang, slow to respond to requests, and then shuts down completely.
Slow operation or failure of the site negatively affects its SEO promotion and user loyalty. First, the speed and availability of a web resource directly affects the ranking in search engines. And secondly, the improper operation of the site causes the loss of customers who go to faster and quieter platforms.
Read also: How hosting affects the ranking and promotion of the site
For an online store, a slow website can be a real disaster. Large marketplaces suffer enormous losses even for a few minutes of downtime.
Why monitor your traffic?
Traffic control is an important aspect of a webmaster's job. Especially if we are talking about a project that is constantly growing and which periodically has spikes in visits.
There are several reasons to pay attention to traffic and resource consumption.
It's time to see that it's time to upgrade to an advanced hosting plan . If the resources are exhausted, the site will begin to hang, and the provider will send letters with an offer to choose another tariff. This moment will definitely not pass you by, but it is better to take measures before it starts. When a site uses about 80% of its resources, any sudden increase in traffic can crash it. It is better to take care of the increase in power in advance, before problems begin.
Predict the increase in traffic during promotions. For example, you are going to launch a promotion on social networks designed to increase the flow of customers to the site. In this case, it is necessary to check the current resource consumption and power reserve for the future surge. It should be understood that after the peak of traffic, the site will not return to its previous positions, and the average level of daily requests will increase. If there is not enough reserve on the hosting, the site will not be able to withstand the influx of customers, and the promotion will create problems instead of taking the business to a new level.
Detect a DDoS attack in time. In order to "put down" the site, hackers artificially create a huge number of requests to the server, which it does not have time to process and hangs. If there is a sudden increase in traffic without any apparent prerequisites, this may indicate an attack by "ddosers". Such events are monitored by technical support, but it will not be superfluous to see the problem in time and notify specialists.
Read more in the article: What is a DDoS attack and how to protect your site/server
What to do if there are not enough hosting resources
If the site has exhausted the hosting resource, the problem is solved simply - you need to switch to an extended tariff. Each provider has 3-5 tariffs with different reserves of resources.
For example, at Cityhost, the most budget tariff is called Gig: the client is allocated one gigabyte of memory on the hard disk, 256 MB of RAM (PHP memory_limit) and 2% load on the server's CPU (processor). The Penthouse plan is 50 GB of disk space, 1536 PHP memory_limit and 15% CPU load. Premium Unlim, the largest unlimited tariff, provides up to 50% server load. The difference is felt.
But if this is not enough, the next step is to rent a virtual server (VPS/VDS). Here, the RAM is already calculated in gigabytes and the available processor frequency increases several times. Is this power not enough? Then the solution will be to rent a dedicated server - it has even more resources that the client uses himself.
But it is worth considering that resource consumption is affected not only by the number of visitors, but also by the architecture of the site. Page weight and scripts also use hosting capacity, and metrics will never show you exactly what resources are being spent on.
If there are not many visitors, but the consumption of resources is high, then it is time to do optimization.
Optimize the code so that scripts consume less resources;
Enable server caching ;
Use compression of media content;
Do not upload media files to the site itself, but use third-party resources, for example, YouTube;
Use a CDN to distribute static content to different servers.
How to find out website traffic on hosting
When starting to study the concept of traffic on the site, webmasters think about the question: can it be calculated in numbers? Is it realistic to predict?
Yes and no. It is impossible to calculate traffic using some equation, multiplying the number of visitors by the number of megabytes. For each site, the situation is individual, as it depends on many indicators.
You can find out your traffic only by looking at the metrics in the hosting account in the "Resources" section (for this, select the "Hosting 2.0" tab in the left panel and click on the site name).
