- What is a Private Blog Network (PBN) and how does it work
- Current data: how many sites are part of PBN today
- What risks are associated with using PBN networks
- What signs may indicate that a site belongs to a Private Blog Network
- What to do if your site is already linked from a PBN network
- Can PBN be considered illegal practice or just "gray" SEO
- What alternatives exist for building a quality link profile
With the development of SEO, many methods of artificial influence on website positions have emerged. One of them is the Private Blog Network (PBN). Despite its attractiveness for rapid growth of link profiles, it is one of the riskiest tools in modern search engine promotion. Below, let's explore how PBNs work, why Google has a hostile attitude towards them, and how to protect your site from potential consequences.
What is a Private Blog Network (PBN) and how does it work
PBN (Private Blog Network) is a network of websites created to place links to a main resource with the aim of artificially increasing its authority in the eyes of search engines. Externally, such sites appear to be independent blogs or news portals, but they are actually managed by one person or company.
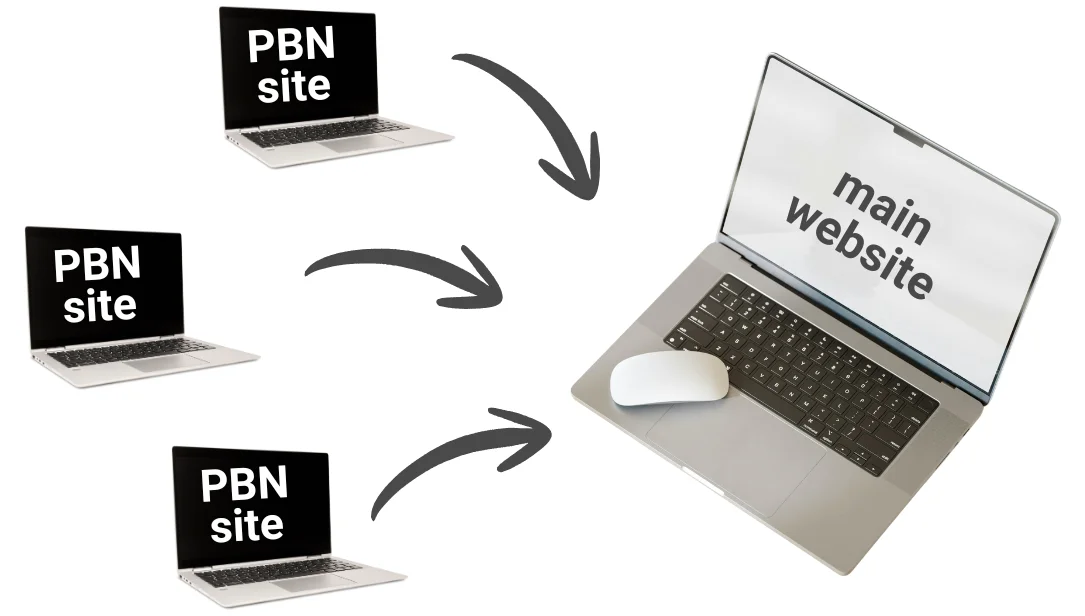
The working scheme is simple:
- An SEO specialist buys or registers several domains, usually with a good history (expired domains).
- Content is placed on each of them, often with different themes, to hide the connection between the sites.
- Links to the main site are gradually inserted into the articles.
This forms a "support network" that artificially boosts the ranking of the target resource.
Example: a company selling eco-products creates 20 pseudo-blogs about healthy lifestyles, diets, and nutrition — and all of them link to its main store. The search engine sees dozens of "authoritative" mentions and temporarily raises the site in the rankings.
It is important to understand that building even a small PBN requires significant resources: dozens of domains, separate hosting for each site, technical masking, and constant maintenance. In practice, the budget spent on maintaining such a network often exceeds the cost of stable hosting for the main site — without the risk of sanctions, loss of positions, and reputational consequences.
Current data: how many sites are part of PBN today
We do not have an honest absolute number of "PBN sites on the entire internet = X thousand or millions" — no one can count this directly. This is a shadow market, and the owners of such networks deliberately mask their projects.
According to an academic web security study by AsiaCCS (2019), during the analysis of over 52 thousand websites, 3.5 thousand resources that were part of PBNs were identified. Researchers recorded clusters ranging from a few sites to several hundred, all controlled by one entity. The backlink ecosystem turned out to be highly profitable: individual providers generated over $100,000 in revenue per month. (Source: Purchased Fame: Exploring the Ecosystem of Private Blog Networks).
