- In Which Areas the Role of Linux Is Increasing
- Linux Administrator: What Kind of Specialists Are We Talking About
Even without delving into artificial intelligence and cybersecurity, we can state that a significant share of gadgets used by people around the world run on Android simply because they are cheaper. Here, for example, is some data from explodingtopics.com — in most countries, Android holds over 70% of the mobile device market. The United States lags behind other countries (strangely enough), but even there, the share of this OS is growing and is already approaching 43%. Android is based on Linux, and system administrators, security engineers, and other specialists are needed at the very least to maintain the operation of the numerous applications running on this system.
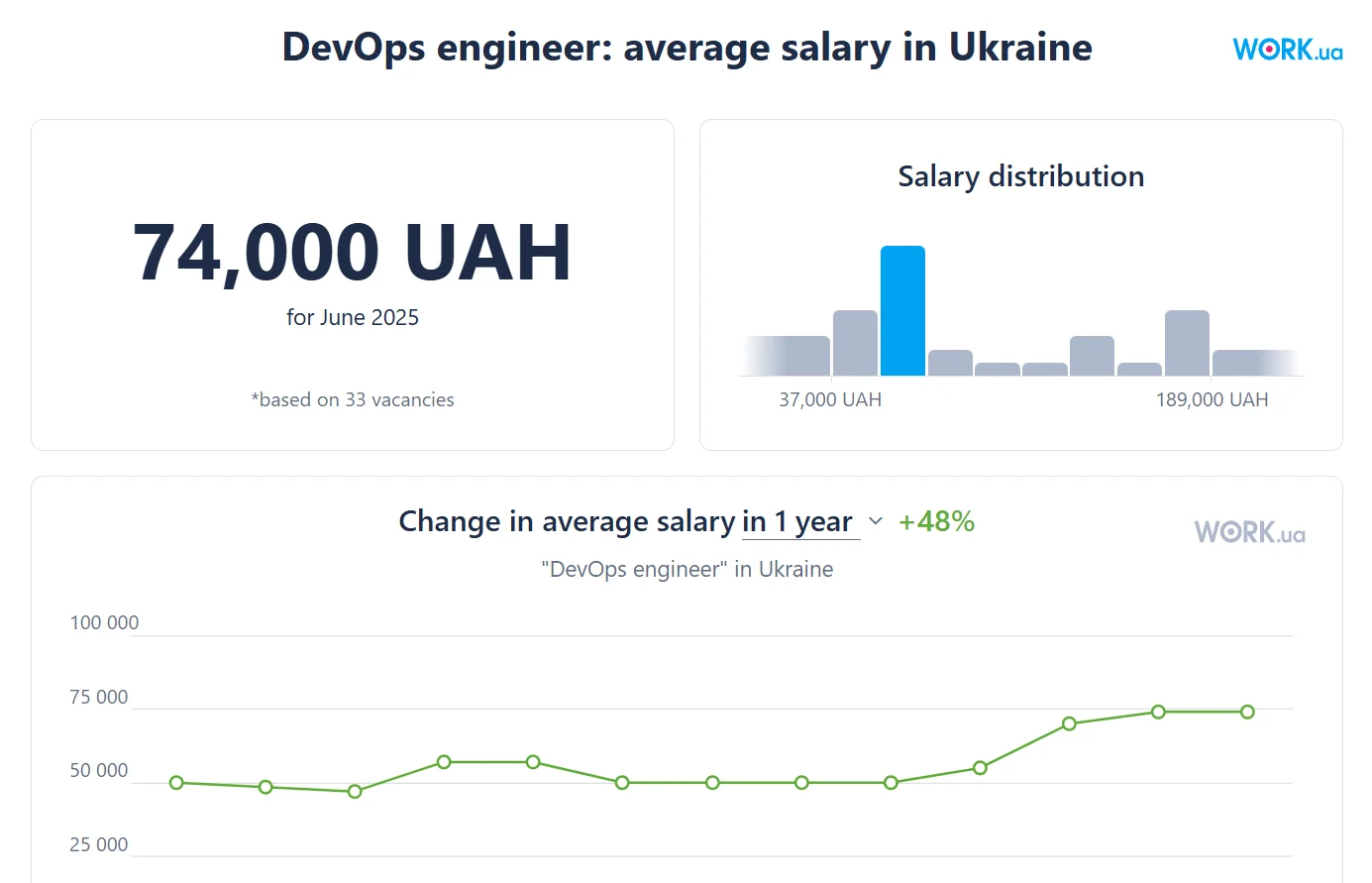
Here is some interesting data from Google Insights for 2024 with forecasts for 2025, which is already well underway. These tables show that the average salary for specialists in this field is increasing. And in Ukraine, with our wartime challenges? Our market has understandably contracted somewhat, but there are also signs of revival, at least according to DOU data. And, of course, Linux administrators are part of this process. According to work.ua, the average salary of a Linux administrator increased by 20% over the year, and the same applies to DevOps engineers. Here's a 2024 article showing that even then the median salary of DevOps specialists was higher than that of developers.