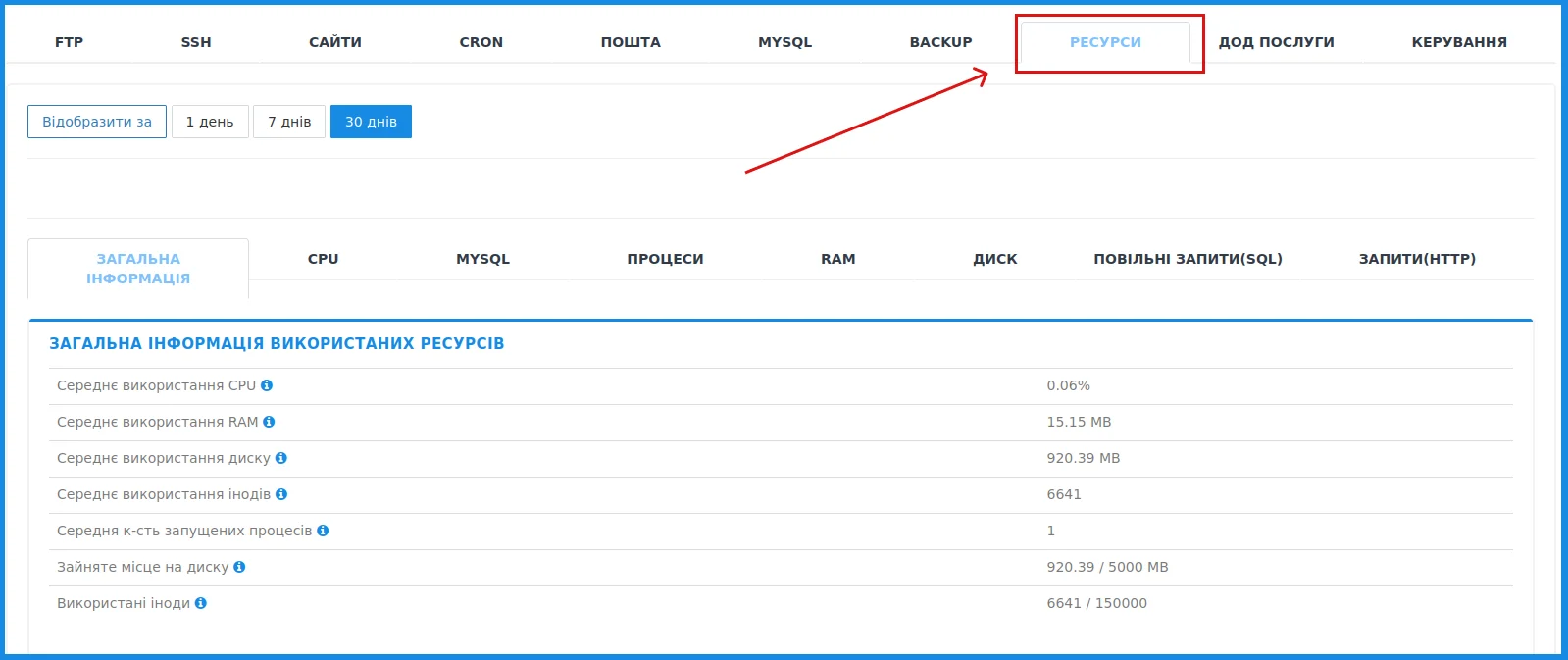
You will see many tabs - this is information about the use of all hosting resources. Statistics in numbers are collected in the "General information" section.
How to see site traffic? If we talk about traffic, it can be found in the "Requests (HTTP)" tab - it is the number of requests directed to the server. They are not necessarily generated by "living people" - part of the traffic is generated by bots, parsers and analyzers.
