In the virtual world, where every click leaves a trace, cookies have become an integral part of user interaction with websites. However, cookies can also become a source of potential problems. They store data about our activity, which, if it falls into unscrupulous hands, can threaten our privacy and security.
Therefore, it is important to understand how cookies work, what information they store, and what security measures we can take. Deleting or configuring cookies allows users to control their virtual destiny, ensuring privacy and security. In this article, we will explore the purposes, types of cookies, and security aspects.
An important component of the smooth operation of a website is inexpensive reliable hosting, as it provides the technical foundation for storing and processing files. Its choice affects many aspects, including the user experience, as the speed of website loading and security largely depends on the hosting.
What are cookies and why are they needed
Cookies are essentially small text files stored by websites on a user's computer or mobile device during their virtual journey. They act like secretaries, recording information about the user and their activity on the site. Their main task is to make the virtual world more convenient for guests by saving their settings and session details.
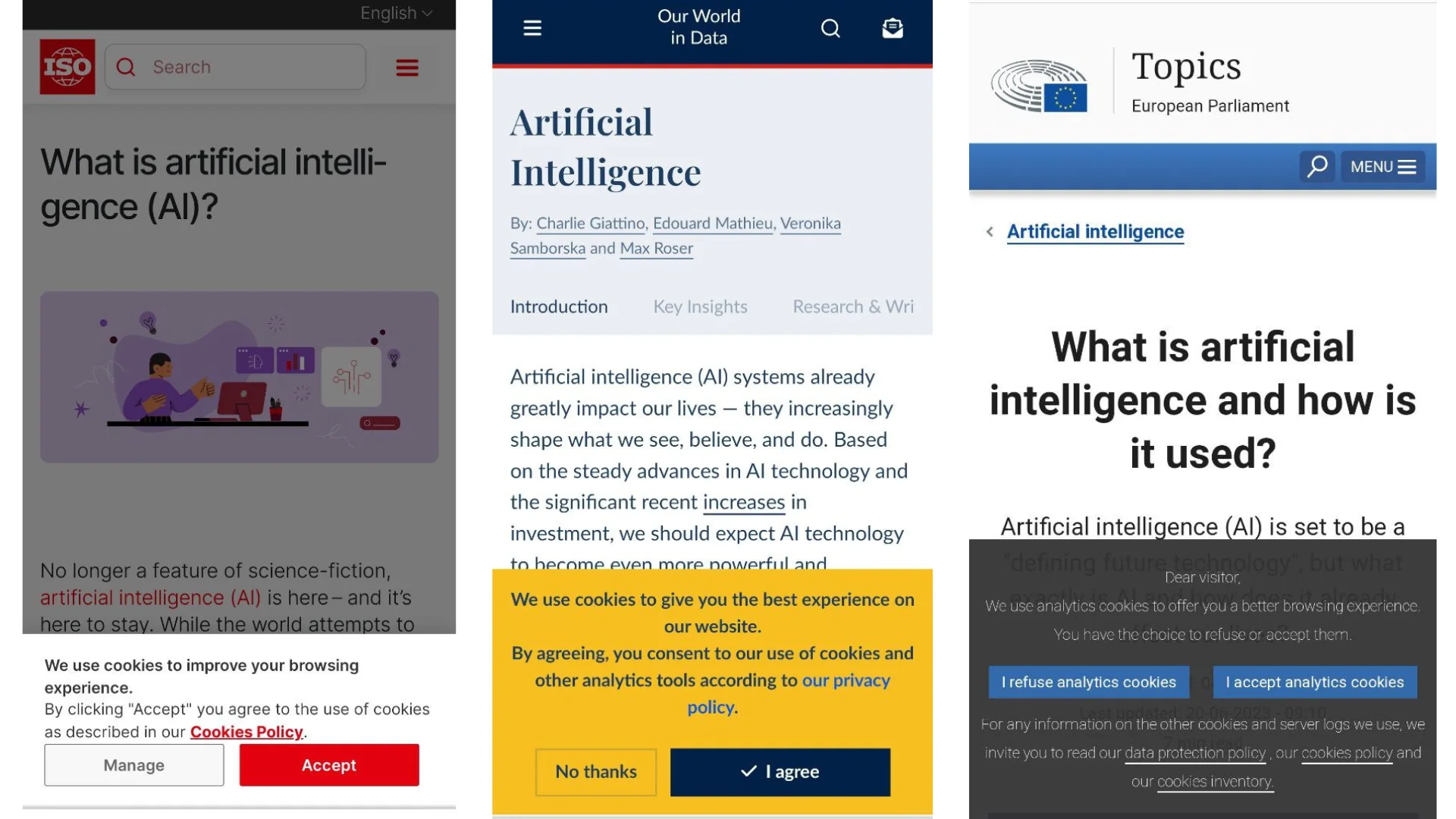
Examples of cookie usage notifications
Thanks to cookies, websites can "remember" the user, allowing for a personalized experience tailored to individual needs. For example, due to cookies, users do not need to enter their login and password upon returning to a site, language settings are retained, and items in an online shopping cart remain in place.
Read also: How to Attract More Comments to Your Blog
How cookies differ from cache
Cookies are not cache, although both are data storage mechanisms in the browser. Cookies record information about the user and their interactions with the website, embodying their virtual experience by saving settings and providing authentication.
Cache, on the other hand, stores static elements of a website, such as images, CSS styles, and JavaScript scripts. The main purpose of caching is to speed up page loading by saving local copies of files. This reduces the amount of data downloaded during subsequent visits to the site.
Types of cookies
Cookies can be classified according to different criteria: some are stored only during the user's active session and disappear after the browser is closed, while others remain on the user's device for a certain period, even after the browser is closed.
