- Signs of ai-generated texts
- Services for checking AI-Generated texts
- How to make AI-Generated text closer to human-written content
Copywriters use AI tools for writing texts in various ways: from generating ideas and brainstorming to writing sections or entire articles. This can significantly speed up the work; however, if generation is used thoughtlessly, without editing or fact-checking, it results in lower-quality texts.
Editors or website owners now face a new challenge: determining whether a copywriter wrote the text independently.
Clients pay copywriters for original articles — generating text on ChatGPT can be done for free. Therefore, the primary need for checking AI-generated content is to assess how diligently the author approaches their work: does the author genuinely write the articles themselves, or are they taking the easy way out and being deceptive?
It's known that while Google doesn't prohibit posting AI-generated texts, such content still has less chance of reaching the top of search results. Texts rank higher for personal experience, reliability, and authority — in short, for being truly useful to readers. Conversely, vague, generalized texts will drop lower in rankings.
Let’s explore how to identify AI-generated text.
Signs of AI-Generated Texts
All the signs discussed here may become harder to detect over time, as models improve and people learn, particularly to better formulate queries to AI. However, this isn't always necessary. It can be said that AI writes at the level of a mediocre copywriter who was too lazy to fact-check or proofread their work.
Fake Information
One of the earliest signs often found in AI-generated texts that haven't been proofread by a human is fake information. These occur so frequently that it has become an online pastime: asking ChatGPT to write its own biography or describe an obscure book — and then sharing the amusing results with the community. There have even been incidents that affected student grades. For example, a grammatically correct and logically consistent essay stating that Lesya Ukrainka was a nurse on Makhno's armored train.
Read also: Fakes and disinformation: learning to recognize false information on the Internet
Style
AI-generated texts often contain repetitive words and structures. Specifically, "in the modern world" is one of ChatGPT's favorite phrases, which it uses to begin many of its texts.
These texts also frequently lack a recognizable style and overuse the same keyword. If the text is marketing-related, it will have too much enthusiasm expressed in very vague terms ("modern technologies", "the culmination of technological development", and so on).
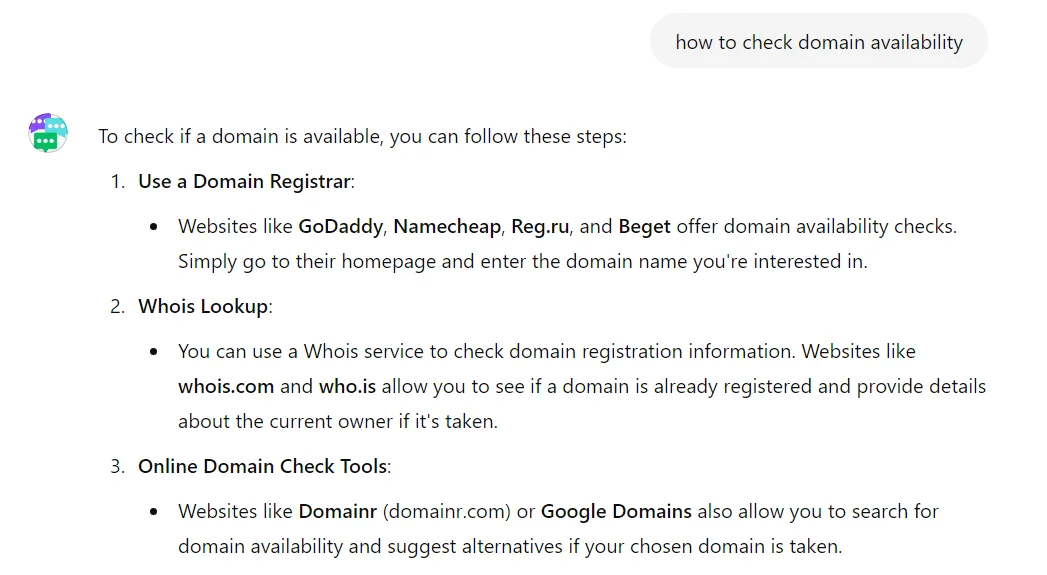
AI also tends to overuse lists. If you see a text that is almost entirely composed of lists, it is 99% likely to be written by AI.
