"Whoever owns information owns the world" — a well-known expression by banker Nathan Rothschild. Now, in the era of information technology, these words have become more relevant than ever, as data leaks can lead to catastrophic consequences, such as significant financial losses and the destruction of reputation. That's why the company owner and every employee must make maximum efforts to ensure cybersecurity in the workplace. Each business has its own methods of combating cyber threats, but there are common rules that help establish a reliable basic defense.
What Is Cybersecurity, and What Importance Does It Have in the Modern World
Cybersecurity is a set of methods to protect computer systems, networks, and software from unauthorized access, theft, alteration, or destruction of data. The leakage of confidential information leads to financial losses, loss of customer trust, and damage to the company's reputation. Moreover, Ukraine actively implements various security standards, such as ISO/IEC 27001, which is mandatory for all organizations, regardless of their nature, type, or size.
The importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated, as a company's system breach can lead not only to financial losses but also to negative consequences for millions of people. A vivid example is the massive disruption in the operation of "Kyivstar" (Ukraine's largest mobile operator), which occurred on December 12, 2023. Everyone has heard about the consequences of the hacker attack:
-
24 million subscribers were unable to use communication and the internet.
-
Malfunctions occurred in the operation of dozens of organizations, including DTEK, PrivatBank, Sheriff, EasyPay, Glovo, and Nova Poshta.
-
The operation of air raid warning systems in Kyiv, Cherkasy, and Sumy regions was disrupted.
Cityhost also fell victim to cyber attacks. On February 28, 2022, our company was one of the first to sever any ties with users from the aggressor country, after which massive DDoS attacks on our infrastructure began. However, we managed to withstand millions of requests, attempts to bring down servers, and system breaches.
Common Types of Cyber Attacks
We've provided just couple examples, but Ukrainian IT infrastructure is constantly under attack. Every company must make efforts to ensure robust cybersecurity, as it can become a target for Russian hackers at any moment. Additionally, other criminals target businesses to cause financial and reputational problems.

We have prepared proven advice for improving cybersecurity, but first, let's discuss the main types of cyber attacks.
Malware
One of the most common ways to harm systems and networks is through malicious software (Malware). Hackers use various viruses, computer worms, keyloggers, and bots to steal, damage, or destroy data. Modern malware can cause various types of harm, such as stealing confidential information, blocking data on personal computers (ransomware), affecting computer systems to damage the entire infrastructure, and using your computing power for spam or supporting cryptocurrency mining programs. According to the SonicWall Cyber Threat Report, 2.7 billion malware attacks were carried out in the first half of 2023, with global cryptojacking exceeding all previous records at 332.3 million, representing a 399% increase.
Ransomware
Ransomware is one of the most common types of malware that blocks access to systems or files and demands a ransom for their restoration. Ransomware quickly spreads through networks, especially through phishing emails and pirated content. To achieve their goal, hackers use asymmetric encryption, employing a pair of cryptographic keys for file encryption and decryption.