Cookies also come in two types, depending on where and how they are created:
-
First-party cookies: Created directly by the website the user is visiting.
-
Third-party cookies: Created by external domains that provide content or services on the website, such as advertising networks or analytics services.
What information do cookies contain about the user
Cookies can contain various information about the user and their virtual journey:
-
session identifiers;
-
data about user activity;
-
login information;
-
user preferences and analytics data, among others.
This information helps websites enhance the virtual experience by providing personalization and ease of use.
Are cookies safe for users
The safety of cookies depends on how they are used and what security measures are taken by website developers. In general, cookies are not harmful by themselves, but they can be exploited by malicious actors to gather information about users or carry out attacks.
To ensure the security of cookies, it is important to use a secure connection (HTTPS), which encrypts the data transmitted between the browser and the server. This helps prevent cookies from being intercepted by attackers. Additionally, using cookies with specific attributes can limit their access via JavaScript, reducing the risk of information theft through cross-site scripting (XSS).
Another crucial aspect is the use of cookies with the Secure attribute, which can only be transmitted over a secure connection. This enhances security, especially when transmitting sensitive data such as session identifiers or login information. You can read more about this in the article.
Why delete cookies and how to do it
Deleting cookies may be necessary for several reasons:
-
Preserving privacy: Removing data that can be used to track the user.
-
Enhancing security: Preventing unauthorized access to accounts or sensitive information.
-
Resolving technical issues: Fixing problems related to website functionality.
To delete cookies, users can use their browser settings.
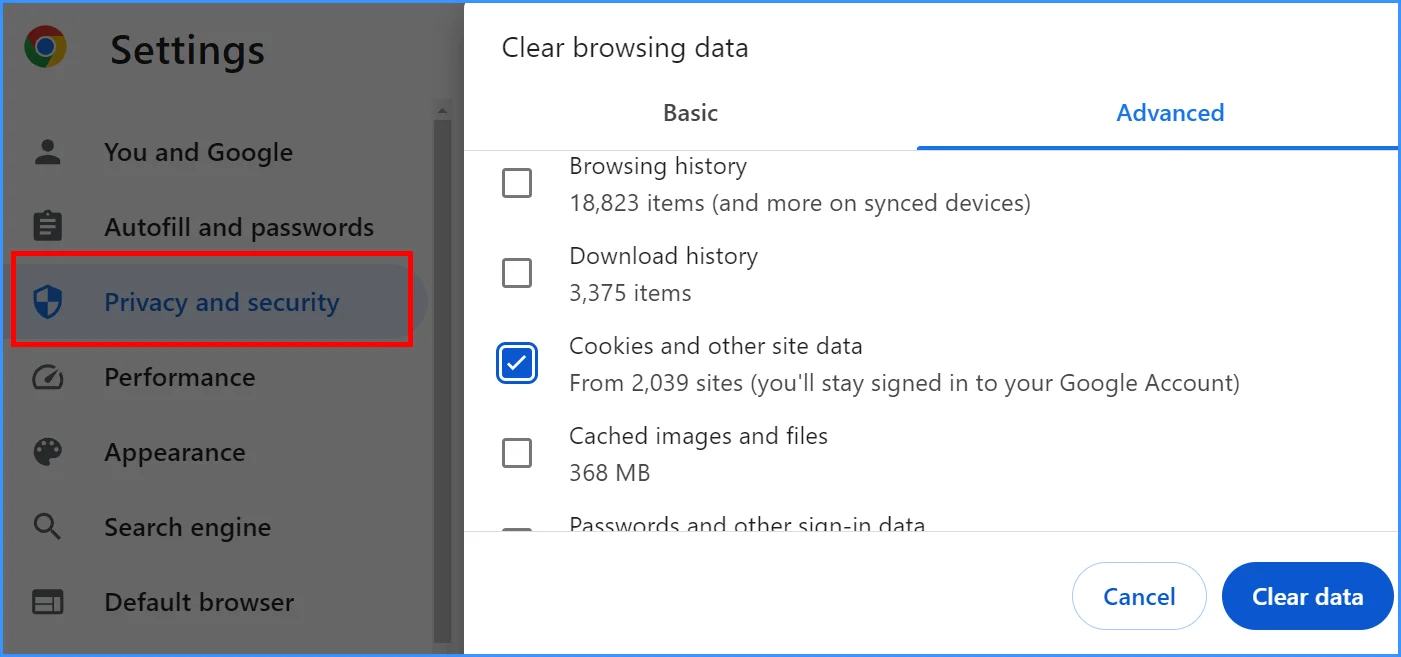
In Google Chrome, this can be done by going to "Settings" → "Privacy and security" → "Clear browsing data" and checking the box for "Cookies and other site data," while unchecking all other boxes.
Similarly, cookies can be deleted in other browsers. For example, in Mozilla Firefox, go to "Settings" → "Privacy & Security" → "Cookies and Site Data" and click "Clear Data".
Read also: Which IT professions to study in 2024 — how not to be left without work in the most popular industry
What happens if you don't accept cookies
Refusing to accept cookies can affect your interaction with websites. One of the main consequences is the loss of personalization, as sites will not be able to retain user settings such as language or theme. This may lead to the need to re-enter your login and password each time you visit a site, reducing convenience.
Additionally, rejecting cookies can cause problems with website functionality, especially for online stores where the shopping cart may not be retained between sessions. Some sites may not function at all without cookies, as they are used to support user sessions and ensure the seamless operation of the website.
Cookies are invisible threads that connect users to the web world. They quietly work in the background, storing information about our preferences, settings, and actions online. This allows sites to "remember" us, creating an individualized experience tailored to our needs.