For example, we asked ChatGPT how to check domain availability — you can see the result for yourself.
All of the issues mentioned above can be corrected with proper queries: "don't use lists", "write in a restrained style", "don't use clichéd phrases", and so on.
But there's one important sign that can't be fixed with any queries — AI-generated texts quickly bore the reader; they are uninteresting and superficial. Notice how long you can read an AI text? If your brain switches off by the second paragraph, this is also a sign of "artificiality" — the neural network isn't capable of writing lively, engaging content. At least, not yet.
Read also: Non-obvious Features in Google Docs: A User's Guide
AI Mistakes
Although language models are improving over time, many errors can still be found in AI-generated texts, such as numerous inconsistencies or using the same word where a human would have used a synonym.
There are also cases where GPT may use too many synonyms and complex words in places where a real person would not.
Here are a few purely technical signs:
- excessive use of the word "may";
- repetitive sentence structures;
- repetition of words or entire phrases;
- problems with sentence agreement, especially when AI writes long texts.
Lack of Individuality
In AI-generated texts, you won’t even find an imitation of personal experience; the sentences will be as generalized as possible.
AI won’t say, "I believe", "I think", "what I liked most", etc.
Of course, no one expects that a text written to promote website pages on external platforms using high-frequency queries will read like a personal blog. However, we must remember that both search engines and readers value texts that are useful and contain something unique. AI lacks personal experience and cannot infuse it into its writing — only a human can do that. This is why professional copywriters with excellent writing styles need not worry about losing their jobs to AI.
Wordiness in AI-Generated texts
This drawback stems from the previous point: without serious human intervention, GPT writes texts filled with excessive wordiness. These texts can be applied to various topics and fit reasonably well, but they won’t address the issue in specific detail. They can be described with the phrase "a lot of words about nothing" — like a student’s essay or a politician’s speech.
In the illustration below, AI generated a description of "Kraft" cheddar cheese. Similar descriptions can be generated by the dozen.

Read also: ChatGPT-4 is available on Bing — How to use artificial intelligence for business for free
Are AI-Generated texts unique
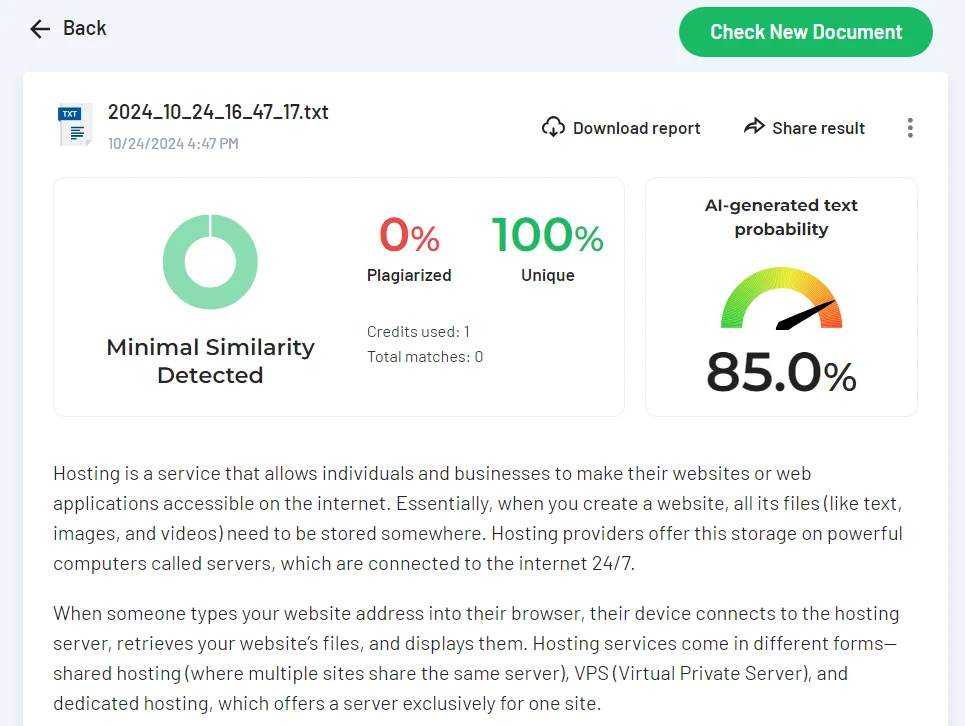
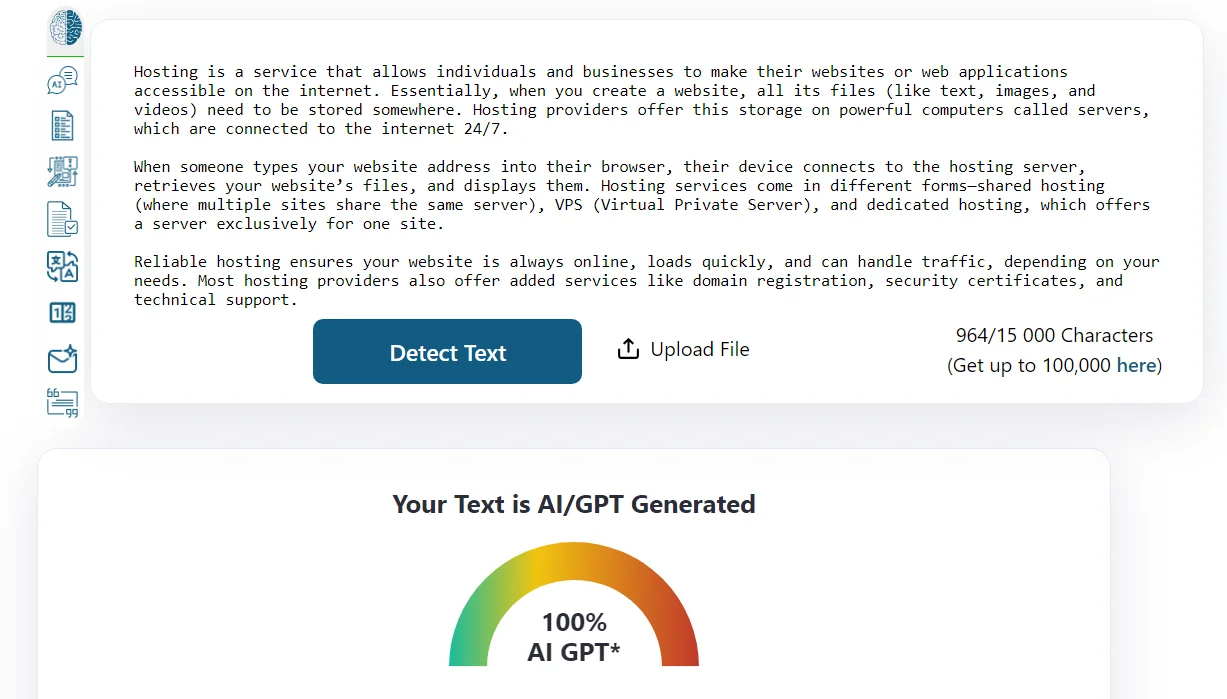
AI-generated texts tend to have fairly high uniqueness. We submitted a text about hosting, fully created by AI, to the Skandy service. This platform simultaneously detects plagiarism and AI generation. As we can see, with 100% uniqueness, the service shows a 85% probability that the content was not written by a human.
Services for checking AI-Generated texts
On this note, we smoothly transition to the topic of tools for detecting AI-generated content. To make an editor's job easier, automated services can be used, and there are plenty of them available online.
However, not all of these services recognize the Ukrainian language, though the field is gradually moving in that direction.