In 2024, Google significantly strengthened the mechanisms for detecting link manipulation, particularly due to the development of the SpamBrain system. The algorithm has learned to better recognize the patterned behavior of sites within PBNs — shared IPs, repeated content patterns, similar domain histories. After this, the effectiveness of such networks noticeably decreased, and the risk of facing sanctions increased.
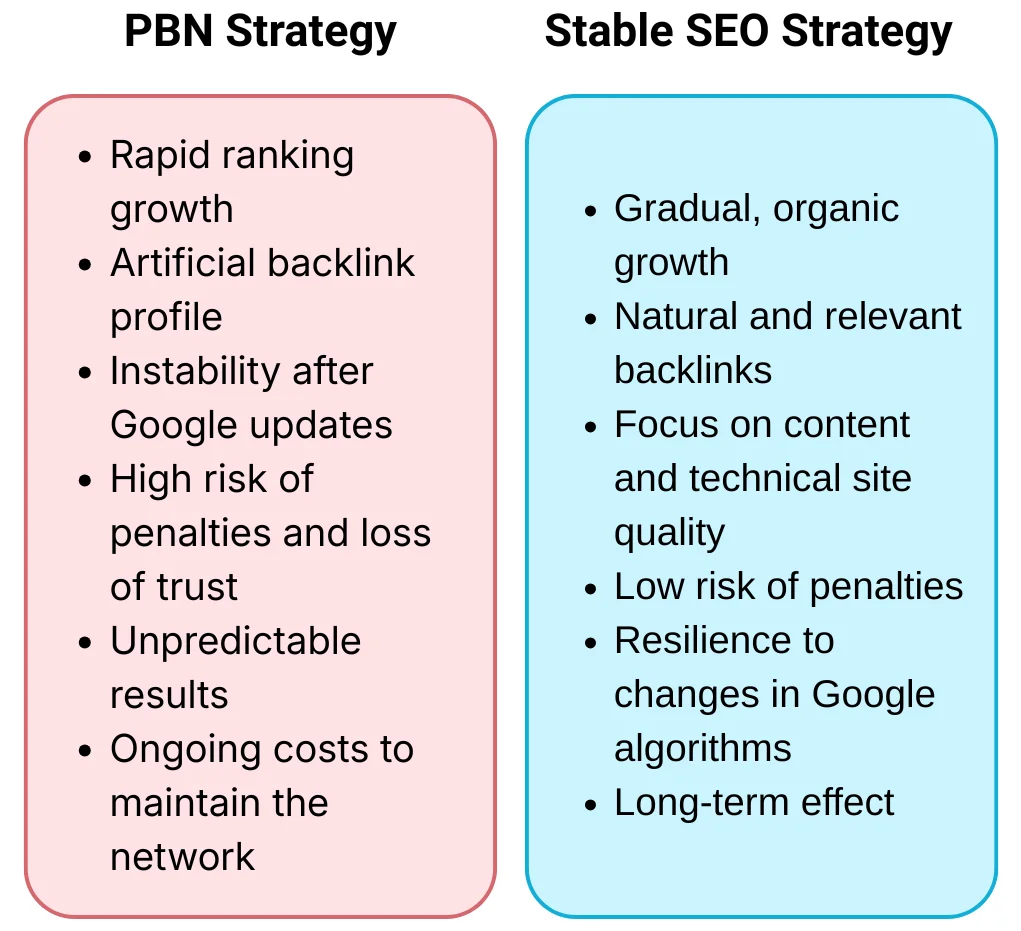
PBNs remain one of the most common yet simultaneously riskiest methods of "gray" SEO. They allow for rapid link mass growth, but their use increasingly leads to loss of positions and de-indexing, making this model strategically unsuitable for stable promotion.
What risks are associated with using PBN networks
The main problem is that Google does not believe in the naturalness of such links. For algorithms, this is an obvious manipulation of PageRank and a violation of Google's spam policies. Each PBN leaves technical "traces".
Risks of using PBNs:
- Sanctions and loss of positions. The March 2024 Spam Update algorithms and the SpamBrain system increasingly accurately detect unnatural schemes. As a result, the site may fall under algorithmic visibility reduction or manual sanctions (manual action).
- Loss of trust. If the network is exposed, the domain authority sharply declines, and restoring reputation after "black" link building is difficult.
- Unstable results. The effect is short-lived — after major Google updates, most sites relying on PBNs experience traffic loss.