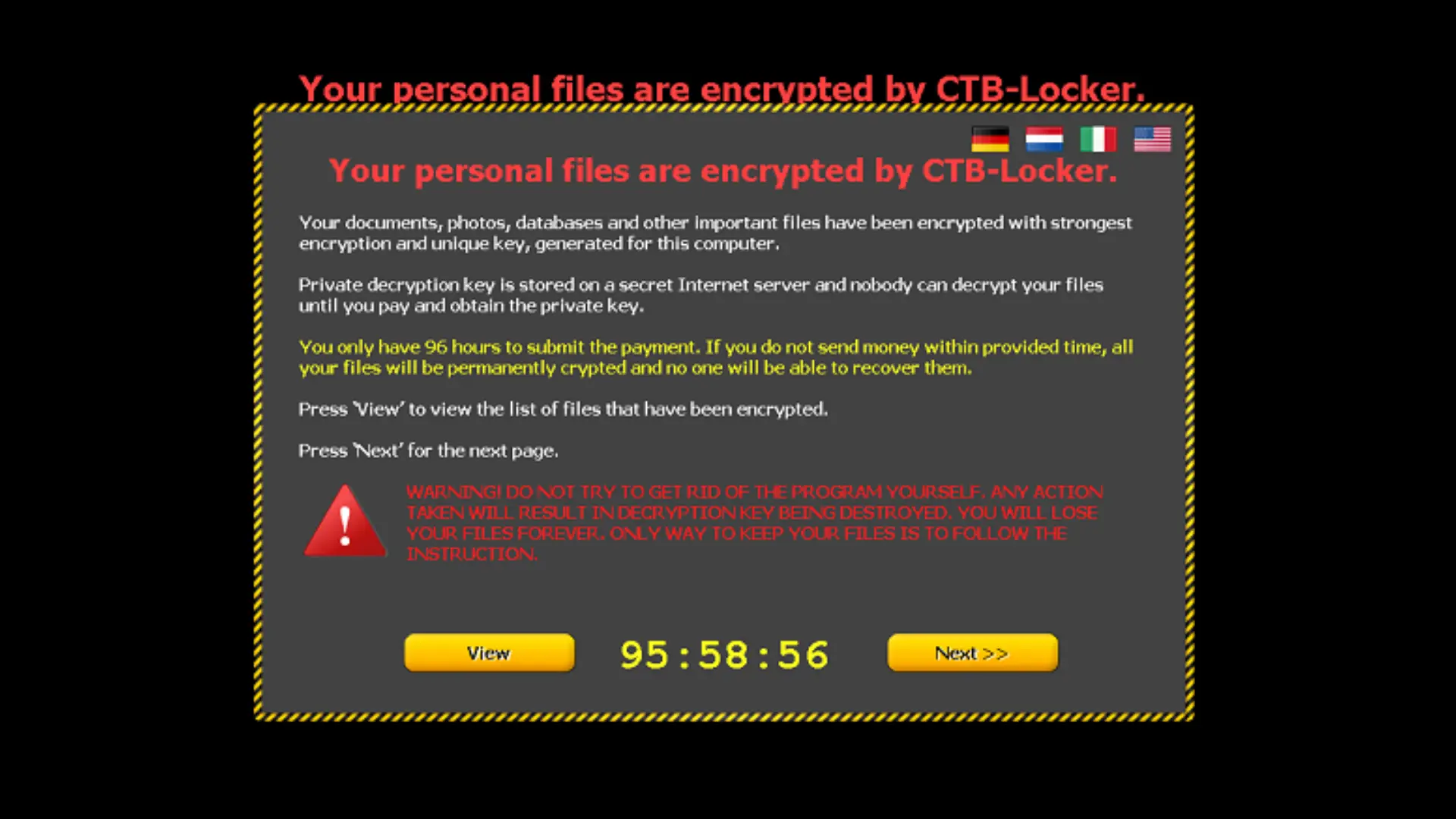 Without the private key, it is nearly impossible to decrypt the file, forcing individuals to pay a ransom.
Without the private key, it is nearly impossible to decrypt the file, forcing individuals to pay a ransom.
Read also: Viruses on the website - how to find them and protect yourself from infection
Phishing Attacks
Phishing is an attack where criminals attempt to obtain personal data by pretending to be reliable organizations. They create fake websites resembling official company web resources, and unsuspecting users enter their data. Phishers use email, SMS, and social networks to distribute links. Fake websites can closely resemble official organization sites, making it challenging even for attentive individuals to recognize the deception. Learn more about phishing and how to protect against it in our article.
DDoS Attacks
DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks overload servers or networks with requests to make them unavailable to legitimate users. On February 28, 2022, our company experienced such an attack, with millions of requests aimed at "taking down" our servers. Attackers use a botnet, a network of virus-infected computers, to simultaneously send a large number of requests to the target resource, causing overload and denial of service. Although such attacks do not lead to data loss, companies must spend considerable time and money to restore the stable operation of resources.