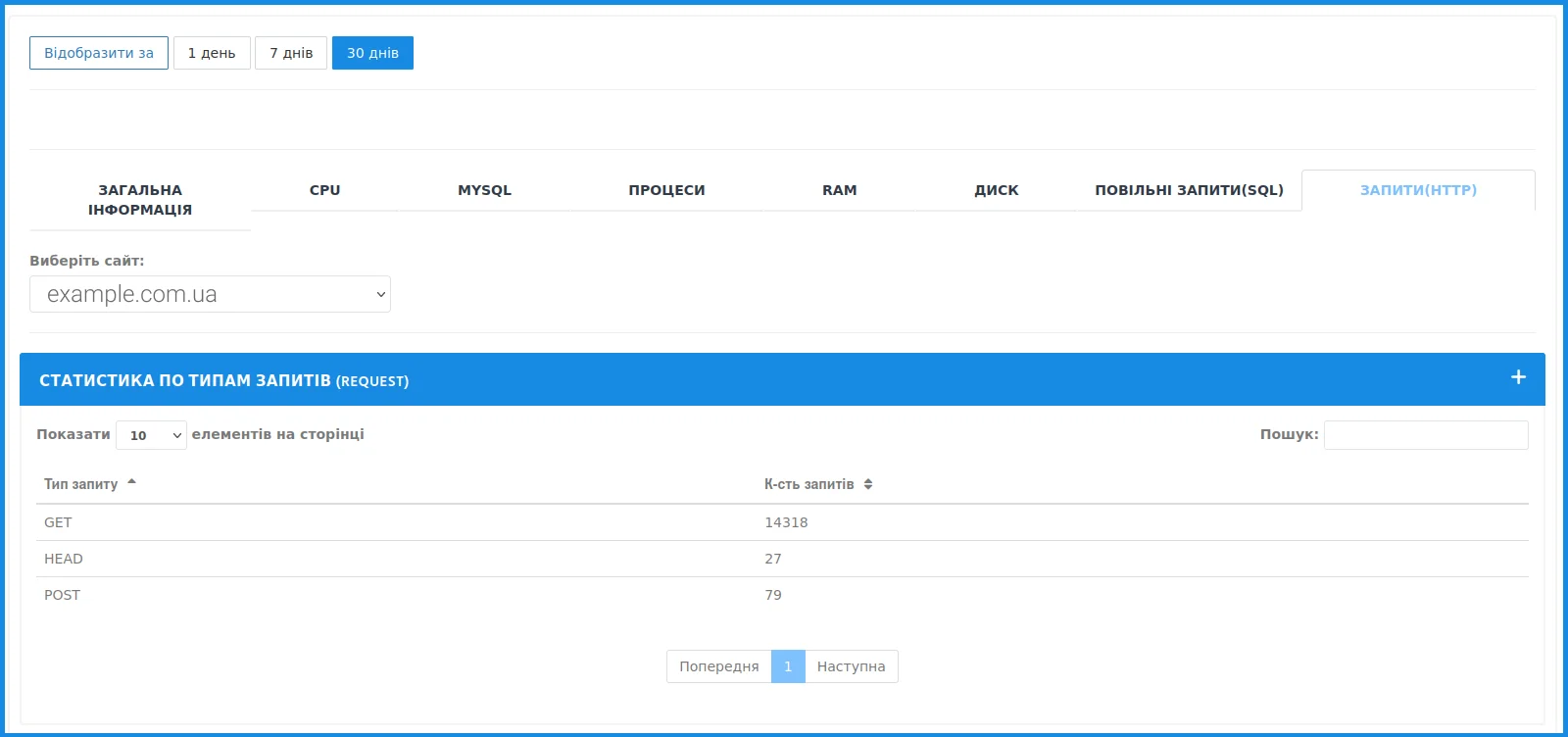
This number may not tell you anything concrete - well, 14 thousand requests per month, so what? To form a complete picture, the traffic is compared with other indicators — CPU (load on the processor), RAM (load on the RAM), MySQL (queries to the database) and others.