ZeroGPT
This tool, according to editors who have worked with it for a long time, tends to have some inaccuracies, often identifying the most general parts of a text as AI-generated. However, the system supports multiple languages, including Ukrainian, which is an advantage.
Here’s how it tested a fragment of AI generated article.
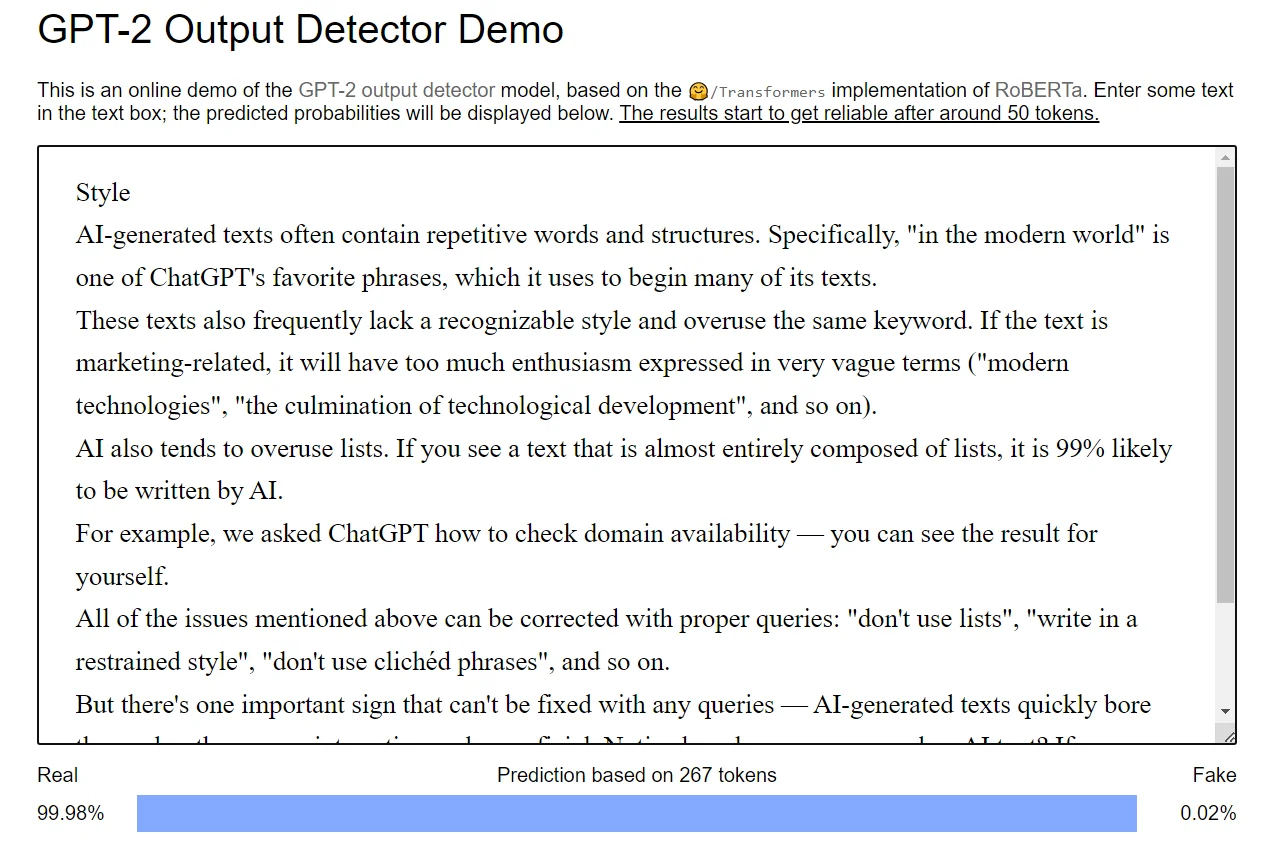
GPT-2 Output Detector
This tool also checks texts in Ukrainian, has a very simple interface, and nothing superfluous. The detector assesses the naturalness of even individual sentences — the website notes that data becomes reliable after 50 tokens. For example, the text we checked (this article) had 267 tokens.