Let’s not look far — in our industry, you can’t take a step without Linux. This OS is used on servers that provide website hosting, and many users install Linux distributions on VPS servers and dedicated servers.
So, we can confidently say that Linux specialists won’t be left without work. Moreover — today, this is a profession where one can earn a good income and not worry about the future.
In Which Areas the Role of Linux Is Increasing
Strictly speaking — everywhere: from the simplest smartphones to artificial intelligence.
Corporate Sector
More and more companies are choosing clouds and cloud services, which require quality administration. Most of these infrastructures run on Linux and therefore require administrators who are knowledgeable about this operating system. Open-source code helps reduce project costs, but it can also have vulnerabilities, making cybersecurity specialists highly valuable.
Linux plays a huge role in developments related to artificial intelligence. In particular, the TOP 500 supercomputers, which play a leading role in these developments, run on Linux.
In addition, Linux is simply popular among developers, who often criticize Windows for being raw, bulky, full of mandatory updates, suboptimal, and vulnerable.
Consumer Needs
Although, according to StatCounter data as reported by It Week, most users do not consider Linux as a desktop operating system, we still actively use it.
As already mentioned, a significant share of devices worldwide runs on Android, which uses a modified Linux kernel. Consequently, numerous applications exist for these systems and need to be maintained. Android also dominates the mobile gaming sector. The Proton compatibility layer helps Windows games run on Linux and Android as well.
Also worth mentioning here are the IoT market, smart devices, and others. This is a vast field of activity.
Linux Administrator: What Kind of Specialists Are We Talking About
In fact, we’re talking about a whole range of different specialists who are in short supply on the market and are needed at various stages of development.
System Administrator
Very often, specialists in other areas of Linux system administration come from this one — and it is the oldest. Simply put, an administrator keeps the hardware functioning well within a company, manages servers, backups, local network setup and maintenance, user accounts, and troubleshooting.
Once, this profession attracted self-taught individuals, but over time it began to require more and more skills and knowledge. Although a sysadmin does not write code, they must have a good understanding of how software behaves. To validate their skills, they should obtain special certifications. For Linux environments, these might include the Linux Professional Institute certificate or Red Hat certifications for Red Hat Enterprise Linux environments. Knowledge of databases (SQL, Oracle, etc.), web servers, and mail servers is also helpful.

Where to Study to Become a System Administrator
There are many courses for system administrators, but to find out if this profession suits you, you can start with a Linux course on Prometheus.
You can also take separate courses on databases, cloud solutions, and technologies and gradually move toward your goal.
The demand for general system administrators is currently lower than for specialists in the following areas, so it’s usually recommended to additionally gain practical experience in data protection or have DevOps qualifications or work toward obtaining them.
You can read more about this profession in the article “Who Is a System Administrator and How to Become One”.
DevOps
This is an engineering specialist responsible for the daily processes required to ensure the timely delivery of applications, software, and updates. They work to make sure code is delivered on time and infrastructure operates smoothly — including cloud solutions and code repositories. It must be said that among Linux administrators, this role is probably the most popular.
Their responsibilities include:
- code delivery (testing, deployment, etc.);
- process automation;
- configuring networks and company cloud services;
- security;
- logging.
One might say that this specialist doesn't write code but manages all the supporting processes around it, but that’s not entirely true: working with infrastructure partially requires coding, as well as knowledge of databases. This role demands solid programming knowledge and an understanding of how hardware works. Many routine operations in this profession are automated, but the role as a whole cannot be automated — too much requires human control and experience.

