- What are quantum computers: explaining in simple terms
- Technological revolution: where quantum computers are used
- The future of quantum computing: forecasts for 2026-2030
Smart machines that have created an artificial reality to conquer humanity and extract energy from it — this is not only a description of the cult film series "The Matrix," but also a theoretical future. Data volumes are growing at an incredible pace, artificial intelligence requires more and more resources, and quantum computers can help cope with all of this. Although we are not physicists, we understand the impact of these computing devices on various technologies. Plus, it is always interesting to learn more about equipment that operates under rules that contradict our everyday logic.
What are quantum computers: explaining in simple terms
To understand such powerful computing devices, it is worth first examining the principle of operation of ordinary equipment, such as a smartphone or laptop. They operate based on a classical bit — the smallest unit of information in computer science, representing one binary digit with two values: 0 or 1. And this is an important point — it can be either 0 or 1, there is no third option.
In contrast, the foundation of a quantum computer is a qubit, which can exist in a superposition of states. That is, it can be both zero and one simultaneously. It is like a coin that is spinning quickly on a table, thus it is both "heads" and "tails" at the same time.
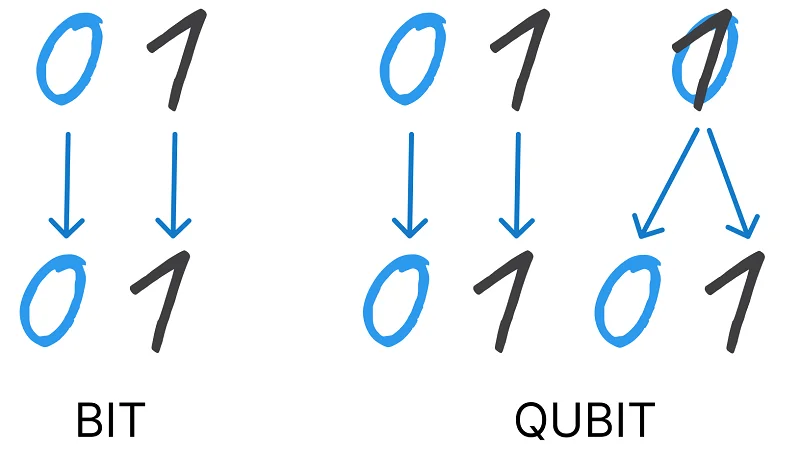
If it's hard to understand, then just imagine a maze with two players, which in our case will be the classical and quantum computers. The first simply chooses a path and goes down it until it hits a dead end, then turns back or looks for other paths. It does this quite quickly, but still gradually, meaning path → check → another path → check and so on. The second player is something like a fog that simply fills this maze and instantly finds the exit.

Read also: Sniffer, scammer, fraud and other "swear words" — a short glossary for beginner IT specialists
Technological revolution: where quantum computers are used
You might think: "Wow, cool device, I need to buy it instead of my old gaming PC to run Cyberpunk 2077 or Microsoft Flight Simulator at max settings, or 3ds Max or Adobe Premiere Pro with the heaviest projects." However, there is neither sense nor possibility in this.
For most companies, the real path to growth is not quantum processors worth millions of dollars, but optimizing existing infrastructure: a fast dedicated server or a properly configured, reliable hosting environment that is ready to handle increased workloads.
A quantum processor operates at a temperature close to absolute zero — -273.15°C, which is colder than open space. That is, it requires cryogenic installations that are approximately the size of a room. And lastly, a small detail — the cost of a quantum computer starts from $10-15 million, and it requires a team of physicists for its maintenance.

