Sometimes it happens that Google simply refuses to rank your site higher in the search results even after you have:
- added visitor-friendly texts relevant to the topic of your resource;
- uploaded unique photos and specified the alt attribute for each of them;
- reduced the loading time of each web page to 1–2 seconds (if you plan to buy hosting for your site from Cityhost — fast page loading awaits you with every tariff plan);
- added schema.org microdata;
- received mentions on authoritative resources.
And often the main reason search engines ignore your site is that meta tags are either missing or incorrectly written.
What Are Meta Tags
Meta tags are HTML elements that help search engines and visitors better understand what a specific web page is about.
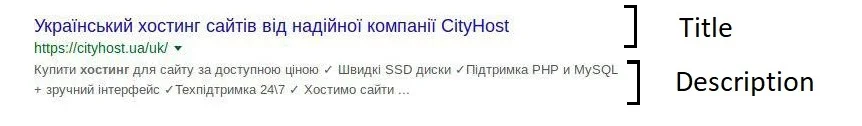
The most important meta tags for search engine optimization are Title, Description, and Keywords.
Title defines the name that appears in the search engine results. It is also displayed in the browser tab title and is the default name suggested when saving a page to bookmarks.
Description is a brief summary of the web page content that appears in the search results under the title.
The Keywords meta tag lists relevant keywords. Since 2014, this meta tag has lost its importance and is no longer one of the main ranking factors, but it still allows for controlled promotion of a page for low-frequency queries that are hard to integrate into the text. In our observations, large advanced websites still use keywords.
Read also: What are keywords and how to choose them
How to Create Optimized Meta Tags
When composing the Title meta tag, try to follow these recommendations:
- must be present on every page;
- optimal length is 30-65 characters;
- should not completely duplicate the H1 heading;
- place the relevant high-frequency keyword as close to the beginning as possible;
- avoid duplicating title metadata — they must be unique on each page;
- think not only about search engines but also about visitors: will they immediately understand the main content of the page after reading the Title.
When writing the Description, consider the following points:
- must be present on every page;
- must be unique;
- optimal length is 70–155 characters;
- write the description with visitors in mind — after reading it, they should want to visit your site;
- add keywords, but avoid keyword stuffing (for example, for a page where a domain name can be ordered, it’s optimal to mention the keyword “domain registration” once);
- include a call to action.
The only thing to avoid when composing Keywords is keyword stuffing — it’s enough to list 3-5 main queries.
Tools for Creating Meta Tags
Now that you know what meta tags are, you probably want to see how they look in search results. If your site runs on a CMS with an SEO plugin (such as Rank Math SEO or Yoast SEO), a preview is usually available right when creating the page.
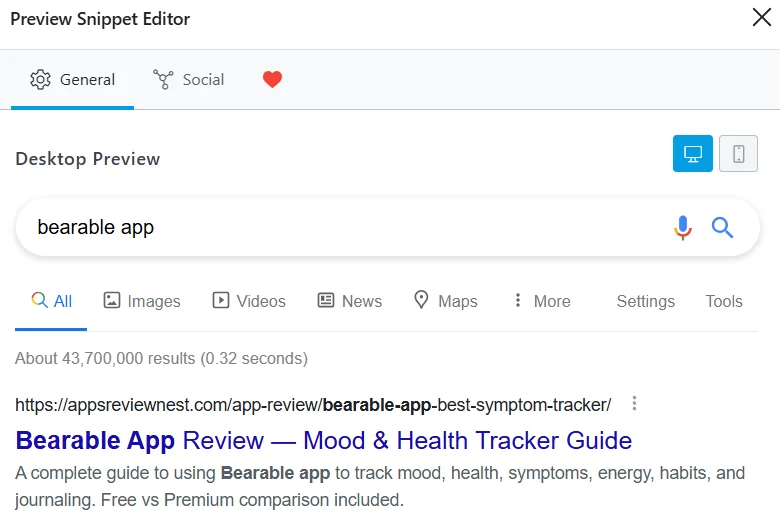
Example of meta tag preview with the Rank Math SEO plugin
If you want to check the appearance of meta tags independently of a CMS or if you have a static site, use special online tools:
To find out what meta tags your competitors are using, you can use the following methods:
- Manual page code inspection. Open the desired page on a competitor's site, right-click, then select “View Page Source”. Usually, title, description, and keywords are displayed right away, but sometimes you’ll need to activate the search and enter the name of the meta tag.
- Chrome extension. The best solution is SEO Meta in 1 Click — it shows all the meta tags of a page in one click.
- Online services. One of the best is Seobility Meta Checker, which offers 3 free checks per day. Go to the link, paste the URL of the web resource page, click Analyze Website, and view the meta tags.
Now you know what meta tags are and what they are used for. Plus, you have information about your competitors' metadata, which will help you easily choose keywords for the Title and Description, as well as determine their optimal length.