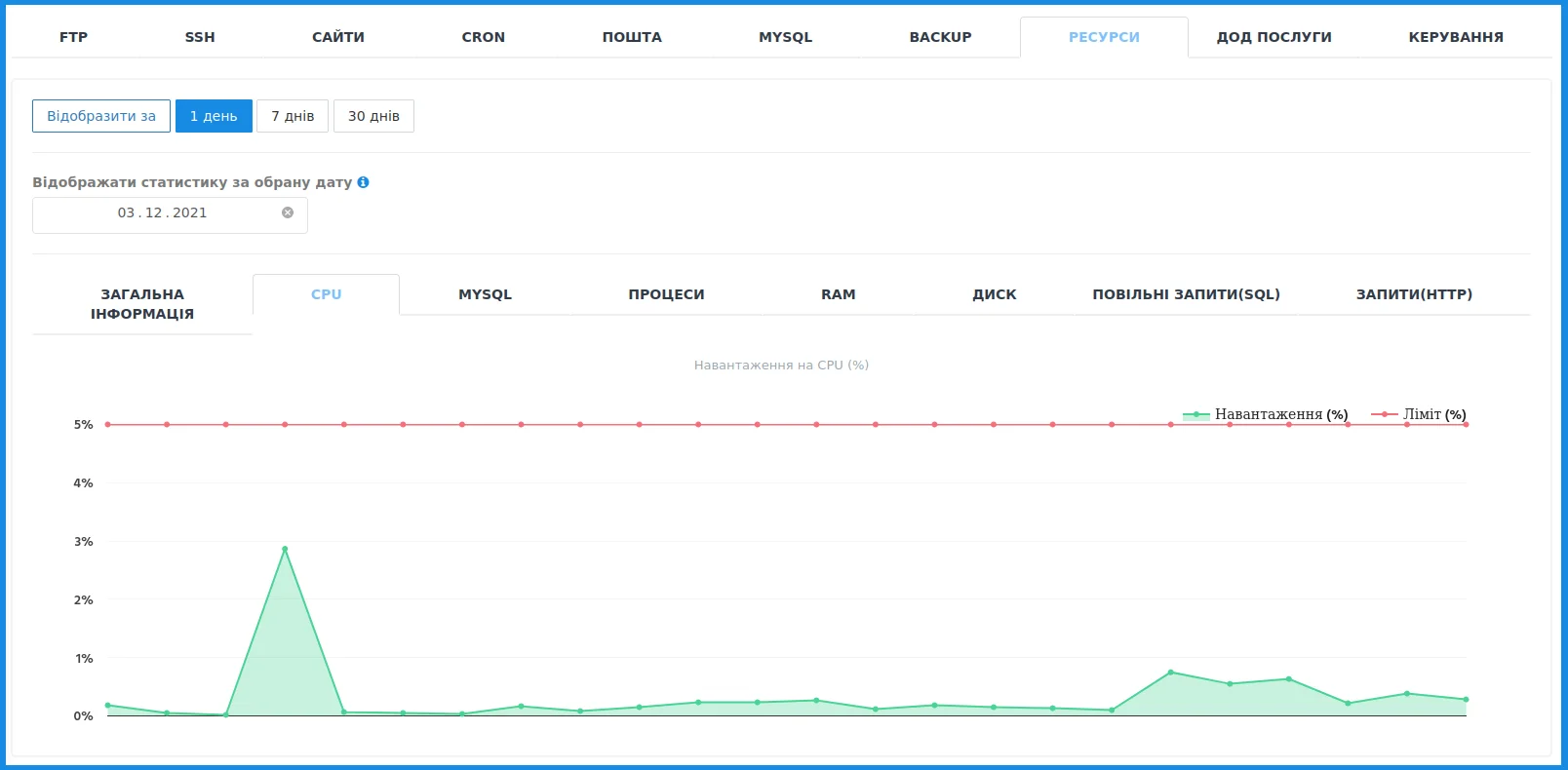
For example, this site receives an average of 300-400 requests per day and consumes less than 1% of the 5% CPU allocated by the tariff. But one day there was a surge of visits associated with the publication of information important to users. The web resource received more than 2000 requests, and the load increased to 3%. So, if the daily load increases to 3000, the owner of the web resource will need to think about expanding the tariff.
By studying these graphs in detail on your hosting account, you can also draw conclusions about whether your site has enough resources and whether the hosting can handle a sudden increase in traffic.
If the green line confidently approaches the red, this is a clear signal that the site has exhausted almost all resources.
Site traffic is a factor that affects site resource consumption. By monitoring this indicator and comparing it with the current hosting load, you will be able to monitor the situation and take timely measures to increase the tariff if necessary.