GLTR IO
This is a verification service based on a mathematical formula: the more frequently a word is used online, the more likely it is to appear in AI-generated texts. Therefore, the easier it is for the system to "predict" a word in the text, the more "robotic" the text is.
Unfortunately, this tool doesn’t support Ukrainian, and Cyrillic characters turn into gibberish during analysis. But for checking texts in English, the tool works quite well.
AI Text Classifier
This service from OpenAI initially had high expectations, but it is now unavailable to users. The creators stated that this model was based on the same principles as the popular ChatGPT, making it effective at analyzing texts using similar algorithms and learning through the process.
Currently, the service page displays the following notice:
"As of July 20, 2023, the AI classifier is no longer available due to its low accuracy. We are working on improvements based on feedback and are exploring more effective methods for identifying text origin, as well as committing to developing and deploying mechanisms that help users understand whether audio or visual content was AI-generated."
Why do we mention an inactive service? Because it's a very telling case. It was one of the first tools and inspired confidence that AI-generated texts could be easily detected by simply pasting them into a window. It was developed by the OpenAI team — the creators of ChatGPT — who are far more trusted than "garage" developers of similar platforms. Nonetheless, they discontinued the tool, demonstrating a high level of responsibility. This indicates that such services are still very imperfect and often make mistakes.
These tools can and should be used, but only as supplementary aids. It's also important to remember that a human copywriter can just as easily produce an uninteresting, shallow text full of errors.
How to make AI-Generated text closer to human-written content
Realizing that a copywriter has delivered a generated text instead of an original one can be an unpleasant surprise. However, there’s nothing inherently wrong with AI content generation. Neural networks help digital workers optimize their workflow and quickly create simple content that doesn’t require much creative input. For instance, a budget website owner can swiftly create product descriptions or basic pages using AI.
AI can save a significant amount of time for those who write texts themselves. You can delegate tasks like drafting article outlines, subheadings, generating additional ideas, or explaining complex terms. It can help write titles and descriptions, suggest ideas for the semantic core, and generally make the job easier.
Thus, in this section, we’re not endorsing lazy approaches by dishonest copywriters but instead sharing tips with authors, webmasters, and business owners for whom content generation serves as a tool and an aid.
Mandatory editing of AI Texts
AI-generated content always needs editing — this is an axiom. Even if the text looks decent, editing can humanize it and significantly improve readability. Here’s what you can do:
- replace frequently repeated words with synonyms or remove them altogether;
- vary sentence structures to avoid monotony;
- fact-check the content;
- reduce the number of lists or eliminate them if not contextually necessary;
- tone down excessive enthusiasm;
- cut down on filler text — often, a whole paragraph from AI can be condensed into a single sentence.
Integrating personal experience into AI-Generated content
It’s essential to add personality, real-life examples, and live cases from your experience into the text.
The more creativity, linguistic tools, and useful tips the text contains — especially those you won’t find elsewhere — the more unique and personalized it becomes.
If the content contains information that isn’t available on other sites, it provides real value and can satisfy the reader’s curiosity. AI can't help with that — this is where human input is irreplaceable.
"Humanization" Services — should you use them
There are now services that attempt to make AI-generated text more "humanized". We personally don’t use them because there’s no need, but a small study of available tools showed that there aren’t many reliable services for working with the Ukrainian language yet. Most of them freeze up or return errors. Out of a half-dozen tested, only one managed to process a text about server rental, but the result wasn’t impressive.