Read also: What is a DDoS Attack and How to Protect Your Website/Server
Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks
Man-in-the-Middle attacks occur when a malicious actor secretly intercepts and relays messages between two parties. MITM attacks are challenging to detect because modern hackers can create the appearance of ordinary information exchange. To gain complete control of data, attackers often use unencrypted or poorly protected wireless networks, such as public Wi-Fi points. They can also redirect traffic to fake websites, lure users to unprotected versions of web resources, and inject their code into authentication forms.
How to Protect Your Company from Cyber Attacks
Strengthening cybersecurity is something that leadership in any-sized company can do without necessarily investing hundreds of thousands of hryvnias. The key is to follow basic cybersecurity rules, as human error is often the primary cause of the loss of confidential information.

Organizing Cybersecurity for Company Leadership
Let's first explore essential tips for organizing cybersecurity for company leadership:
-
Implementation of Cybersecurity Policy: Create a fundamental document outlining requirements for passwords, data protection, use of internal and external resources, and a detailed instruction in case of cyber threats.
-
Cyber Hygiene Training: Conduct regular training sessions to educate employees on recognizing phishing emails, fake websites, and protecting against malicious software. For example, employees can take a course on the basics of cyber hygiene from "Diia".
-
Virtual Office Organization: To make the workspace more controllable from the IT perspective and provide additional data protection, establish a virtual office on a VPS/VDS or dedicated server. This allows limiting access rights, setting up secure communication channels, simplifying data copying and recovery, and detecting anomalies.
-
Backup Management: Identify crucial data and create backups. Most mobile apps and computers allow configuring automatic backup creation.
-
Paid Software Usage: Utilize only paid productivity and antivirus software, as attempting to save on such essentials often results in significant losses.
-
Program Updates: Developers regularly address vulnerabilities by releasing new versions with enhanced security. Ensure that each device is using proven software of the latest version.
-
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA, requiring users to provide multiple proofs of identity. While it may take employees a bit more time for authorization, it significantly complicates unauthorized access.
Numerous useful cybersecurity courses are available online for free or at a nominal cost. Effective antivirus software, such as Bitdefender, Norton Small Business, or Avast, costs an average of 750 hryvnias per year per device. Renting a Cityhost VPS server ranges from 270 to 1500 hryvnias per month. And even renting an entire dedicated server is quite affordable for businesses of any scale, starting from startups and FOPs - the budget tariff costs from UAH 2,300/month. Thus, ensuring reliable cybersecurity for a company is much cheaper than dealing with the aftermath of a cyber attack, which could cost hundreds of thousands of hryvnias.
Basic Cyber Hygiene Rules for Employees
As mentioned earlier, the human factor is a key cause of the loss of confidential information.
This is why employees must know and adhere to basic cybersecurity rules:
-
Strong Passwords: Create unique and complex passwords using uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
-
Protection Against Phishing Attacks: Never open links and attachments from unknown sources.
-
Unverified Devices: Connect external drives to work devices only after virus scanning, preferably following detailed analysis by the IT department.
-
Secure Networks: Never use unreliable or open Wi-Fi networks to access work-related, i.e., confidential, data.
-
Knowledge of Responsibilities: Employees are forbidden to disclose confidential information and the company's intellectual property.
-
Full Transparency: If a situation seems suspicious or dangerous, such as noticing a breach or data leak, promptly contact the cybersecurity department and management.
These rules may seem very simple, even commonplace. You might be aware of them and follow them – that's great. However, many are aware but forget these recommendations, leading to significant problems for the company and its employees.
In the era of information technology, cybersecurity plays an incredibly crucial role. Investing in cybersecurity helps preserve finances, a good reputation, and competitiveness. Neglecting basic rules can result in substantial damage and a blow to the company's image.
Hackers continually attempt to target organizations using malware, ransomware, phishing methods, DDoS, and more. Therefore, it is essential to invest in effective antivirus software, virtual office organization, licensed software, and regular updates, as well as employee training and support for a security culture. Remember, it's better to invest in protecting the company than to lose it forever!