How to Train as a DevOps
Skills needed for DevOps:
- working with Linux systems;
- Continuous Integration (CI) — code delivery and deployment. This requires knowledge of utilities, version control systems, code repositories, and CI systems (Jenkins, GitLab CI, CircleCI, GitHub Actions, Azure DevOps);
- Continuous Delivery (CD) — all skills related to delivering code to the end user. This includes Linux (again), Docker, Ansible, and various network protocols;
- working with cloud services — in particular Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure;
- managing servers and cloud servers. This involves a great deal of knowledge in the area of infrastructure as code (Code-as-Infrastructure);
- microservices.
Despite how intimidating this list may sound, specialists often say they started with open courses and YouTube videos. Here’s a beginner course on Prometheus that helps you get oriented in the topic and suggests further reading. All of these areas offer certifications that confirm a specialist’s skills and help with career advancement. Here is a short list of sources where you can get certified — Red Hat, HashiCorp, DevOps Institute, MIT, Linux, Jenkins.
DevOps salaries on the market can exceed those of developers, but it should be noted that this applies to highly qualified professionals. Overall, hiring specialists say that today’s market faces a shortage of workers above the middle level. So, you’ll need to put in the effort, but once you gain experience, you can be confident in your job security.
Read also: What Does Overqualified Mean and Why Employers Reject Candidates Who Are Too Good
Support and Security Engineer
In fact, every system administrator encounters some level of system security work early on. They create backups, work to prevent threats, maintain system stability, minimize data loss, and more. However, support and security engineers go deeper into this field:
- logging;
- configuring and updating systems;
- managing access policies, passwords, and the like;
- setting up firewall protection;
- disaster recovery;
- security auditing and vulnerability assessment.
These are the specialists who ensure system resilience, counter threats, and maintain stable operation. They are needed by defense forces, logistics companies, financial institutions, software development companies — essentially anywhere sensitive and valuable information is present.
Cybersecurity specialists operate at different levels: from SOC analysts who monitor systems and respond to alerts, to security auditors and testers who search for vulnerabilities — with skills similar to those of hackers, but without harmful intent.
Where to Study to Become a Support and Security Engineer
Here’s a personal story published on DOU, where the author describes their journey into this field. To summarize, the basic knowledge needed at the start includes:
- the OSI model (Open Systems Interconnection);
- the TCP/IP model;
- fundamentals of information security, the CIA model (Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability).
Practical experience is also important, for example, with platforms like Try Hack Me or Hack The Box.
As for useful courses, the author mentions CyberOps Associate Version 1.0 by Cisco. You can also try starting with Google Cyber Security, a basic course that is often freely available on Prometheus for beginners. It’s an entry-level course that provides the knowledge needed for a SOC analyst — and it doesn’t sound too overwhelming.
Here’s also a course from GOIT, which is suitable for beginners. And a handy list of certifications that help validate skills in various areas of data protection.
Driver and Embedded Systems (IoT) Developers
As of 2025, there are over 30 billion IoT devices worldwide. These include medical gadgets, sensitive sensors, navigation systems, avionics, manufacturing automation devices, drones (indispensable to the military), and embedded systems in common consumer electronics like tablets. AI is being actively integrated into IoT. Many of these systems run on Linux: the Linux Foundation is developing a dedicated operating system for IoT called the Zephyr Project.