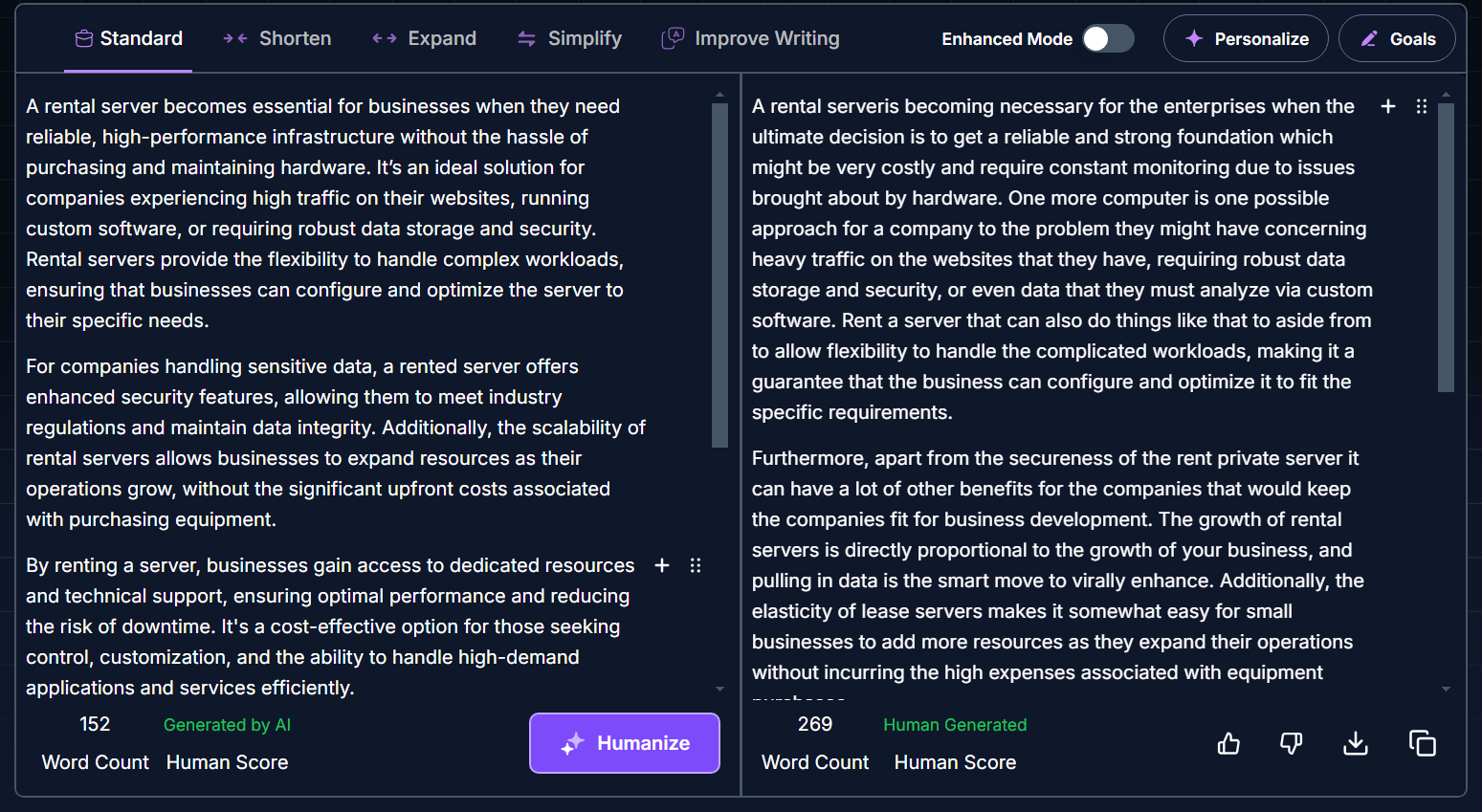
Perhaps these services will improve over time, but for now, we don’t recommend wasting time on them.
Neural networks are designed to assist people, not replace them — they can’t independently create high-quality content. However, if AI-generated text is carefully edited by a human, it becomes difficult to distinguish from human-written text.
If you have to use AI, combine it with your own experience and online tools rather than relying solely on AI. A text created in conscious and active collaboration between AI and a human is valuable from the perspective of both Google and the reader, and thus, there will be no need to flag it as AI-generated.