- Financial losses. Building a PBN is expensive (domains, hosting, content, link masking), but there are no guarantees of results.
Using PBNs is a game with fire: while everything works, it seems that you have "outplayed" the algorithm. But one update or manual check is enough, and years of work can disappear along with positions.
Also read: What is an SEO audit of a site and how to conduct it independently
What signs may indicate that a site belongs to a Private Blog Network
Although PBN operators carefully mask their resources, a careful SEO analyst can recognize typical patterns:
- Shared NS servers, IP addresses, or the same hosting provider.
- Identical design templates or CMS.
- Identical analytical IDs (Google Analytics, Tag Manager).
- Lack of real audience — comments, views, subscribers are fake or absent.
- Low-quality content created solely for keywords.
- Excessive number of external links — if a blog with 10 articles has dozens of links to external sites, this is a risk signal.
What to do if your site is already linked from a PBN network
Falling under the influence of a PBN network can happen even unconsciously. In modern SEO, competition is so high that negative link attacks are used as pressure tools. Competitors may massively place low-quality or spammy links on third-party resources, forming an unnatural link profile and increasing the risk of algorithmic distrust from search engines. That is why regular monitoring of backlinks is an essential part of SEO hygiene.
Most site owners learn about problematic links only after a drop in positions or upon receiving a notification in Google Search Console. However, the situation can often be corrected — provided that consistent and measured actions are taken.
- Check backlinks. Use Ahrefs, Semrush, or Google Search Console (the "Links" section). Regular audits help identify dubious or artificial sources and abnormal patterns in the link profile before they become a problem.
- Disavow "toxic" links. If necessary, create a disavow.txt file and upload it via the Disavow Links Tool. Google considers this list as a recommendation: the specified links may be devalued or ignored during the evaluation of the link profile. This tool should only be used in cases of mass spam, artificial links, or after receiving a manual action.
- Strengthen the natural profile. Build quality, contextually relevant links from authoritative media, blogs, and partner resources. This helps form a balanced link profile and increase overall trust from Google algorithms.
For example, after one of the spring algorithm updates, an IT company from Kyiv recorded a drop in organic positions. An audit of the link profile revealed a massive influx of irrelevant and artificial links from sites of various themes, including gambling, diets, and cryptocurrencies.
After checking backlinks, disavowing spammy domains using disavow, and gradually increasing quality publications in relevant Ukrainian media, the site began to recover organic traffic within a few months.
Combating toxic PBN links is not a one-time action but a long-term protection strategy. Regular audits, prevention, and timely responses help minimize risks. In case of traffic decline, search engines may gradually restore trust in the site, provided there is a stable and natural link profile.
Also read: What are nofollow and dofollow links, and why both types are needed for SEO promotion of a site
Can PBN be considered illegal practice or just "gray" SEO
Formally, PBN is not illegal activity: creating your own websites and publishing content is not prohibited by law. However, for Google, the use of PBN is considered a violation of policies regarding manipulative links, as such networks are created to influence search results.
In the SEO community, PBNs are usually classified as Black Hat or Grey Hat SEO practices — that is, methods that contradict Google's recommendations. Although in some cases they may yield short-term effects, such a strategy is always associated with increased risks: from link devaluation and loss of positions to manual sanctions. It is no coincidence that PBNs are often compared to doping in sports — quick results can lead to long-term consequences.
What alternatives exist for building a quality link profile
Abandoning PBNs does not mean abandoning promotion. On the contrary, it opens up opportunities for organic and stable growth.
- Content marketing. Create unique analytical materials, guides, and research that genuinely help users. Such content has significantly higher chances of receiving natural links.
- Guest publications. Collaborate with thematic media, blogs, or partners. Quality content with a relevant link is one of the most reliable alternatives to PBNs.
- Partnership projects. Joint case studies, webinars, and interviews build trust and provide natural mentions without manipulation.
- Digital PR. Expert comments, news, and press releases in authoritative media often yield significantly greater effects than dozens or hundreds of links from dubious sources.
- Directories and forums. Verified business directories, industry guides, and active professional communities can be a safe source of links if they are relevant and genuinely beneficial to the reader.
In addition to external links, do not ignore internal linking. Logically connected pages help search engines better understand the structure of the site, index content faster, and correctly determine priorities.
PBN networks can provide quick but unstable effects. In cases of detecting inorganic links, positions are often adjusted, sometimes for a long time. In contrast, long-term value is created by content, real mentions, partnerships, and links that arise because the site is genuinely useful. This approach is slower but more stable and significantly less risky.