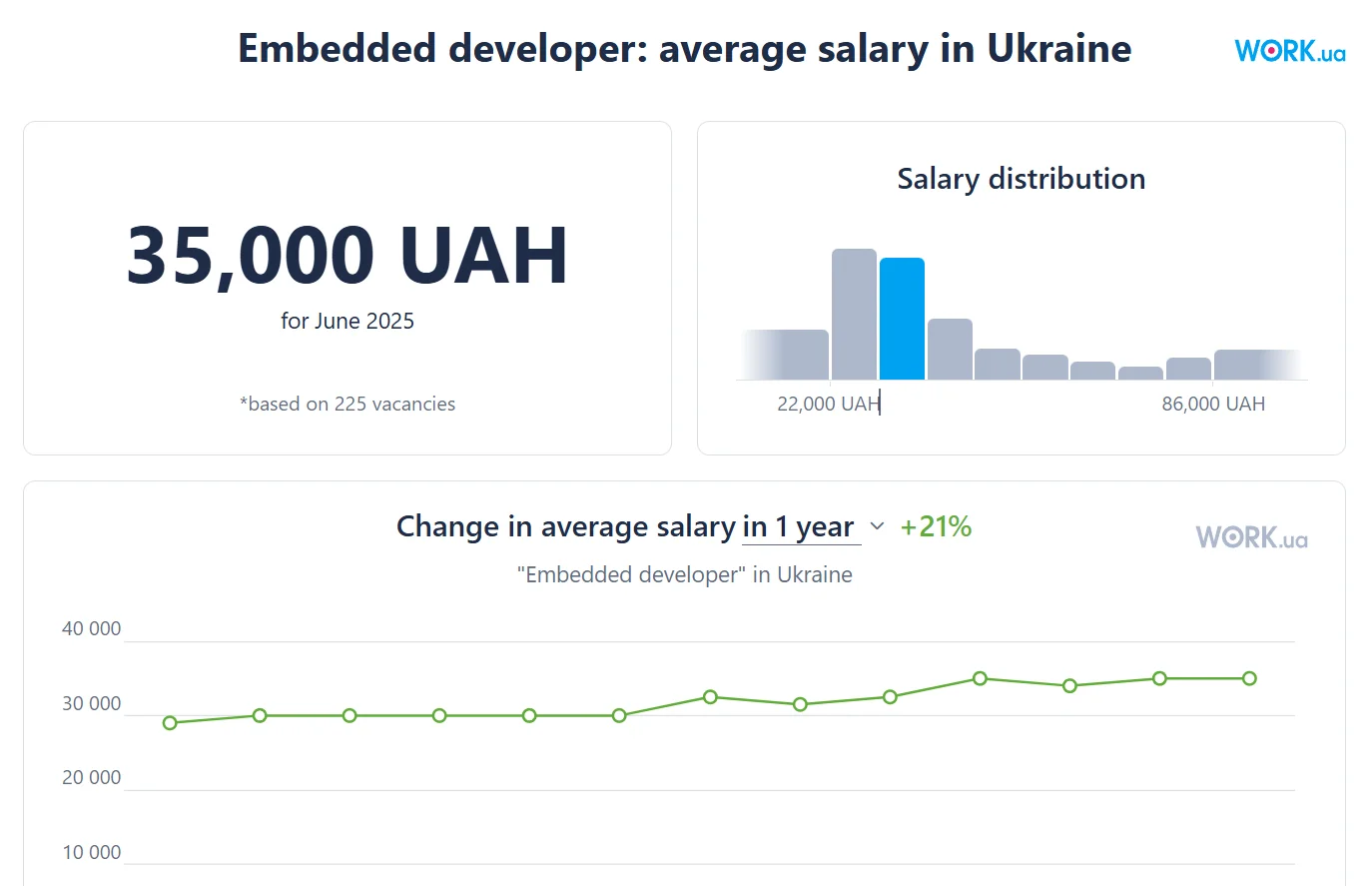
An embedded developer is no longer a system administrator but a developer who must work closely with hardware — otherwise, progress in this field is impossible. According to Work.ua, the salary of such developers in Ukraine has increased by 27% since last year.
Skills needed by developers include: C/C++, Python/Unix Shell, working with Linux, hardware architecture and its understanding, working with microcontrollers, knowledge of communication protocols, code optimization and testing.
Where to Study to Become an Embedded Developer
Many enthusiasts start by purchasing a single-board computer like a Raspberry Pi and programming microcontrollers, home automation systems, and simple gadgets. There are plenty of guides for this. For example, you can learn for free directly on embedded.com.
There are also courses where you can gain foundational knowledge. For instance, Coursera offers many options in this direction — though they are paid.
It should be added that despite the abundance of available courses, all the above-mentioned specialists would benefit from a higher education, which provides a strong theoretical foundation. This is available at several Ukrainian universities, and you should look for related specialties such as system administration, programming, etc.
Another good option is to monitor the websites of large companies like EPAM, SoftServe, Luxoft, and similar ones for free or low-cost training opportunities. The best graduates of such courses get jobs at major companies or Trainee positions with minimal pay but excellent hands-on experience.
In all cases, it's important to follow what leading experts in the field are writing. They often provide their own reading lists, recommended courses, and certifications.