So let's better analyze where quantum computers are actually used and what benefits they have already brought.
Pharmaceuticals and medicine — creating innovative drugs
The traditional process of developing a new drug takes 10-15 years, and its cost reaches $1.3-4 billion. But only a small portion of promising compounds turn out to be truly successful. For example, in 2021, a detailed document was published on the website of the Congressional Budget Office of the United States about research and development in the pharmaceutical industry, which stated that approximately 88% of drugs do not receive approval after clinical trials. And the main reason is the inability of classical computers to accurately model quantum-mechanical interactions between drug molecules and proteins in the human body.
A vivid example of the benefits of quantum computers for medicine is the collaboration between Moderna and IBM. As early as 2023, IBM's website published news that the American company Moderna is investing in the development of quantum computing and researching its use in the development of future mRNA drugs. And on July 17, 2025, a material was published stating that IBM and Moderna demonstrated the ability of quantum computers to effectively predict secondary structures of mRNA for sequences whose complexity was previously a barrier. This will accelerate the design phase of new vaccines and cancer therapies, as it will allow unstable molecules to be filtered out before expensive laboratory syntheses begin.
Another problem is choosing the right catalysts and conditions for the Suzuki-Miyaura reaction, which allows creating carbon-carbon bonds. This often happens through ordinary experiments, as accurate modeling of the transition states of molecules requires calculating electronic correlation, which even supercomputers cannot handle. And here, the company IonQ, together with AstraZeneca, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and NVIDIA, developed a process for quantum modeling of this reaction using the IonQ Forte processor. According to Yahoo Finance data, this process allowed reducing the time to develop a solution for modeling catalytic reactions by more than 20 times, from several months to just days. And this is indeed an important event in 2025, as it enables solving complex problems, increasing the speed and efficiency of drug development.
Financial sector — predicting defaults and combating money laundering
One of the biggest risks for a bank is a sudden deterioration in the credit rating of a borrower. Each such drop, especially if it concerns a company's transition from the "investment" category to the "speculative" one, entails the need to increase capital reserves and losses. And classical machine learning models, even considering their constant improvement, often miss weak signals at early stages, leading to delayed reactions.
In 2021, Crédit Agricole CIB joined forces with Pasqal and Multiverse Computing to implement quantum neural networks. The experiment lasted more than 1.5 years, during which quantum algorithms were trained on historical data to detect nonlinear correlations that preceded defaults in the past but were unnoticed by classical algorithms. And in 2023, the press center of Crédit Agricole CIB published news that the experiment was successful, demonstrating that quantum models can predict rating downgrades with higher accuracy and lower training data volume requirements compared to classical counterparts. This allows the bank to adjust its credit portfolio in advance and avoid billion-dollar losses.
Automotive industry — optimizing sensors and creating batteries
In 2021, results of the quantum computing competition held by BMW Group and Amazon Web Services (AWS) were published, where the task was to find a solution for placing sensors on a car to "see" the world around it in 360 degrees and move safely.
The winner was Quantum Computing Inc. (QCI), which applied entropy-based quantum computing technology. The team modeled a problem with 3854 variables and over 500 constraints. And thus managed to find the optimal configuration of 15 sensors that provides 96% coverage for the autonomous vehicle. It took only 6 minutes to find a solution, while previous solutions based on classical or hybrid algorithms took hours or yielded less accurate results.
Energy and ecology — the first quantum computer in the Middle East for industry
On May 20, 2024, news appeared on the Pasqal website about the signing of a contract between Aramco and Pasqal to deploy the first quantum computer in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The company kept its word, and in November 2025, another material was published about the deployment of the Pasqal quantum computer, which operates on neutral atom technology, at Aramco's data processing center in Dhahran.
One of the important tasks is the effective management of oil fields, which requires a precise understanding of how fluids (oil, water, gas) move through porous rocks under immense pressure. The critical nature is explained by the fact that errors in modeling lead to inefficient drilling and leaving significant amounts of resources underground. And this 200-qubit machine on neutral atoms aims to solve flow modeling and drilling optimization tasks with new efficiency.
The future of quantum computing: forecasts for 2026-2030
We have already figured out what quantum computers are and where they are applied. And throughout 2025, and indeed the last 5 years, many cases of integrating quantum processors into various areas of life have emerged. So a logical question arises — what will happen to them in the future. And here it is worth noting right away that all recent news indicates a shift from theoretical discussions, laboratory experiments, and isolated cases of use, which are talked about more than shown incredible results, to more concrete, practical, commercial applications.

In general, it is worth highlighting the following directions for the development of quantum computers over the next 5 years:
- Increase in the number of qubits. We already see how IBM is developing systems with an increasing number of qubits, which is quite logical, as this directly affects the ability to solve complex problems. And of course, this trend will continue, thereby increasing the chances of achieving "quantum advantage".
- Solving the cooling problem. This is a very important issue, especially since scaling systems requires huge cryogenic installations. That is, the more qubits, the harder it is to dissipate heat from the controlling electronics. And already leading companies are looking for solutions, for example, in photonics and silicon qubits that can operate at higher temperatures.
- Reducing the error rate. In addition to the cooling difficulties, a major problem is the high error frequency. So in the next 5 years, companies will focus on this aspect, trying to make computations more reliable, even if fully fault-tolerant systems are not yet perfect.
- Expansion of commercial applications. Theory is good, but money is even better. We already see the application of quantum computing in logistics (the use of the HONE engine allowed optimizing the operation of Pier 300 terminal), pharmaceuticals (the same quantum simulation of mRNA secondary structure), finance (predicting defaults with neutral atom processors). So it can be assumed that in the next 5 years, quantum algorithms will manage autonomous fleets of trucks and drones, model drug interactions with body proteins at the atomic level, become the standard for real-time asset portfolio management, and fraud detection.
- Hybrid computing. With all the advantages of quantum computers, we should not forget about classical devices. And the most realistic scenario is not the replacement of quantum computers, but their tandem with classical supercomputers (it’s strange to understand how quickly humanity is developing that we already consider supercomputers as classics).
- Changing cryptography. In the next 5 years, universal quantum computers capable of breaking modern cryptographic algorithms are unlikely to appear. However, there may already be an active transition of governments and large corporations to post-quantum cryptography (PQC). This will allow systems to become resilient even to attacks from quantum computers in the distant future.
And Ukrainians also have a significant impact on the development of technologies. Although quantum computers are often associated with giants like IBM or Google, Ukrainian engineers and scientists are making a substantial contribution to this industry. For example, Maxim Sich and Andriy Yamshanov (co-founders of the British company Aegiq) presented to the world in 2025 their own quantum computer Artemis, which uses photonic technologies instead of superconductors, allowing it to operate without bulky cooling systems.
Read also: Inventions of Ukrainians in the IT industry
So now you understand that quantum computing is no longer a technology of the distant future. They are already being applied, and in the coming years this trend will only accelerate. The main focus will shift from theoretical achievements to the creation of reliable, albeit specialized, systems that can provide tangible commercial benefits to users in narrow fields. And if solutions to the problems of errors and cooling can be found, they will become a real tool in the arsenal of high-tech companies.